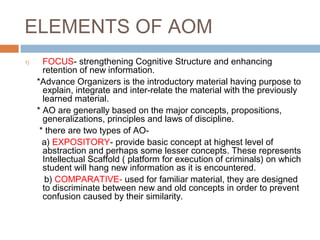
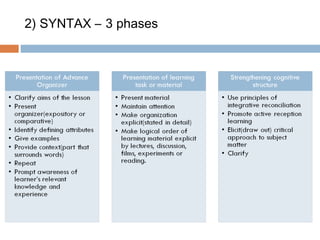
The Advance Organizer Model proposed by David Ausubel focuses on meaningful learning through strengthening students' cognitive structures. It involves presenting introductory material called advance organizers before new content to explain and relate it to prior knowledge. There are two types of advance organizers - expository which provide overviews at a high level of abstraction, and comparative which differentiate new from old concepts. The model has implications for curriculum design through its principles of progressive differentiation and integrative reconciliation.