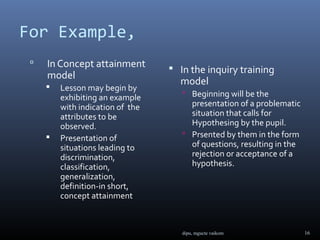
This document discusses models of teaching and their components. It defines teaching models as instructional designs that specify environmental situations to cause specific changes in student behavior. There are four families of teaching models: information processing, personal, social, and behavioral systems. Each model has four key components - syntax, social system, principles of reaction, and support system. The document provides examples of models within each family and describes the components.













![3. Principles of reaction
[rules to be followed]
This defines the nature of reaction expected
from the teacher to every pupil activity.
The principles of reaction give guidance to the
teacher as to how he is expected to react to each
activity of the learners, to suit the characteristics
of the model selected.
dipu, mgucte vaikom 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modelsofteaching2012-121202234122-phpapp01/85/Models-of-teaching-19-320.jpg)

