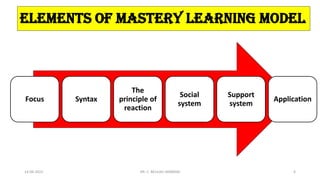
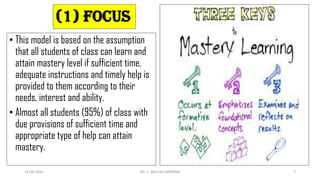
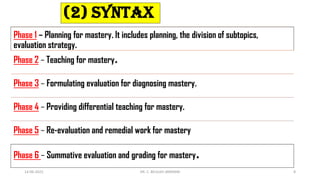
Benjamin Bloom's mastery learning is an instructional strategy introduced in 1968 that focuses on helping all students achieve a satisfactory level of performance through individualized learning and sufficient time. The model emphasizes that every child can master the material with adequate support, and it encourages a methodical approach to learning that includes planning, differentiation, and continual assessment. The overall goal is to foster a deep understanding of subjects before students progress, enhancing both cognitive and affective outcomes.