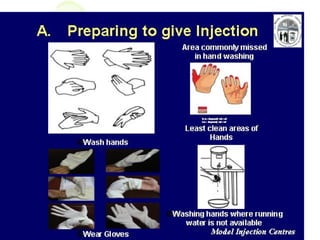
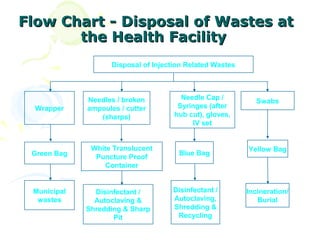
This document discusses infection control measures used in healthcare settings. It defines infection control as measures to prevent the spread of infections between patients and healthcare providers. Infection control is based on how infectious agents are transmitted and includes standard and additional precautions. Standard precautions include personal protective equipment like gloves and masks, proper hand washing, waste disposal, and cleaning/disinfection. They aim to prevent transmission of bloodborne pathogens from all patients. Additional precautions may be needed based on how an infection spreads.