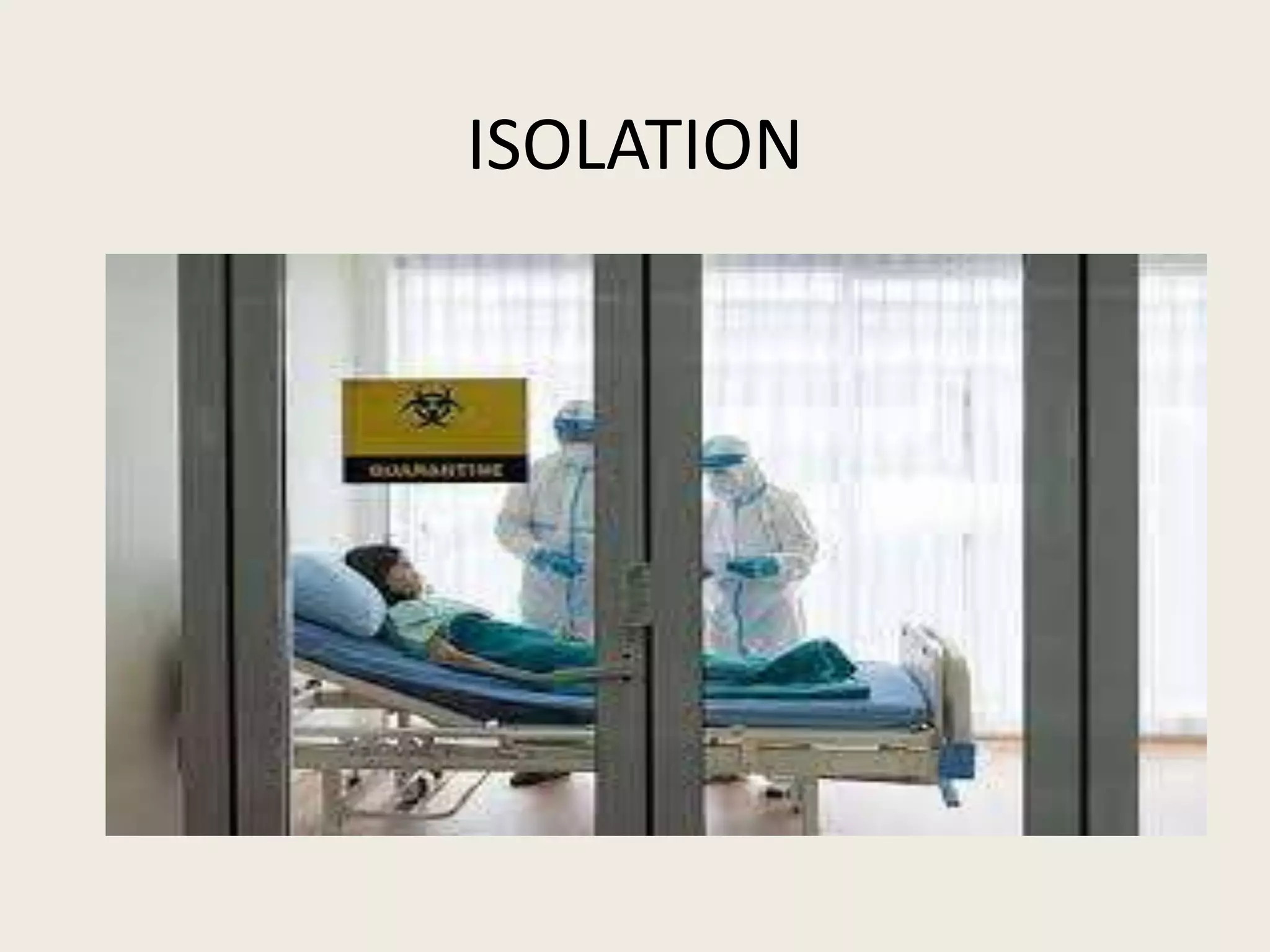
1. Isolation is the separation of infected patients from others to control the spread of disease. It includes strict, respiratory, protective, enteric, wound, blood, and discharge isolation depending on the transmission route.
2. Standard precautions like hand hygiene and PPE use should be followed for all patient care. Transmission-based precautions include contact, droplet, and airborne precautions depending on the disease.
3. Contact precautions involve single rooms, dedicated equipment, and thorough disinfection. Droplet precautions require masks within 3 feet and covering of secretions. Airborne precautions require enclosed rooms with special ventilation and filtration.