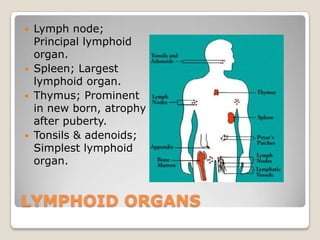
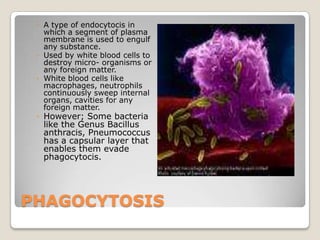
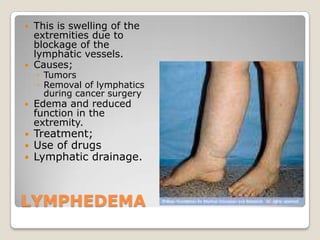
The document summarizes the lymphatic and immune systems. It discusses that the lymphatic system maintains fluid balance and immunity by returning fluid from tissues to the bloodstream. The immune system fights foreign substances through innate and adaptive defenses, including barriers, leukocytes, and acquired immunity. Lymphoid organs like lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, and tonsils are involved. Phagocytosis by white blood cells helps destroy microorganisms. Hodgkin's disease is a cancer of the lymph nodes most common in young adults. Lymphedema is swelling from blocked lymphatic vessels and can be caused by tumors or cancer surgery.