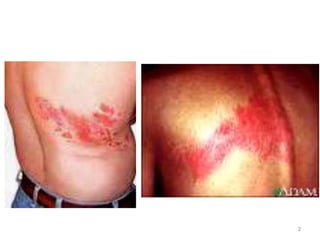
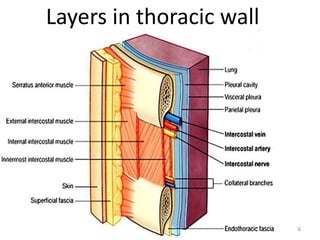
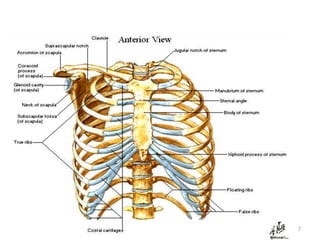
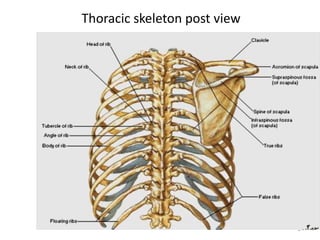
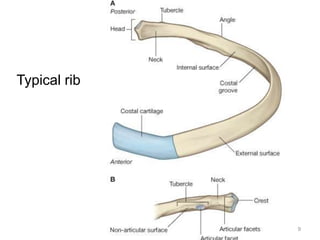
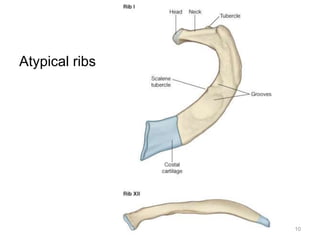
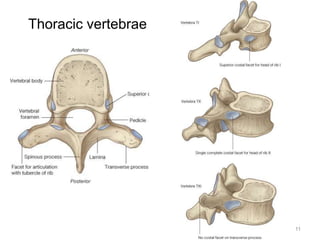
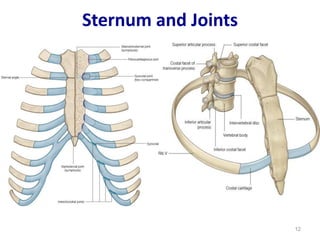
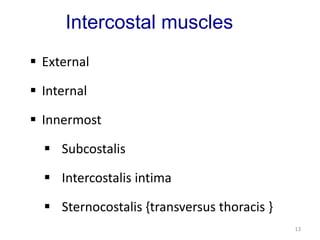
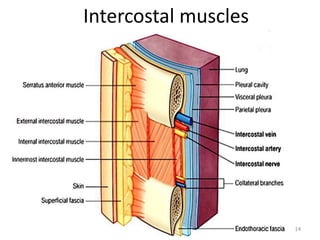
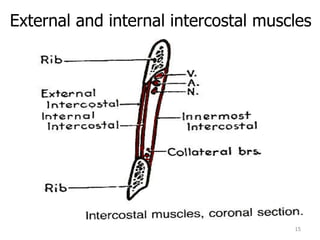
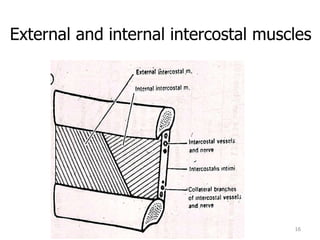
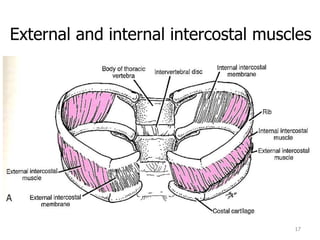
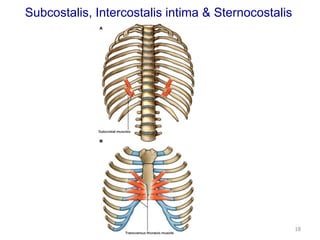
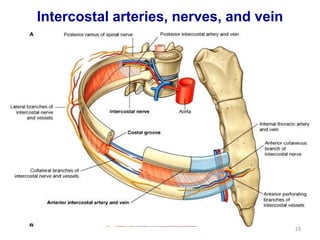
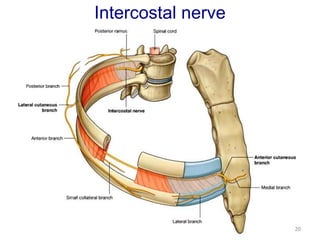
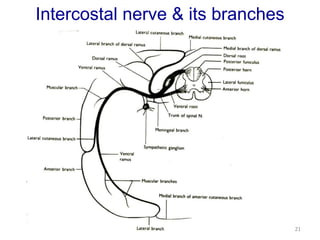
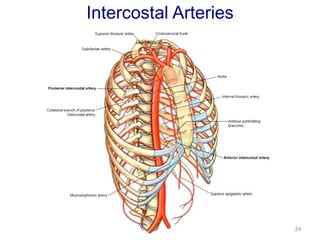
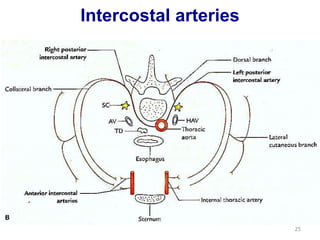
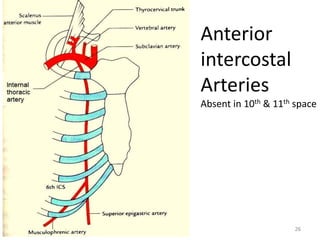
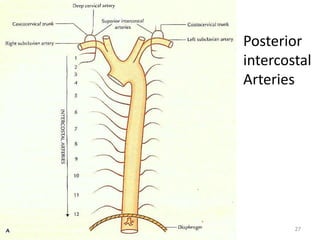
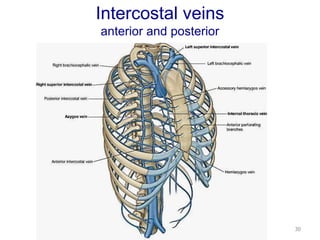
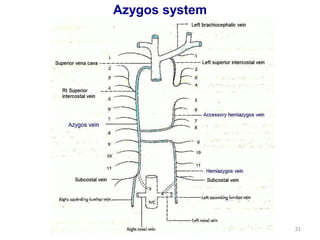
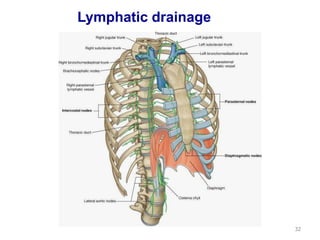
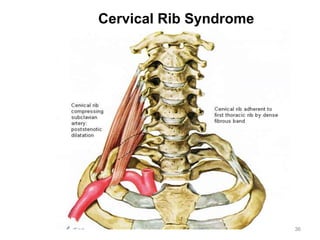
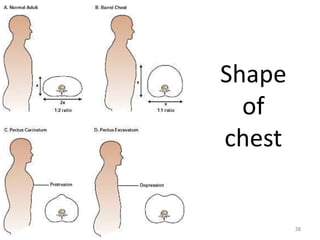
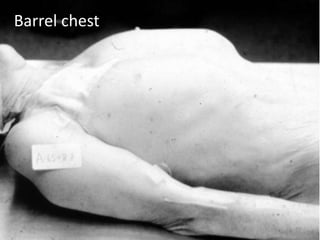
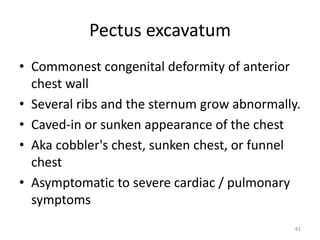
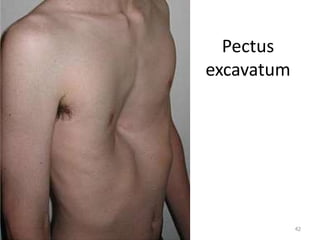
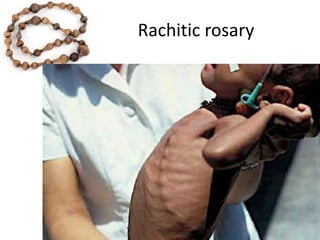
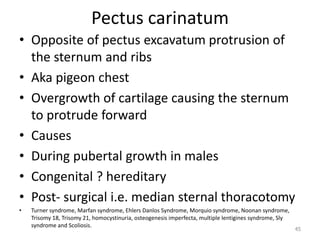
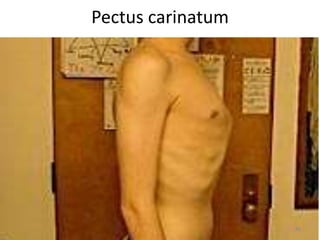
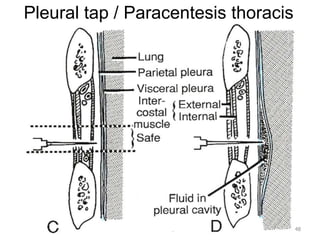
This document discusses the anatomy of the anterior thoracic wall and intercostal spaces. It begins by outlining the learning objectives which are to describe the boundaries and contents of a typical intercostal space, including the muscles, nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics. It then provides detailed slides and explanations of the typical and atypical structures found in the intercostal spaces, including variations. Examples of clinical correlations and applied anatomy are also discussed, such as barrel chest deformities, congenital chest wall anomalies, and procedures involving the intercostal spaces.