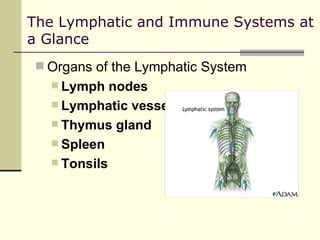
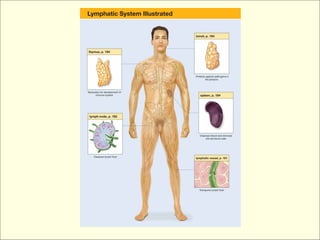
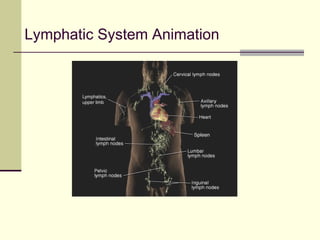
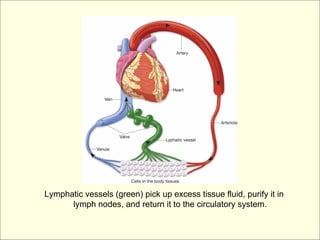
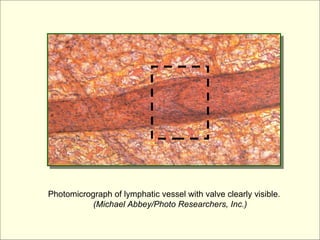
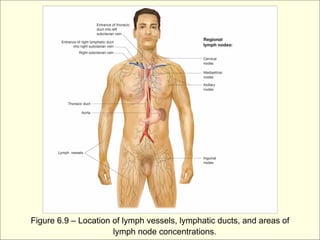
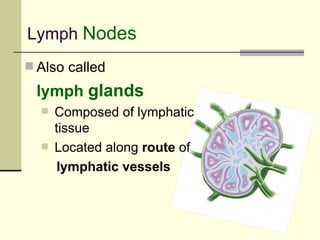
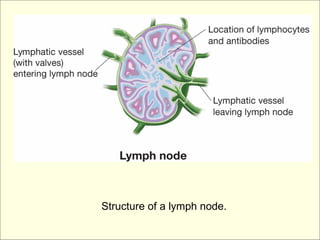
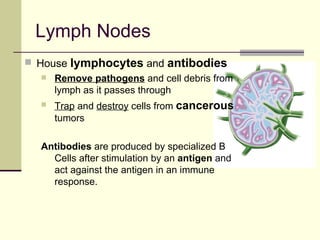
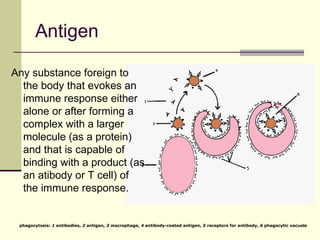
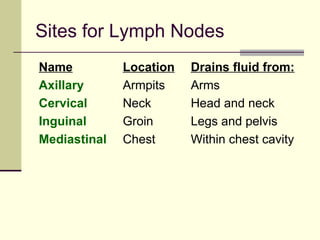
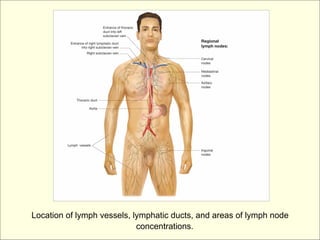
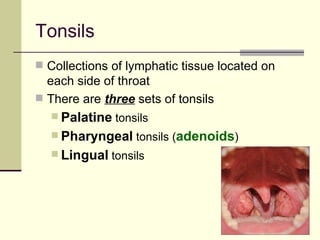
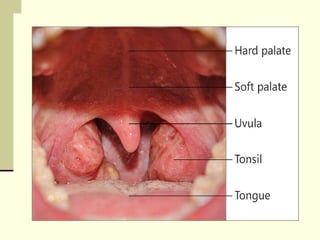
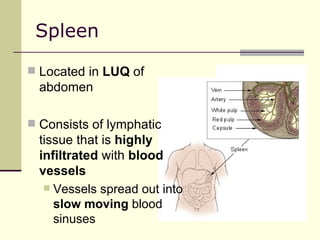
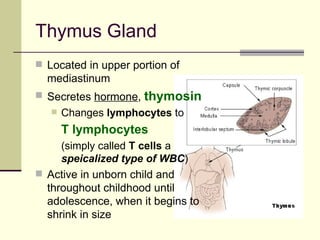
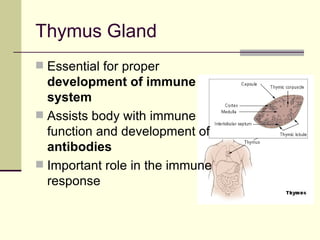
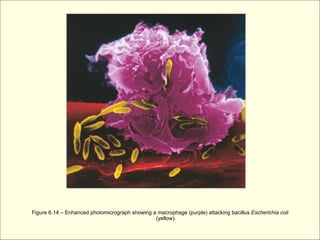
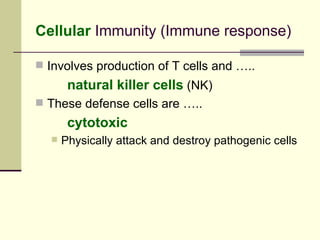
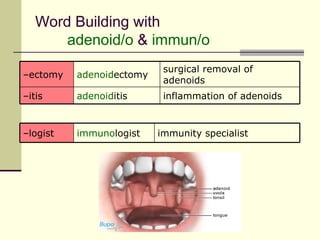
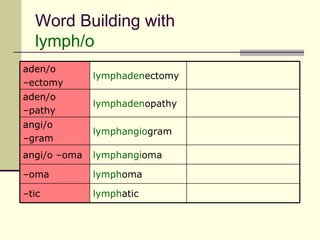
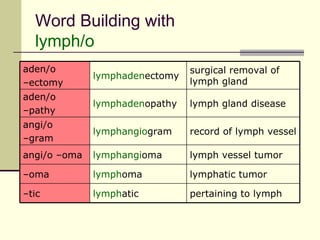
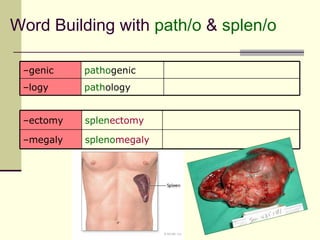
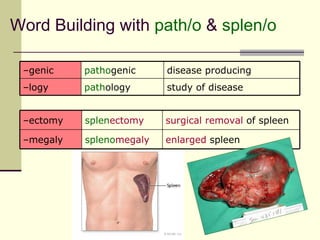
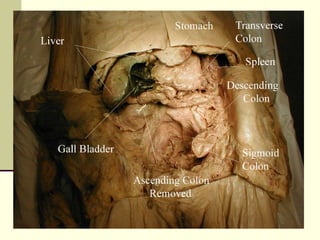
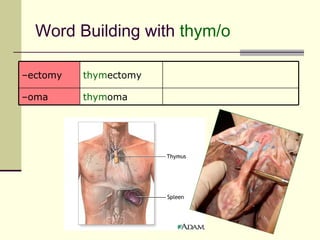
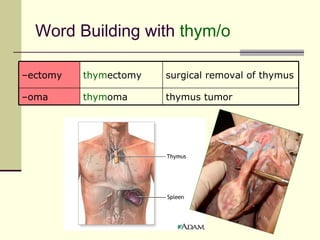
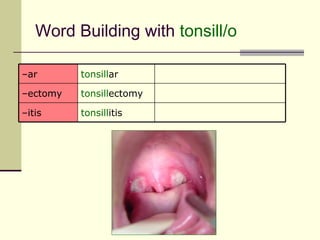
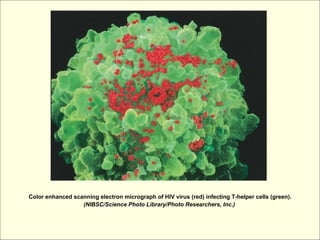
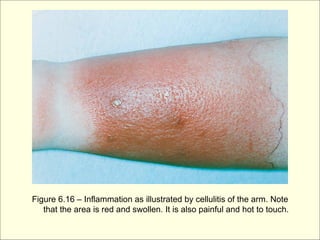
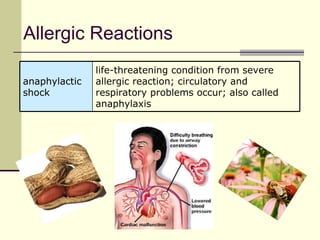
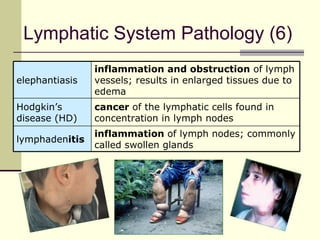
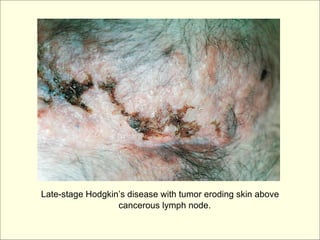
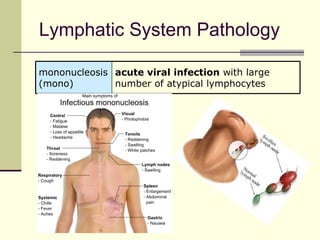
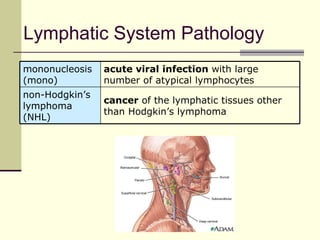
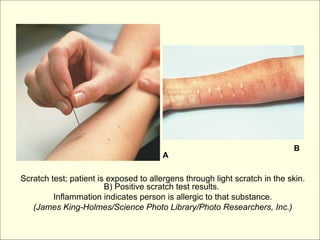
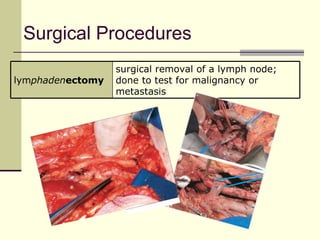
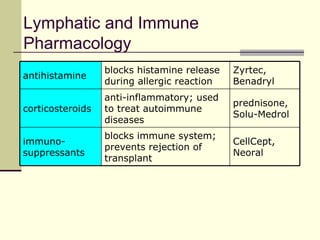
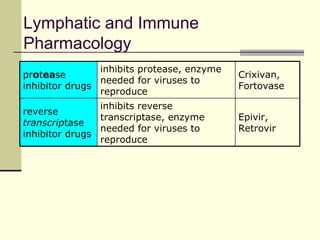
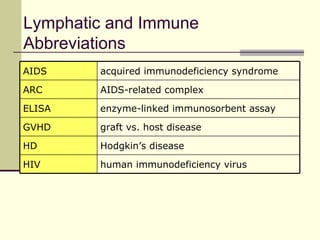
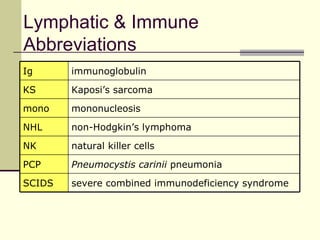
The document provides an overview of the lymphatic and immune systems, including their functions of transporting lymph fluid and fighting disease, the organs that make up these systems such as lymph nodes and the spleen, and medical terminology related to the lymphatic and immune systems like combining forms and suffixes used in medical terms.