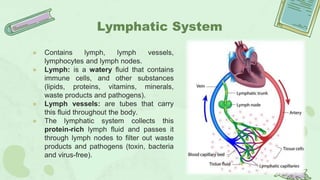
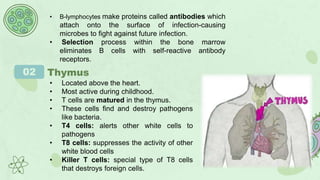
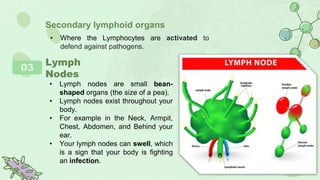
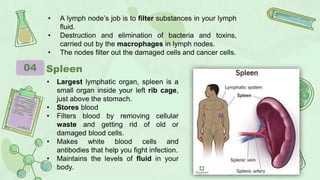
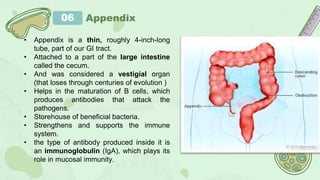
The primary lymphoid organs that create lymphocytes are the bone marrow and thymus. The bone marrow produces B cells and some T cells, while the thymus matures T cells. Secondary lymphoid organs where lymphocytes are activated include lymph nodes, the spleen, tonsils, appendix, and Peyer's patches in the intestine. These organs work to filter the lymph and blood, recognize and eliminate pathogens and foreign cells, and support immune system functions.