The immune system is a complex network of organs, cells and proteins that defends the body
- 1. What are the organs of the immune system? The defense system of the human body is made up of entire organs and vessel systems like the lymph vessels, but also of individual cells and proteins. The inner and outer surfaces of the body are the first barriers against pathogens (germs). These surfaces include the skin and all mucous membranes, which form a kind of mechanical protective wall. Several things support this protective wall: • The body’s own antibacterial substances can disable different pathogens from the environment at an early stage. A certain enzyme found in saliva, the airways and tear fluid destroys the cell walls of bacteria. • Many pathogens that are breathed in get stuck to mucus in the bronchi and are then moved out of the airways by hair-like structures called cilia. • Most pathogens that enter the body together with food are usually stopped by stomach acid. • Normal flora, harmless bacteria that reside on the skin and many mucous membranes in the body, also help to protect the body. The cough and sneeze reflex can also help to remove pathogens.
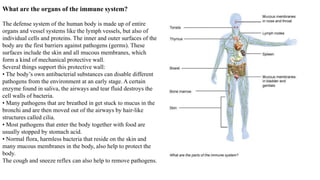
- 2. The parts of the immune system The immune system is made up of organs that control the production and maturation of certain defense cells, the lymphocytes. We have 2 groups of the immune organs. 1. The primary immune organs: - the bone marrow; - the thymus. 2. The secondary immune organs: - the lymph nodes; - the spleen; - the tonsils; - other specialized tissues in the mucous membranes (in these places, the defense cells have constant contact with non-self substances and pathogens).
- 3. Bone marrow Bone marrow is a sponge-like tissue situated inside of the bones. Most defense cells are produced and then also multiply here. They then migrate from the bone marrow into the bloodstream and reach other organs and tissues, where the defense cells mature and specialize. At birth, many bones contain red bone marrow, which actively builds defense cells. During the course of life, more and more red bone marrow turns into fat tissue. Adults only have red bone marrow in a few bones, for example in the ribs, in the breast bone and in the pelvic bone.
- 4. Thymus The thymus, also called the thymus gland, is only fully developed in children. From adolescence onwards, it is slowly turned into fat tissue. The gland-like organ is situated behind the breast bone above the heart. Certain defense cells are differentiated in the thymus: the so-called T lymphocytes, or T cells for short, among other things, are responsible for coordinating the innate and the adaptive immune system. The T in T lymphocytes stands for thymus, the place where they mature. T cells move through the body and constantly watch the surfaces of all cells for changes. To be able to do this job, they learn in the thymus which structures on cell surfaces are self and which are non-self. When coming into contact with a non-self body, T cells turn into so-called T effector cells, which trigger and regulate different defense reactions. This type of cells includes T killer cells, which can destroy cells infected with a pathogen. T helper cells are another kind of effector cells, which support other immune cells in doing their work. In childhood, the thymus tissue also produces two hormones – thymosin and thymopoietin – which regulate the maturation of defense cells in the lymph nodes.
- 5. Lymph nodes The lymphatic system of lymph nodes and vessels is important for continually exchanging substances between the blood and the tissue in the body. Fluid constantly leaves the blood, and defense cells and proteins migrate into the surrounding tissue. Most of the fluid is later taken back into the blood vessels. The rest of it is removed by the drainage system of the lymph vessels, which forms a fine net of thin-walled vessels in the body. The lymph nodes filter and clean the lymph fluid (lymph) on its way to the larger lymph vessels. The lymph finally travels to a vein called the superior vena cava, where it enters the blood stream. Lymph nodes work like biological filter stations. They contain different defense cells, which trap pathogens and activate the production of specific antibodies in the blood. If lymph nodes become swollen, painful or hard, it can be a sign of an active defense reaction, for example in an infection or, in rare cases, in malignant changes of the body’s own cells.
- 6. Spleen The spleen is situated in the left upper abdomen, beneath the diaphragm. It has a variety of tasks in the defense system. In the unborn child, the spleen mainly produces blood and defense cells. After birth this organ is mainly responsible for removing blood cells and for specific defense functions. As part of the immune defense, the functions of the spleen include the following: - It stores different defense cells that are released into the blood to get to the organs, if needed: macrophages, also called scavenger cells, can attack non-self substances and pathogens directly. T lymphocytes inspect cell surfaces, help in controlling defense and can also directly destroy cells that have been recognized as non-self or as pathogens. B lymphocytes produce antibodies, if needed. - It is responsible for removing red blood cells (erythrocytes). - Blood platelets (thrombocytes), which are responsible for blood clotting together, are stored and removed in the spleen. So there is always a lot of blood flowing through the spleen tissue. At the same time this tissue is very soft. In heavy injuries, in an accident, for example, the spleen can therefore rupture easily. The spleen then needs to be operated on, because otherwise there is a danger of bleeding to death. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, and the spleen has to be removed, other defense organs take on most of its tasks.
- 7. Tonsils Tonsils also belong to the defense system. Due to their special position at the throat and palate, their defense cells come into contact with pathogens especially soon, and can activate the immune system immediately. Their tissue contains mainly lymphocytes. In addition to the palatine tonsils on the right and left side, which are commonly just called tonsils, there are also the adenoids above the roof of the throat, the lingual tonsil at the base of the tongue, and more lymphatic tissue on the sides of the throat. This lymphatic tissue can take on the function of the adenoids, if these have been removed. Lymphatic tissue in the bowel and in other mucous membranes in the body The bowel plays a central role in defending the body against pathogens: More than half of all cells that produce antibodies are found in the bowel wall, especially in the last part of the small bowel and in the appendix. These cells recognize pathogens and other non-self substances, and mark and destroy them. They also store information on these non-self substances to be able to react faster the next time. The large bowel also always contains bacteria that belong to the body, the so-called gut flora. These bacteria in the large bowel make it difficult for other pathogens to settle and to enter the body. The immune system of the bowel tolerates the bacteria of the gut flora. Other parts of the body where pathogens may enter also contain lymphatic tissue in the mucous membranes. All this tissue together is also called mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Pathogens might enter the body through the airways or the urinary tract, for example. Lymphatic tissue can be found in the bronchi and in the mucous membranes of the nose, the urinary bladder and the vagina with the defense cells being directly beneath the mucous membrane where they prevent bacteria and viruses from attaching.