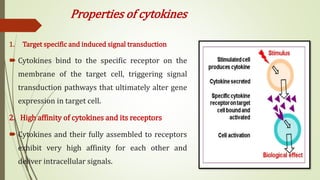
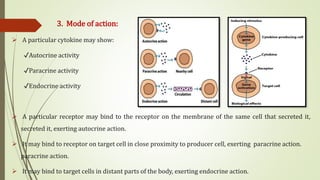
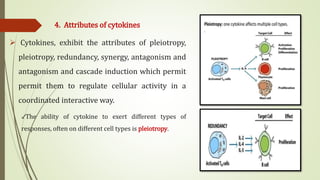
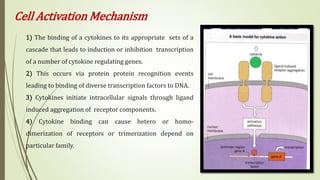
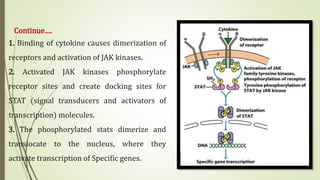
Cytokines are low molecular weight proteins that are secreted by cells of the immune system and other cells to regulate immune responses. They act as signaling molecules between cells through specific high-affinity receptors. Cytokines control processes like activation, growth, and differentiation of immune cells. They are classified based on their cellular source (monokines, lymphokines) or functional roles (interleukins, interferons, tumor necrosis factors, colony-stimulating factors, chemokines, growth factors). Binding of cytokines to their receptors triggers intracellular signaling cascades that regulate gene expression. Dysregulation of cytokines can contribute to diseases like cytokine release syndrome. Key cytokines discovered at the National Cancer Institute, like interleukin-2, interleukin-