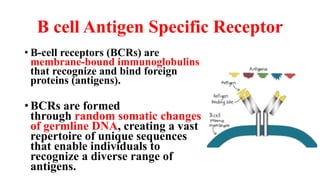
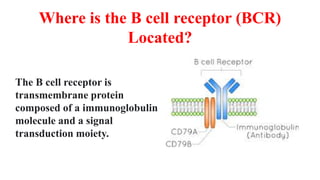
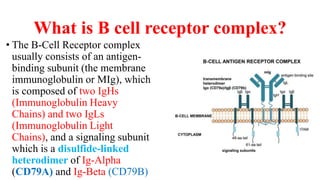
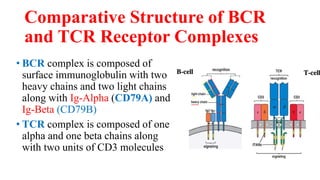
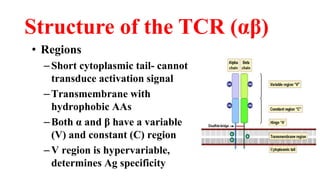
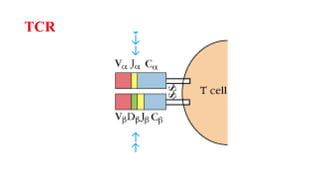
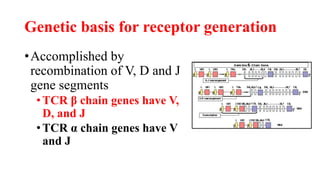
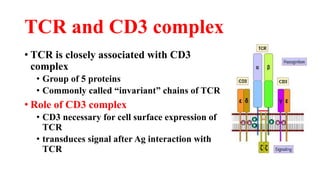
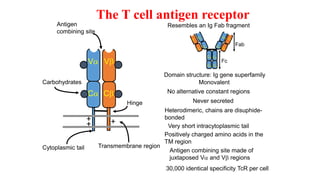
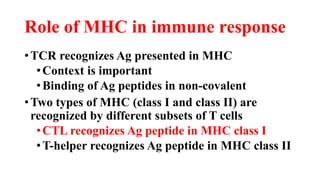
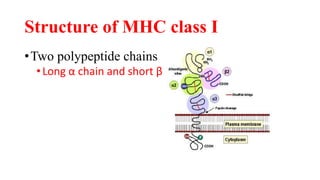
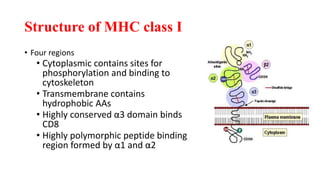
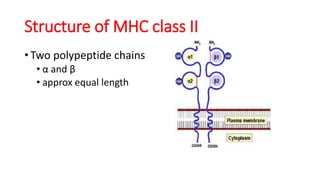
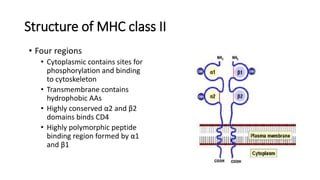
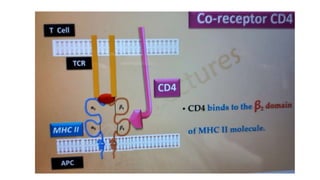
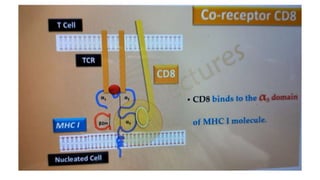
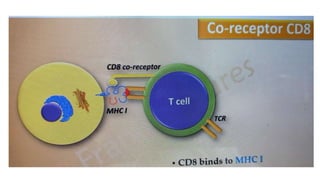
B and T cell antigen receptors are membrane-bound proteins that recognize antigens. B cell receptors (BCRs) are composed of immunoglobulin molecules that recognize intact antigens, while T cell receptors (TCRs) recognize processed antigens presented in the context of MHC class I or II molecules. BCRs are formed through somatic recombination, creating a diverse repertoire. TCRs also undergo genetic recombination of gene segments to generate diversity. Both BCRs and TCRs contain variable regions that determine antigen specificity and transduce activation signals upon antigen binding.