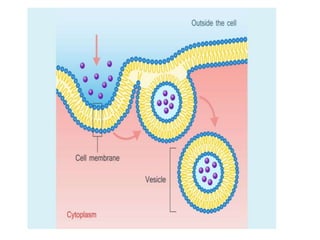
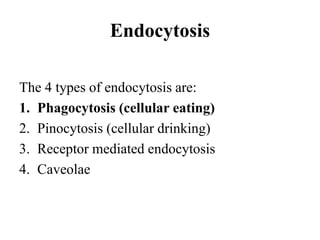
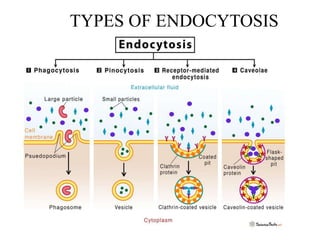
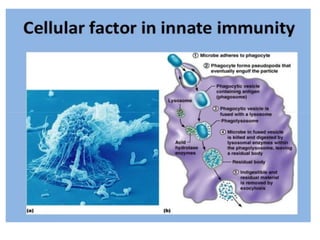
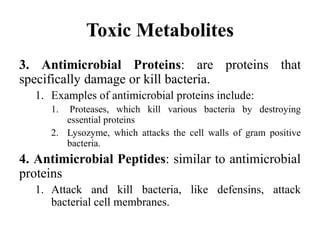
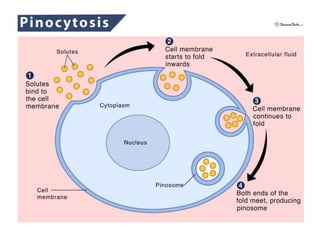
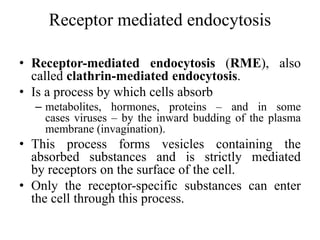
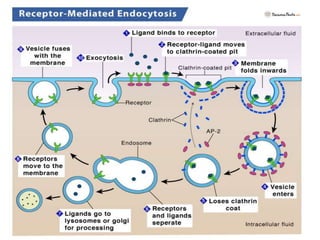
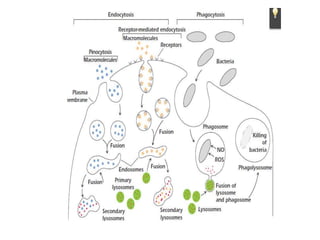
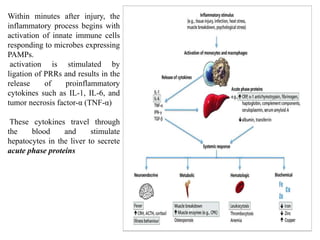
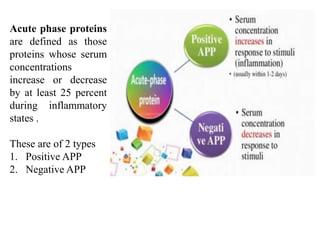
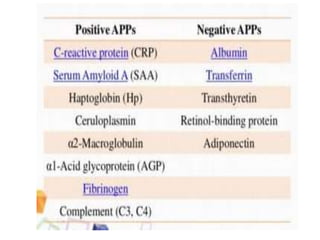
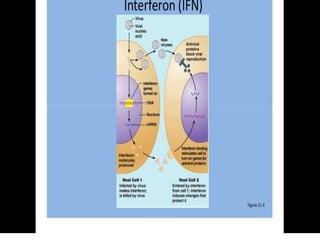
This document discusses endocytosis and inflammation. It defines endocytosis as the process by which cells take in material from outside through membrane vesicles. There are four main types of endocytosis: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and caveolae. Phagocytosis specifically refers to the engulfing of large solid particles by immune cells, aided by opsonins and surface receptors like toll-like receptors. Inflammation is the immune response to infection or injury, marked by redness, swelling, heat and pain. Key events are the recruitment of phagocytes and the release of cytokines and acute phase proteins from the liver to combat pathogens and initiate healing. Fever occurs as part of inflammation and is induced by