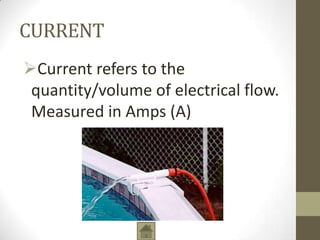
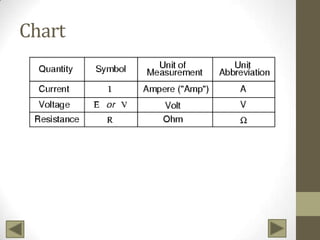
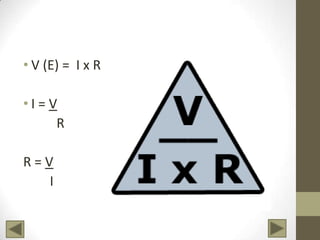
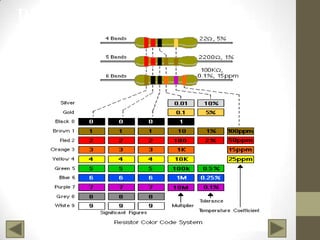
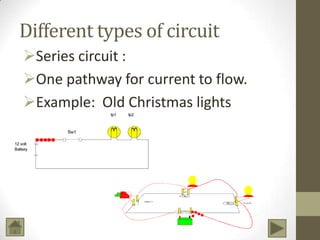
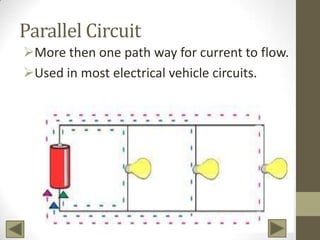
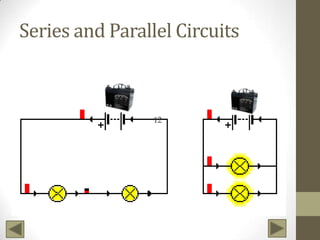
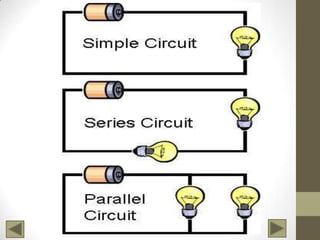
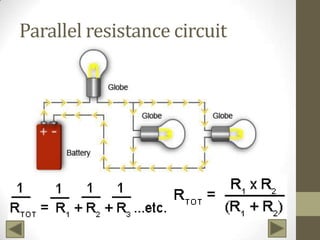
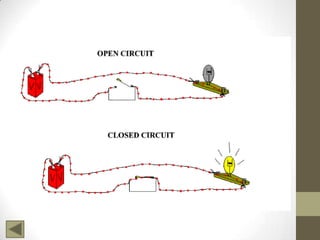
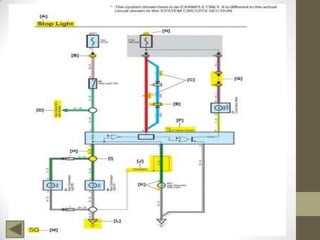
Ohm's Law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. Voltage is the "push" of electricity and is measured in volts. Current is the flow of electricity and is measured in amps. Resistance opposes the flow of current and is measured in ohms. Ohm's Law states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. Using Ohm's Law, the voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit can be calculated if two of the three values are known. Resistors are used to decrease voltage in a circuit and are marked with color bands to indicate their resistance value. Circuits can be connected in series or parallel, and understanding circuit diagrams