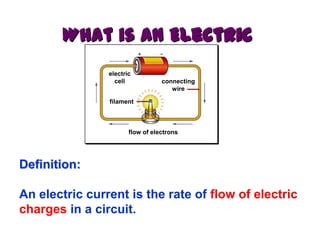
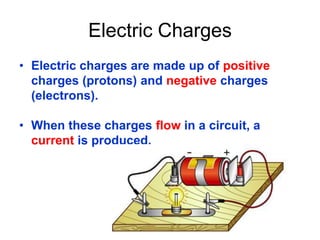
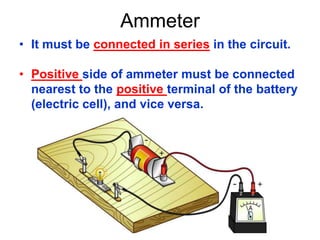
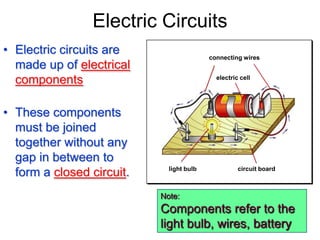
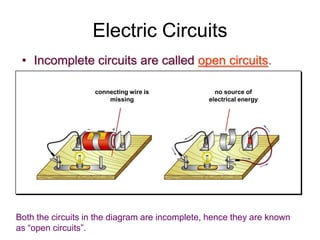
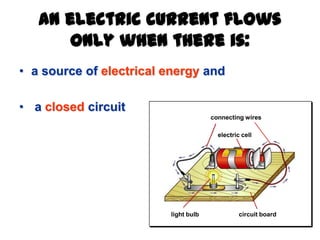
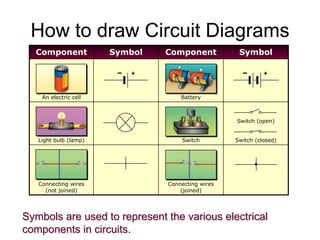
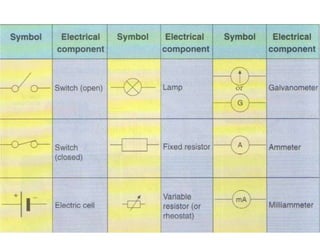
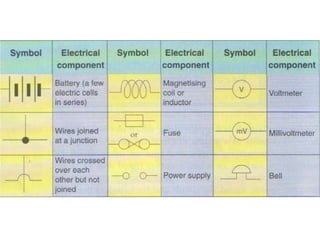
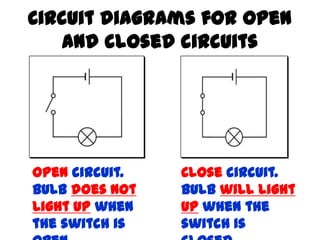
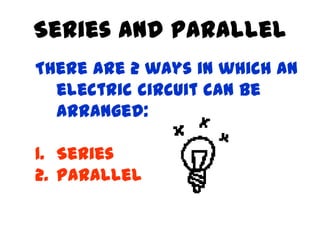
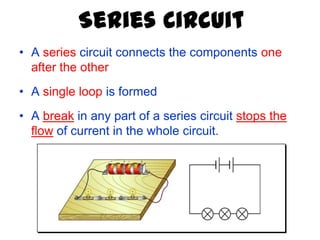
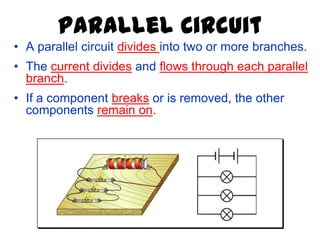
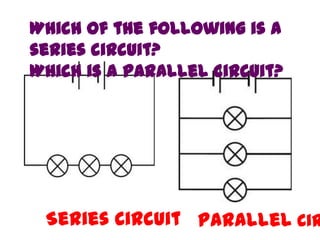
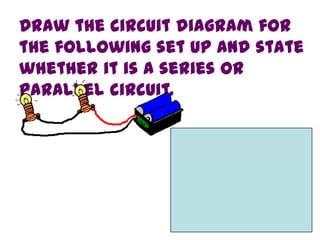
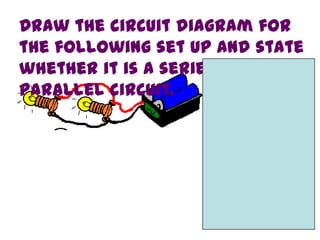
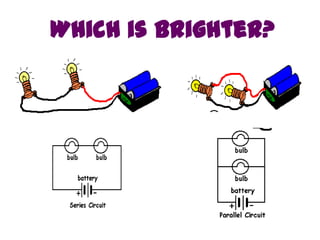
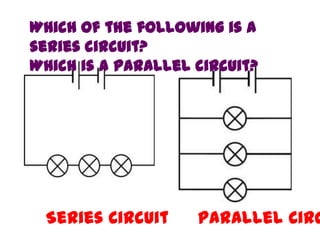
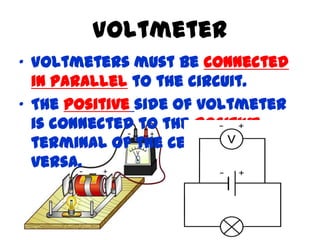
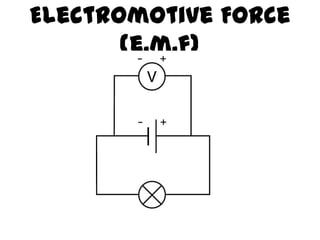
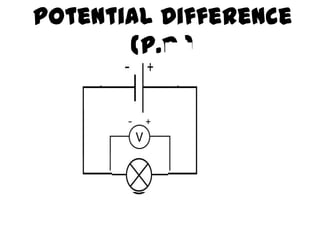
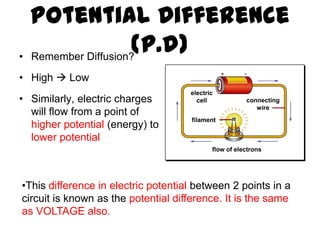
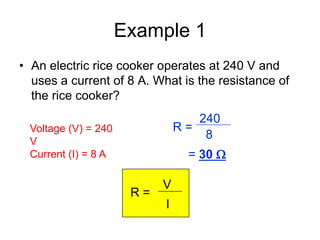
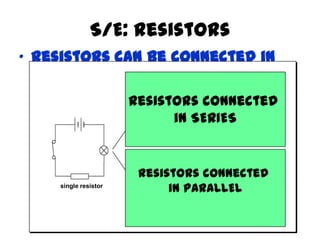
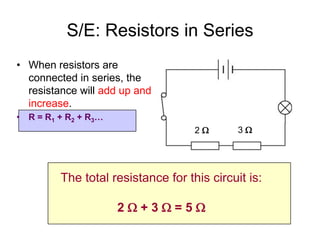
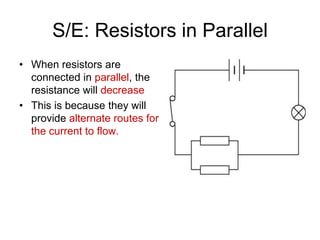
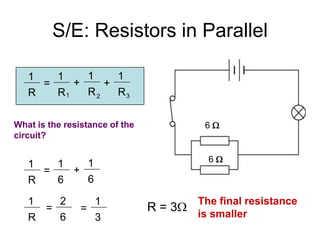
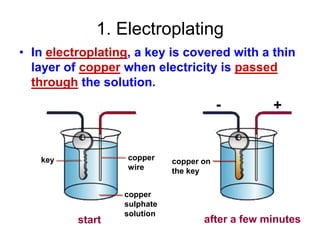
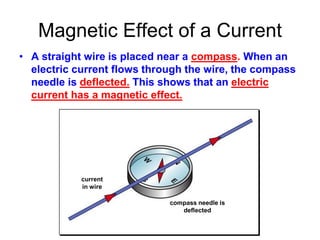
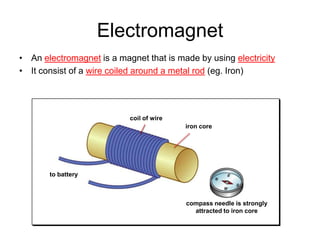
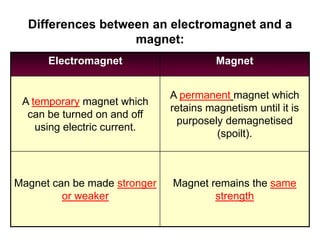
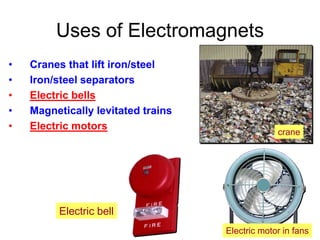
The document discusses electricity, including what electricity is, how electric circuits work, different circuit components like batteries, switches, resistors, and how to draw circuit diagrams. It explains key concepts such as current, voltage, resistance, and the differences between series and parallel circuits. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts and how circuits with different components can be arranged.