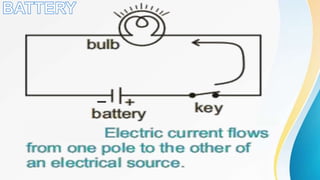
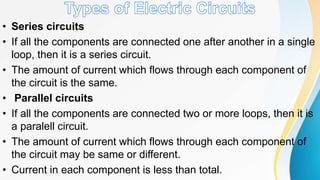
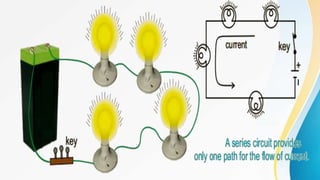
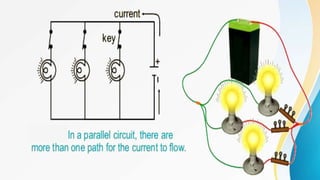
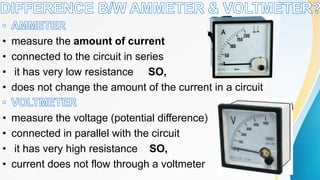
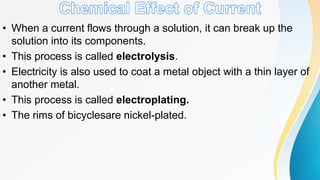
Electricity can produce light, heat, and sound. There are two types of electricity: static and electric current. Electric current is the flow of negatively charged electrons through a conductor. Current is measured in amperes using an ammeter. Circuits can be connected in series or parallel. Resistance hinders current flow. Ohm's law relates voltage, current, and resistance. Electricity has many uses and hazards that require safety precautions.