Embed presentation
Downloaded 28 times


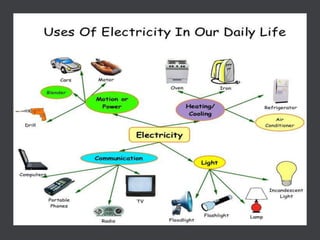









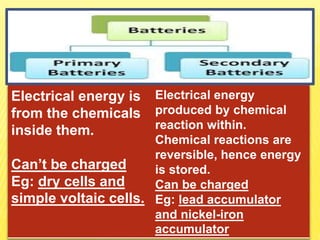



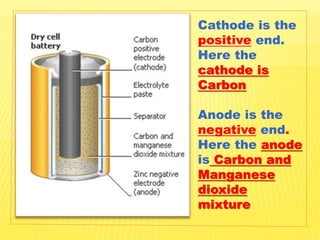
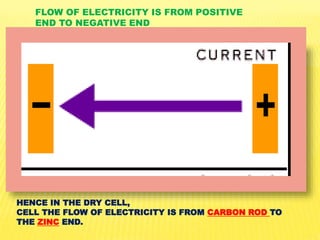


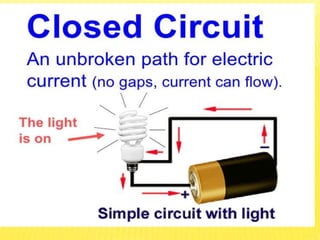
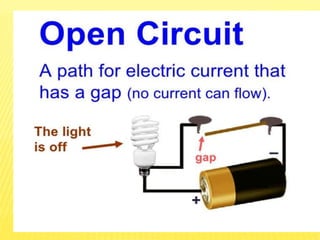
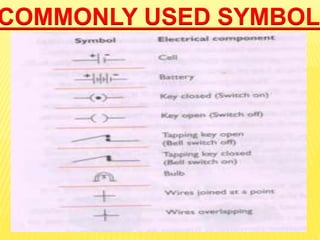

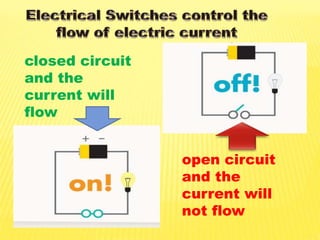
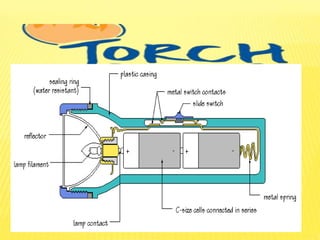
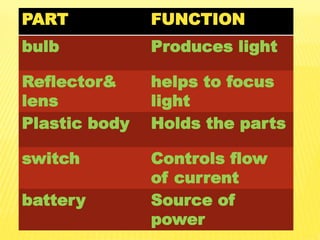
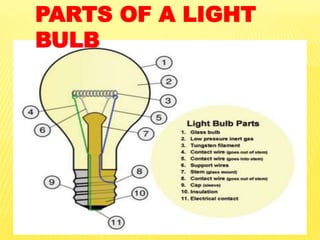

This document discusses electricity and electrical circuits. It defines conductors as materials that allow electric current to pass through and insulators as materials that do not allow current to pass through. It explains that batteries and generators are common sources of electric current and that batteries produce electricity through chemical reactions, with primary cells being non-rechargeable and secondary cells being rechargeable. The document also provides diagrams of open and closed circuits and labels the basic parts of a simple light bulb.



























