Embed presentation
Downloaded 169 times


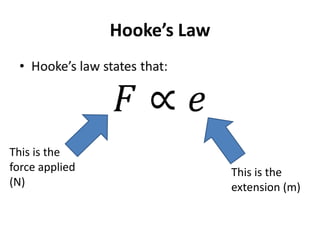

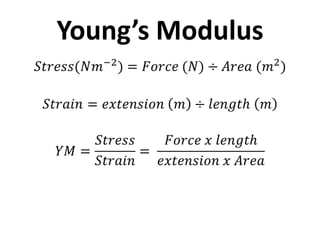

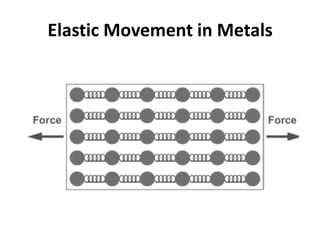
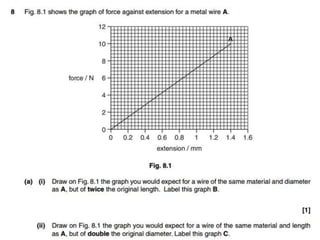




Hooke's Law states that the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied. It can be written as Force = Spring Constant x Extension. Young's Modulus is a material property that indicates how much a material will deform under stress. When stress is applied to a metal, the positive ions will spread apart as the atomic bonds stretch like springs. If the metal is within its elastic limit, it will return to its original shape when the stress is removed.











