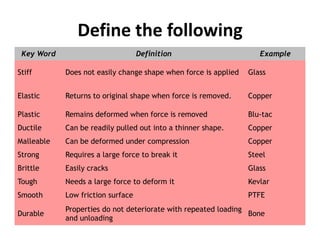
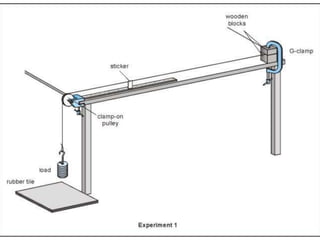
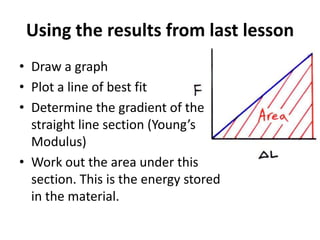
The resistivity of a material depends on:
- Its atomic/molecular structure
- Temperature
- Presence of impurities
Some key points:
- Metals have low resistivity due to free electrons
- Non-metals have high resistivity due to lack of free electrons
- Resistivity increases with temperature for most materials
- Adding impurities increases resistivity by scattering electrons
The resistivity, ρ, of a material is a constant for a given temperature and purity. It is measured in Ωm.
To calculate resistance, R, we use:
R = ρ * l / A
Where l is the length of the material and A is