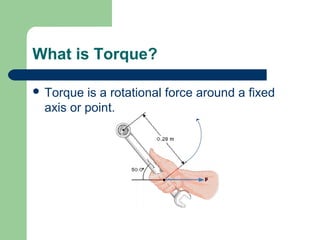
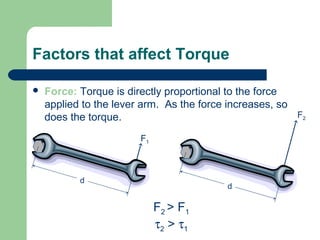
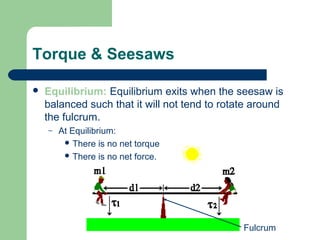
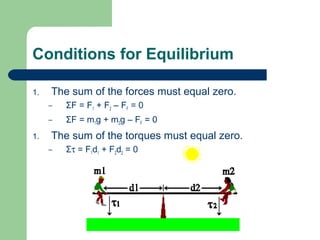
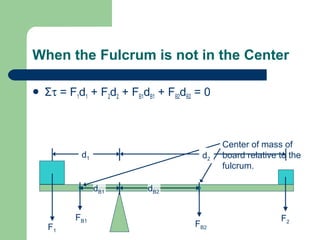
Torque is a rotational force that depends on three main factors: the distance from the axis of rotation (lever arm), the angle of the applied force, and the magnitude of the applied force. Torque causes an object to rotate and is measured in Newton-meters. Systems in rotational equilibrium have no net torque, meaning the sum of all torques acting on the object is zero. This allows seesaws and diving boards to remain balanced. Solving rotational equilibrium problems involves drawing free body diagrams and setting the sum of torques equal to zero.