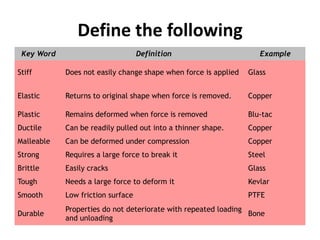
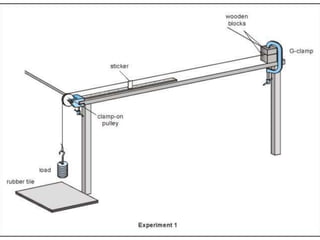
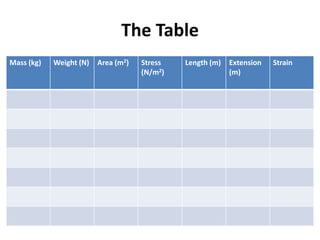
This document defines key terms related to Young's modulus including:
- Stress is the force applied per cross-sectional area of a material.
- Strain is the extension in length resulting from stress.
- Brittle materials break without plastic deformation.
- Elastic materials return to their original shape after deformation.
It also provides examples of materials that exhibit properties such as being stiff, elastic, plastic, ductile, malleable, strong, brittle, tough, smooth, and durable. The document outlines measurements needed to calculate stress and strain and discusses working out uncertainty when multiplying or dividing units.