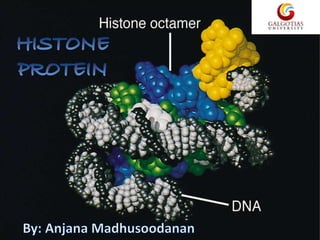
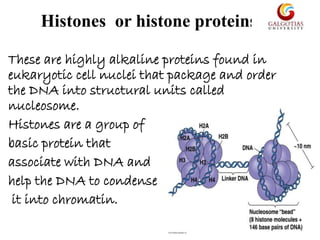
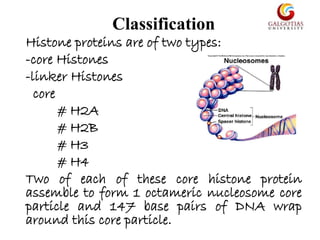
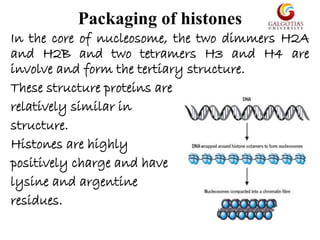
Histones are highly alkaline proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes and chromatin. There are two main types of histones - core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, H4) and linker histones (H1, H5). Core histones assemble into an octamer that DNA wraps around to form the nucleosome. Linker histones sit on top of the nucleosome and help compact DNA further. Histones can undergo modifications like methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation that affect how tightly DNA is packaged and gene expression. They play a key role in compacting DNA and regulating chromatin structure and transcription.