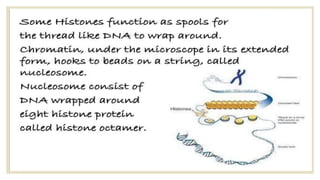
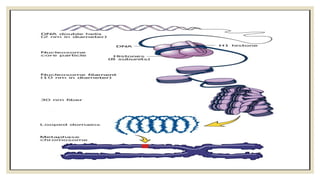
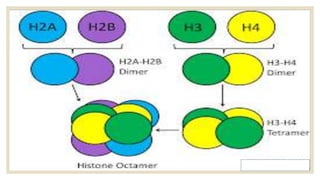
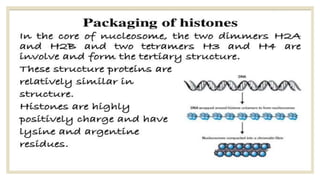
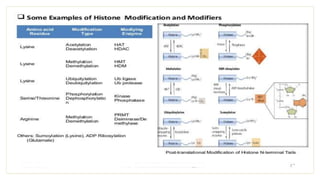
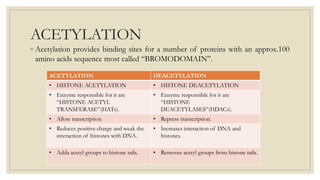
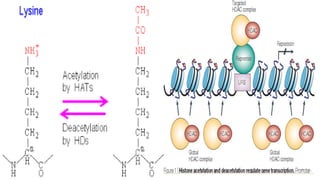
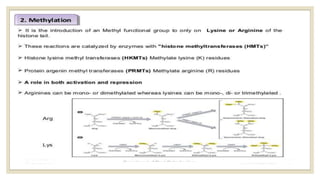
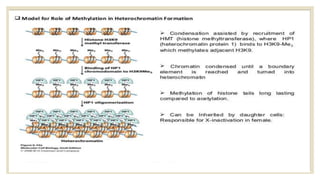
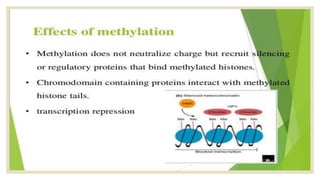
Histones are positively charged proteins that DNA wraps around to form nucleosomes, the basic unit of chromatin. The four core histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, contain high proportions of lysine and arginine amino acids. H2A, H2B, and H1 contain more lysine while H3 and H4 contain more arginine. Histone modifications like acetylation and phosphorylation can regulate gene expression by altering chromatin structure and accessibility to transcription proteins. Acetylation reduces the positive charge of histones and weakens their interaction with DNA, allowing transcription. Phosphorylation also weakens histone-DNA interactions and influences chromatin structure and cellular processes like DNA