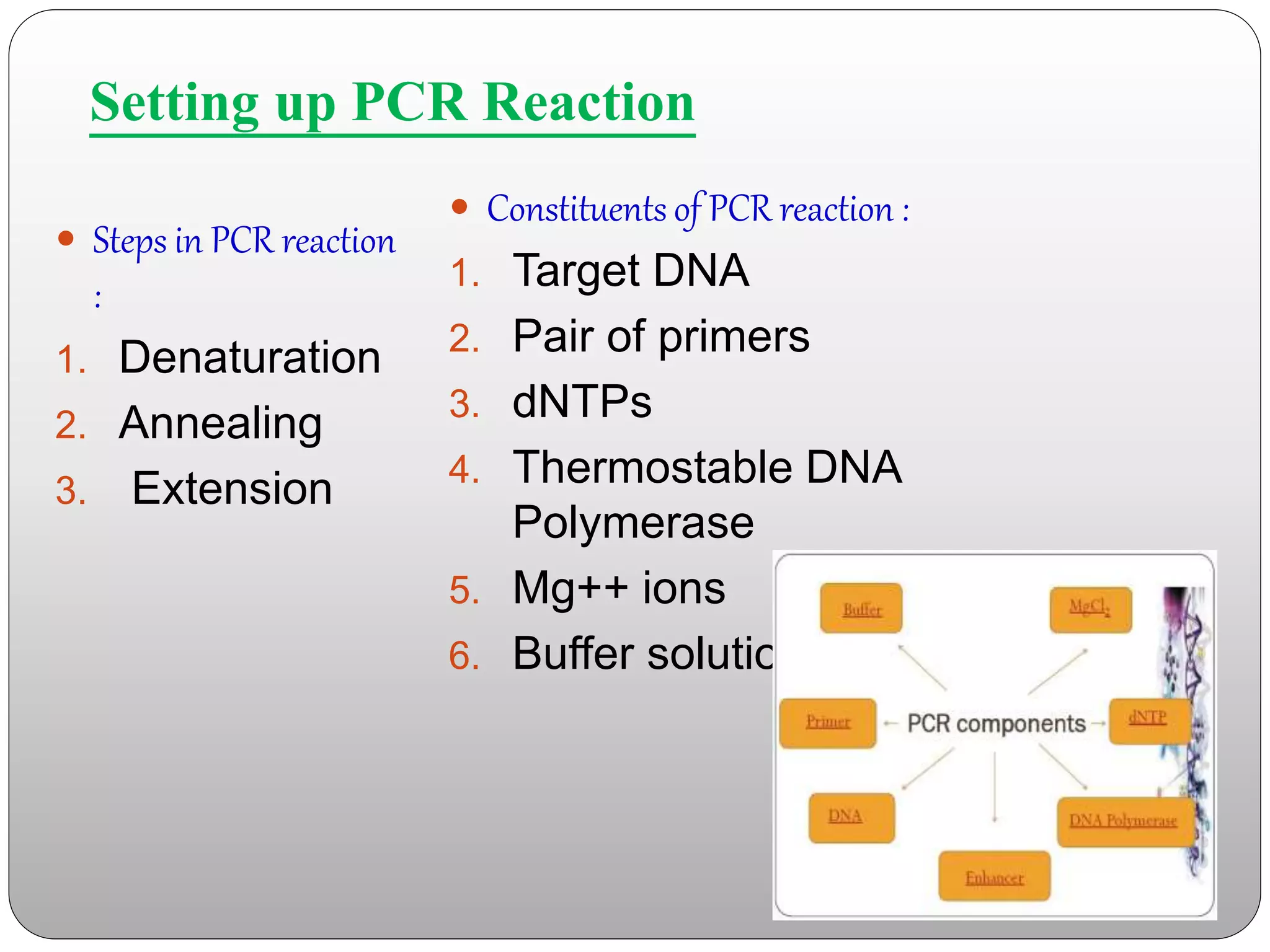
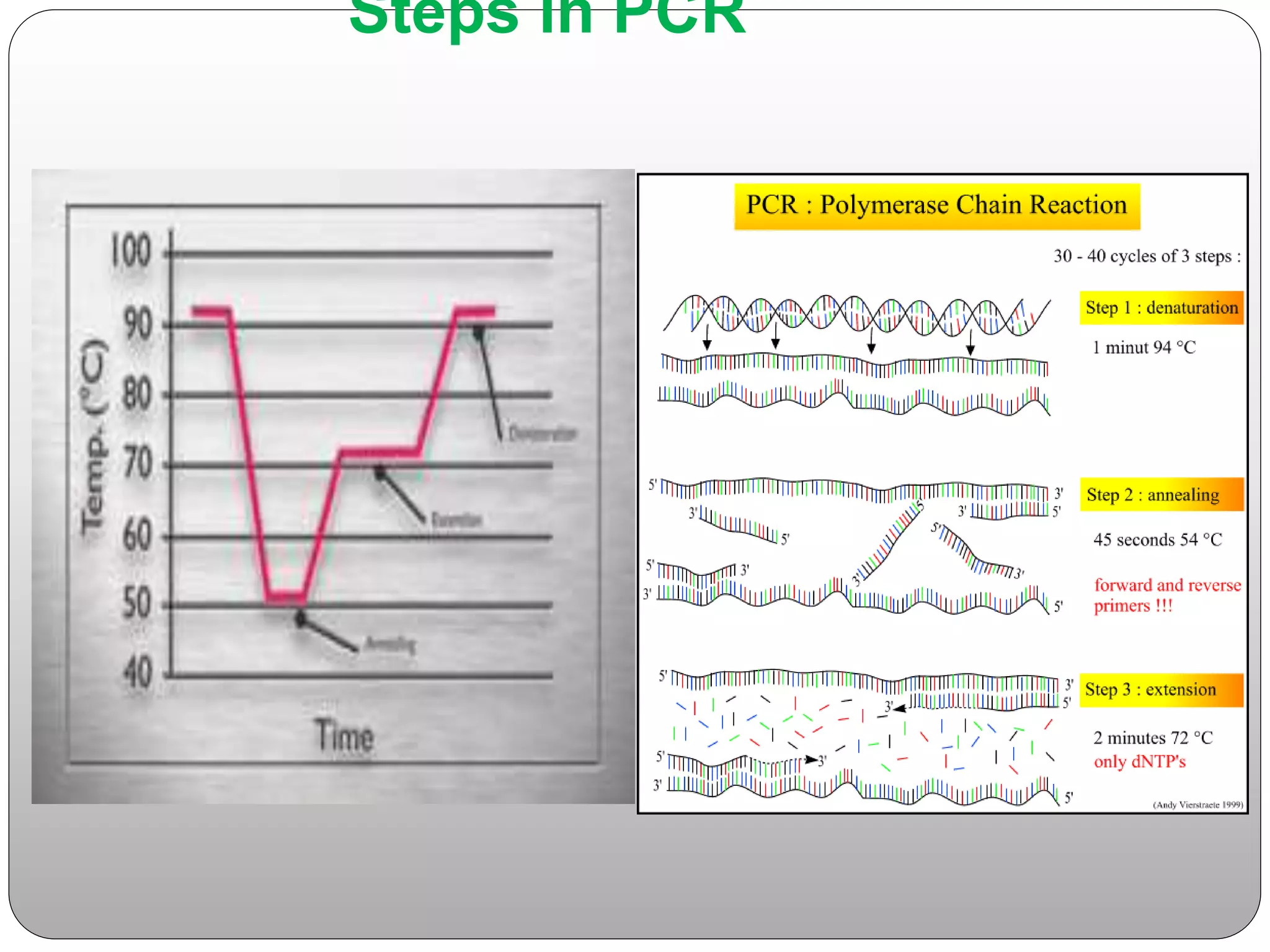
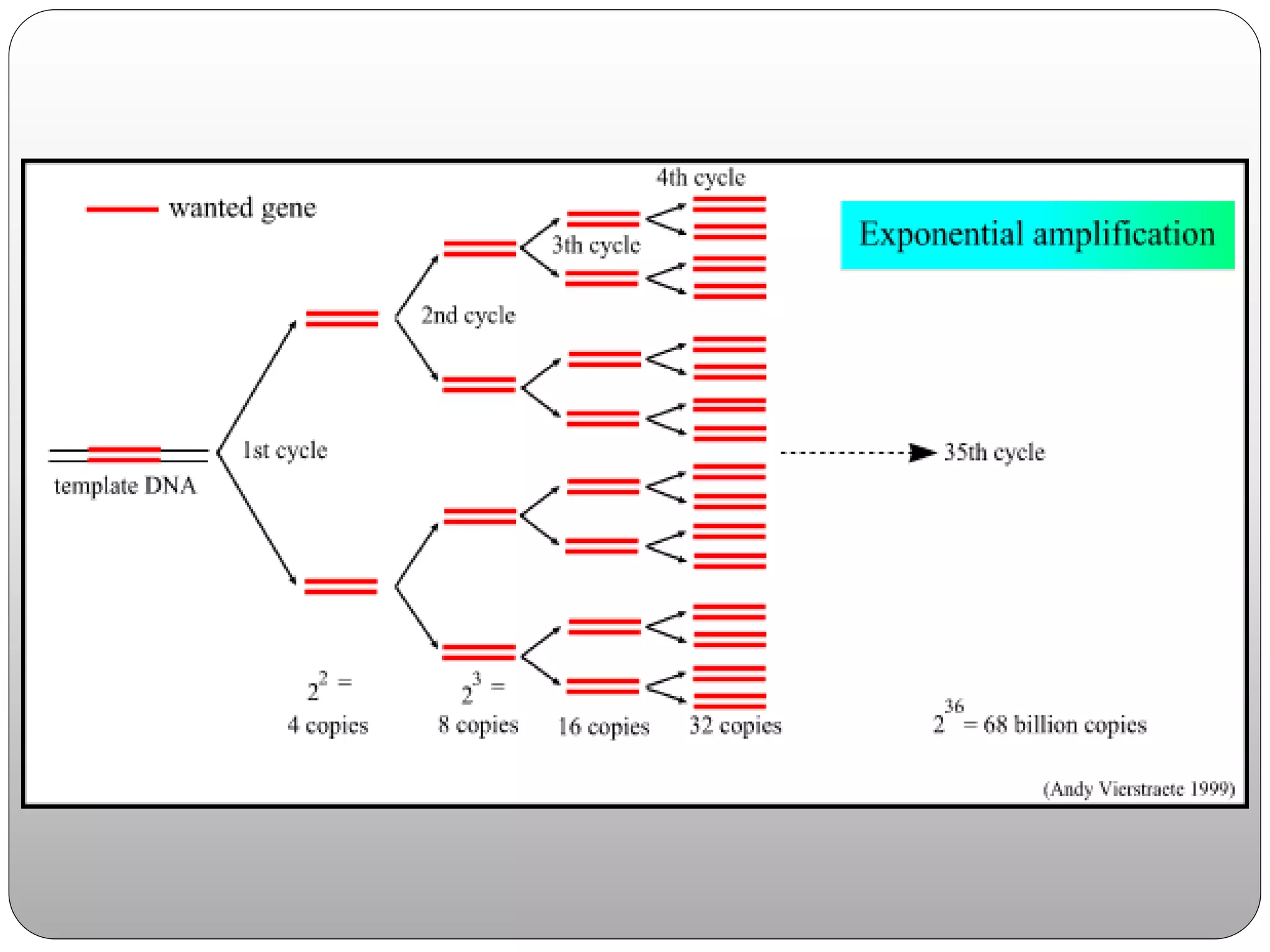
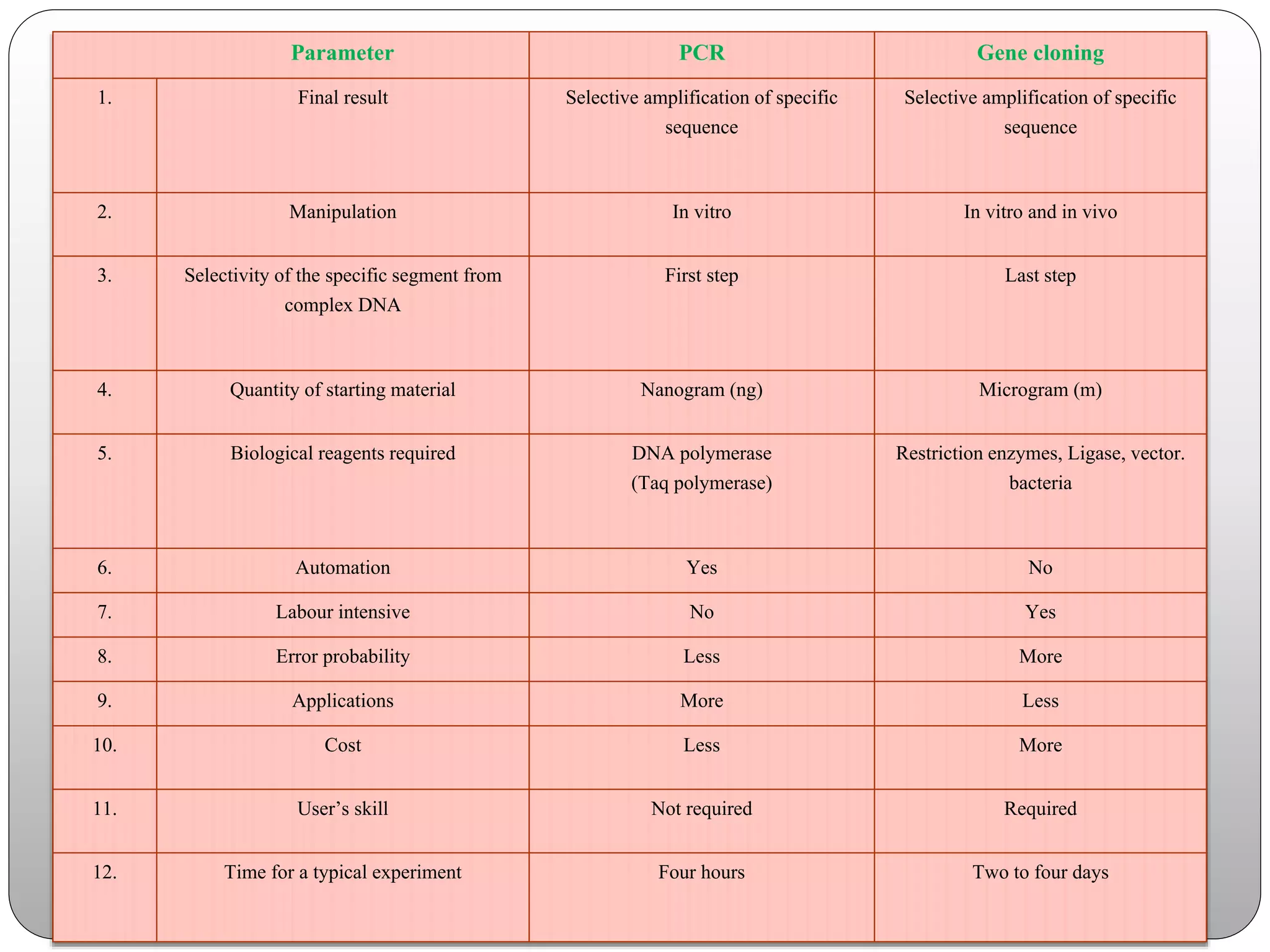
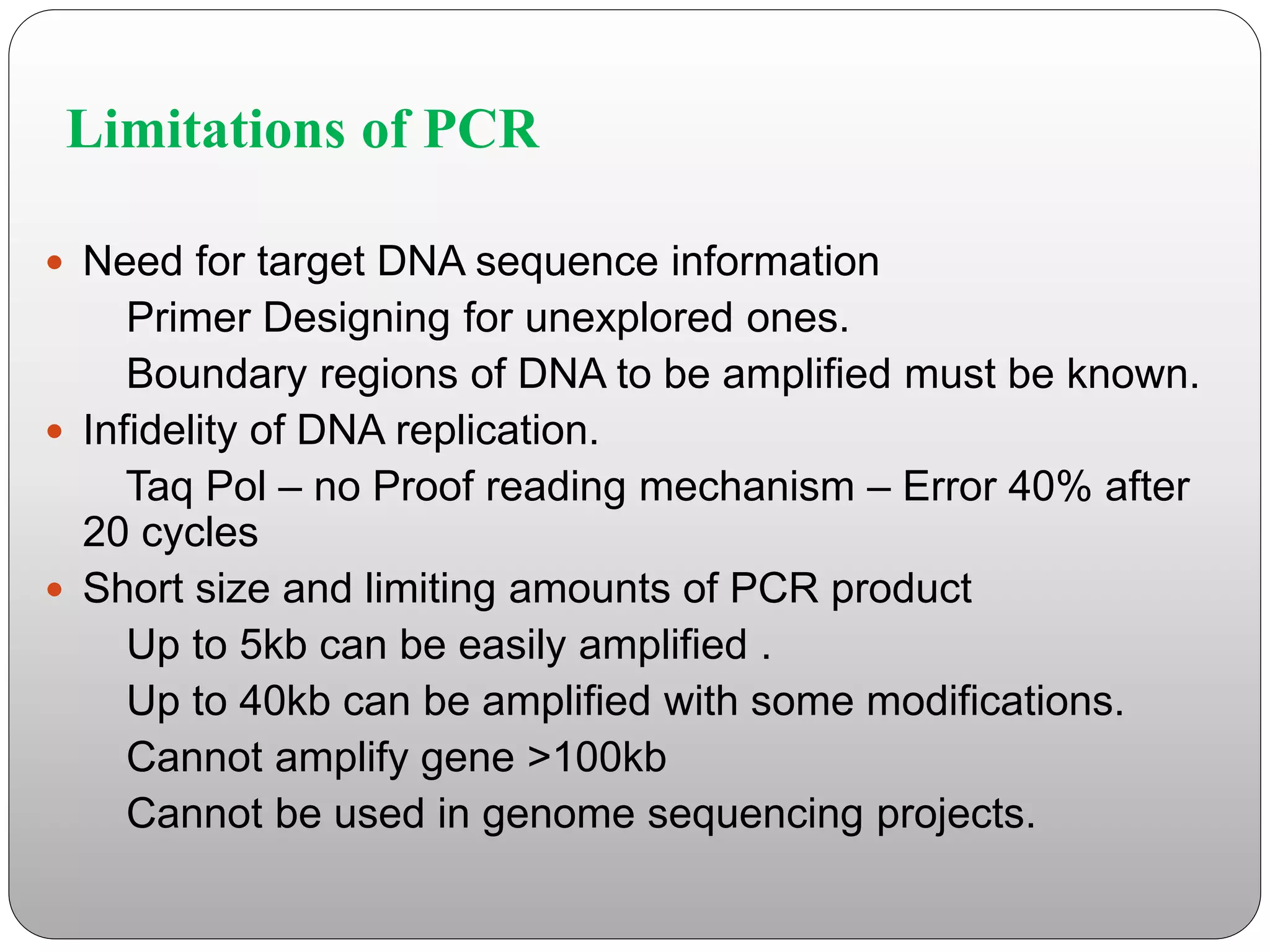
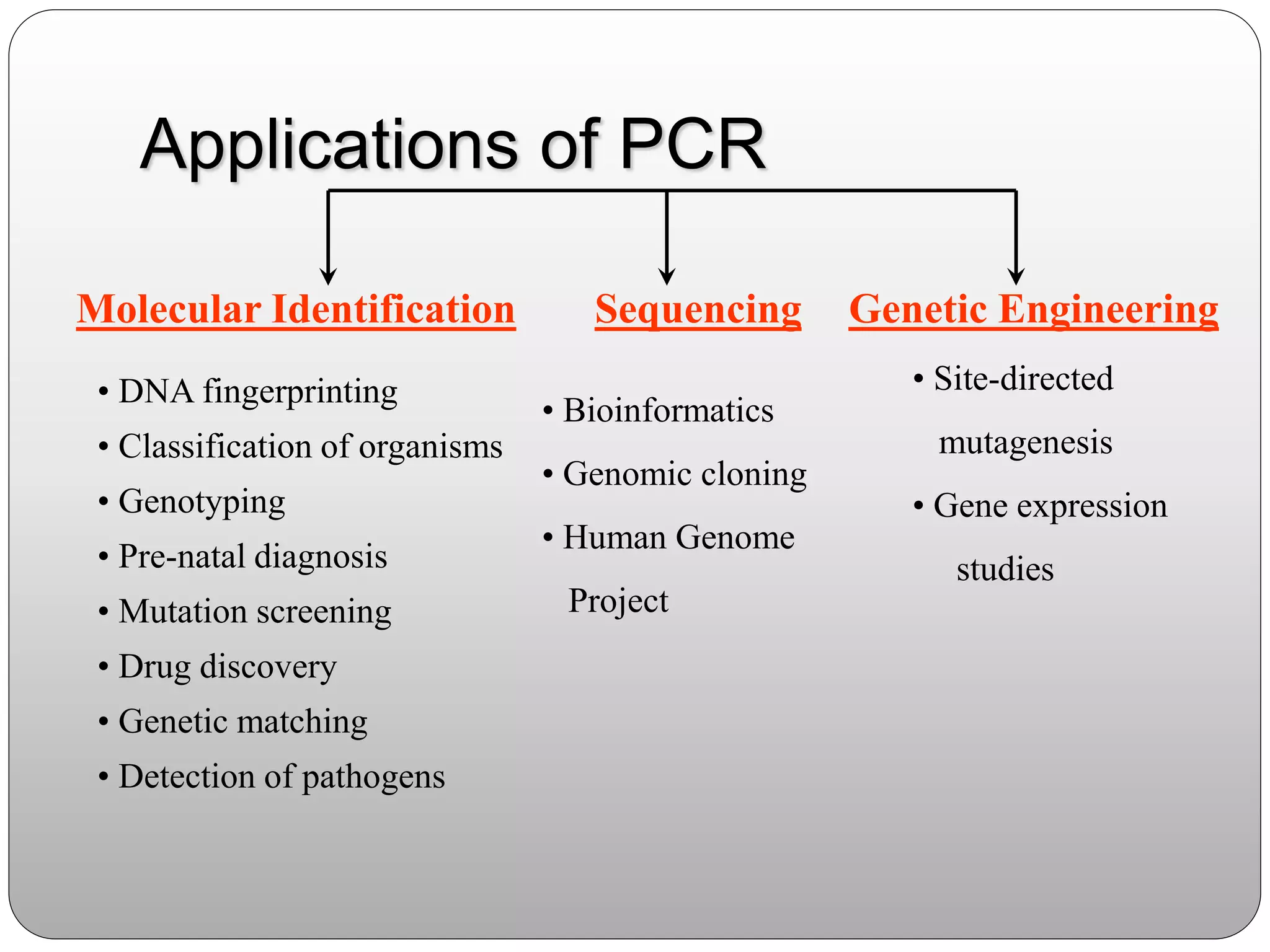
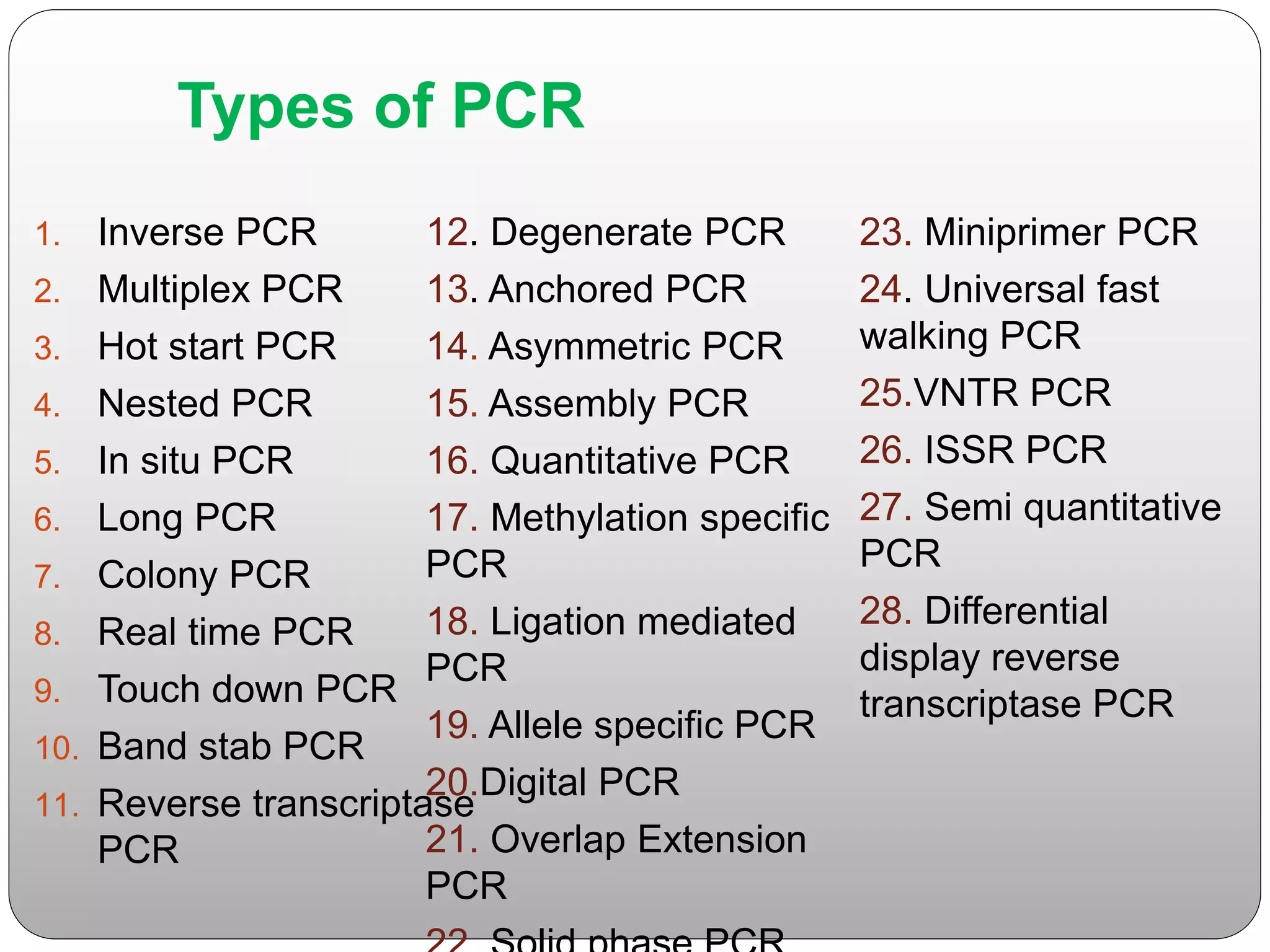
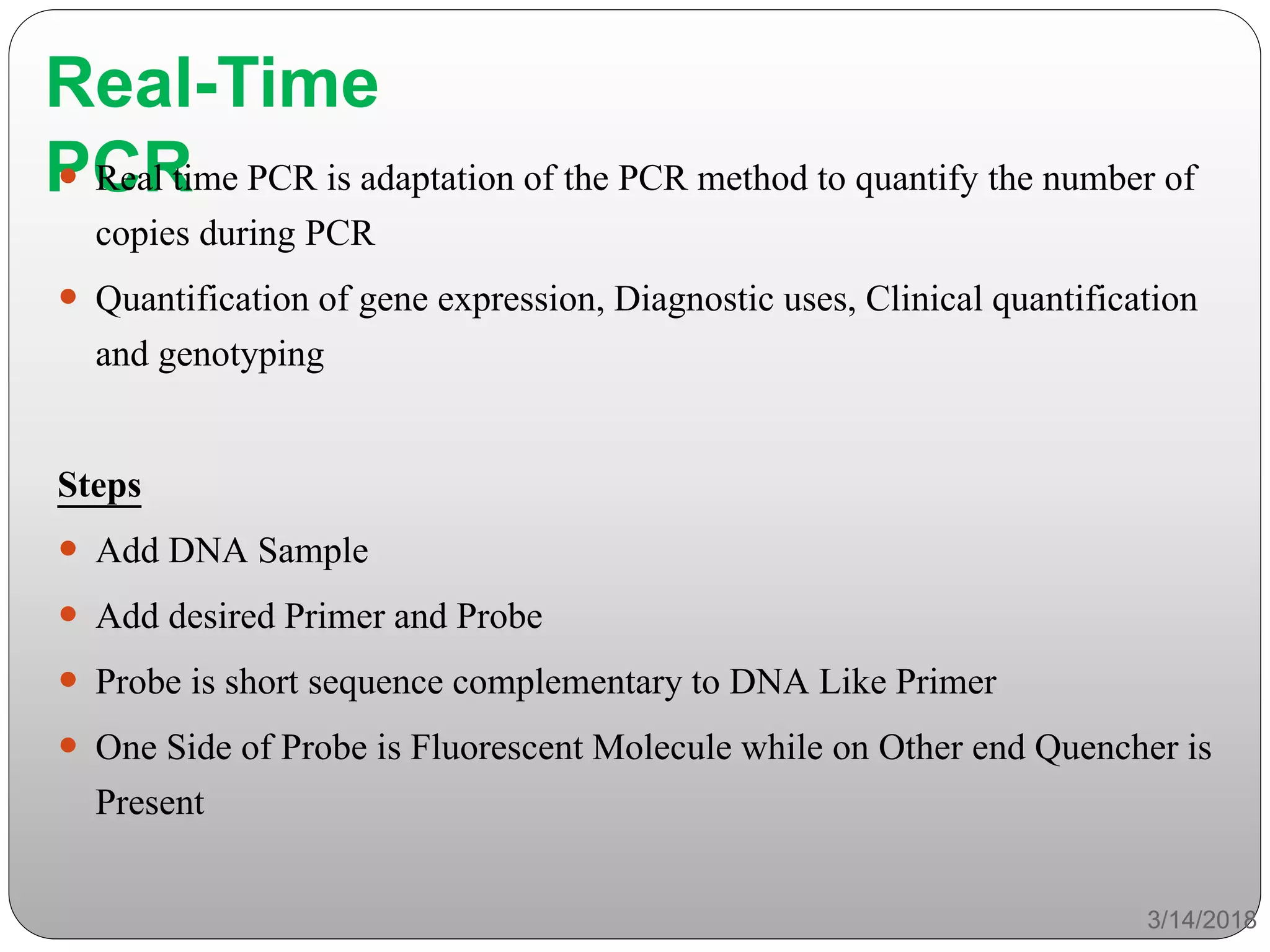
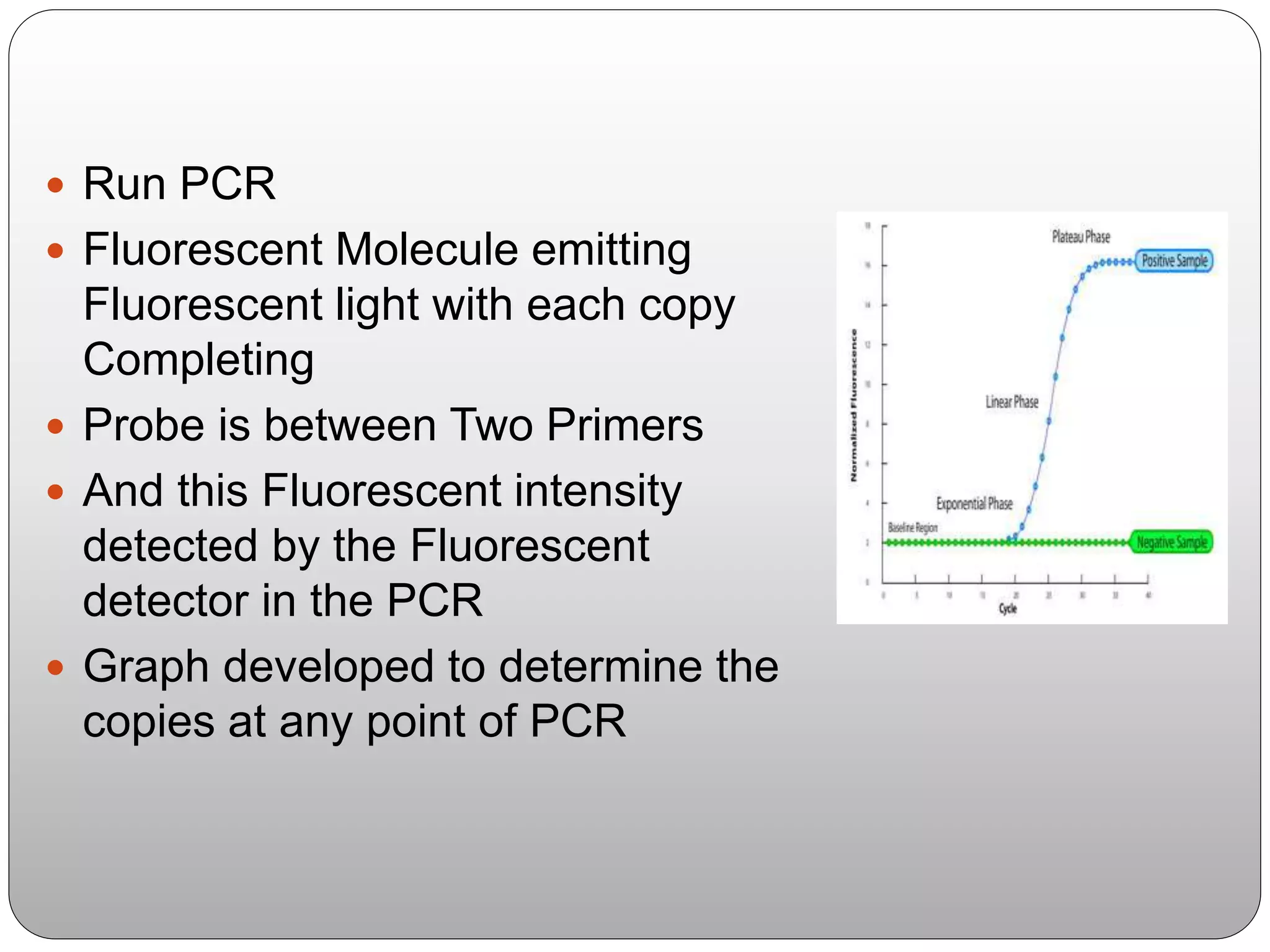
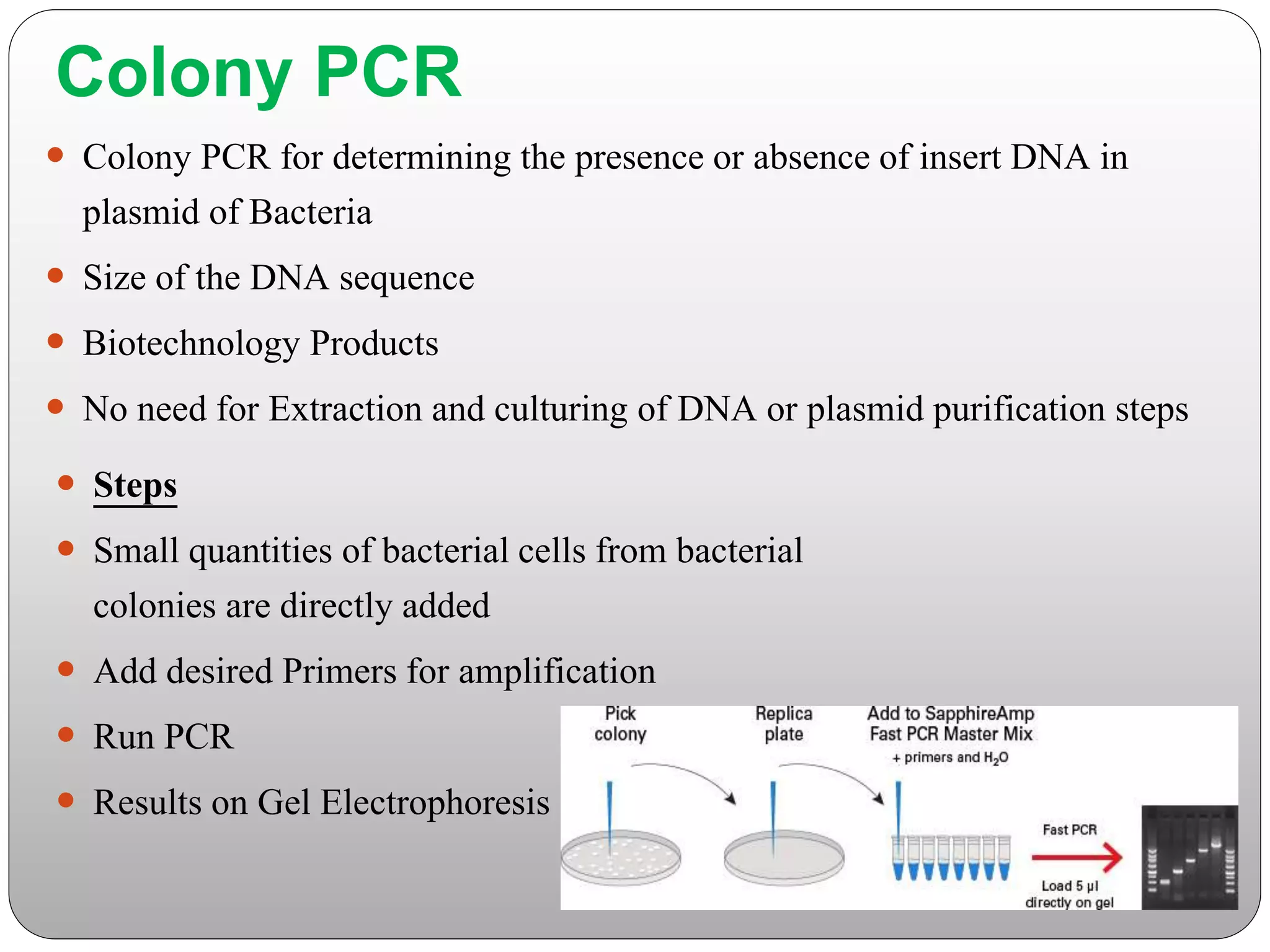
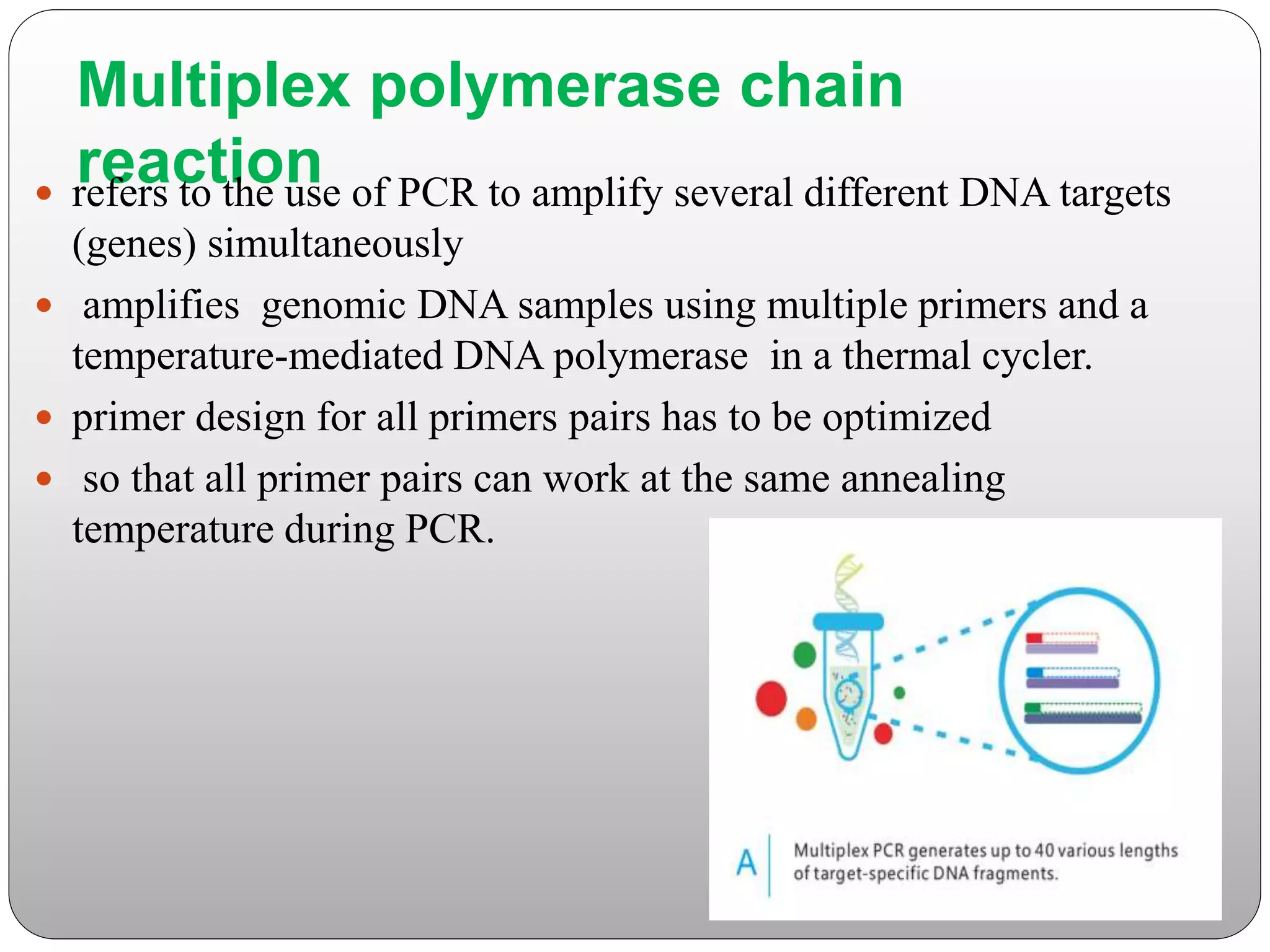
The document discusses polymerase chain reaction (PCR), its history, the basic steps and components involved. PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA through repeated cycles of heating and cooling. It allows for exponential amplification of DNA, enabling small amounts of genetic material to be analyzed. The document outlines the key aspects of setting up a PCR reaction and factors important for optimal results such as primer design, annealing temperature and polymerase used. Several types of PCR are also described briefly, including real-time PCR, asymmetric PCR and nested PCR.