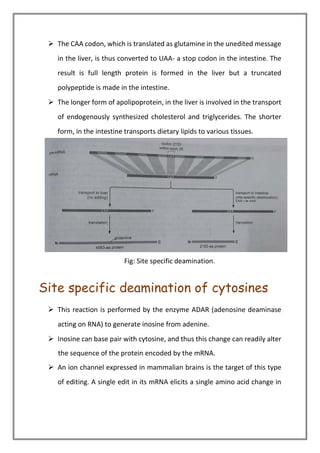
RNA editing modifies the RNA sequence after transcription, primarily through site-specific deamination and guide RNA-directed uridine insertion or deletion. These processes alter protein coding information, influencing key biological functions such as cholesterol transport and brain development. The fully processed mRNA then undergoes transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, facilitated by specific proteins and energy requirements.