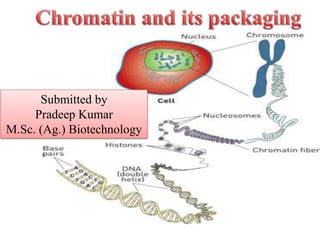
Chromosome packaging
- 1. Submitted by Pradeep Kumar M.Sc. (Ag.) Biotechnology
- 2. o Cells contain a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane in eukaryotic cells, and a nuclear region in the prokaryotic cells. o In a non-dividing cell the nucleus is filled with a thread-like material known as "chromatin". o Chromatin is made up of DNA and proteins (mainly histones and some non- histone acidic proteins). o The chromosomes themselves are macromolecular entities that must be synthesized, packaged, protected, and properly distributed to daughter cells at cell division.
- 3. • The packaging of tremendous amount of genetic information into the small space within a cell has been called the ultimate storage problem. • Chromosomal DNA exist in the form of very long molecules, which must be tightly packed to fit into the small confines of a cell. • The structure of DNA can be considered at three hierarchical levels: a. The primary structure of DNA is its nucleotide sequence b. The secondary structure is the double stranded helix c. The tertiary structure refers to higher order folding that allow DNA to be packed into the confined space of a cell.
- 4. • One type of DNA tertiary structure is supercoiling which takes place when the DNA helix is subjected to strain by being over wound or under wound. • Energy is used to add or remove any turns, strains is placed on the molecule, causing the helix to super coil, or twist on itself. • Molecule that are over rotated exhibit positive supercoiling. • Under rotated molecules exhibit negative supercoiling. • Supercoiling is a partial solution to the cells DNA packing problem because super coiled DNA occupies less space than relaxed DNA.
- 6. • Supercoiling relies on topoisomerases enzymes that add or remove rotation from the DNA helix by temporarly breaking the nucleotide strand, rotating the ends around each other, the rejoining the broken ends. • Overrotation or underrotation of a DNA double helix places strain on the molecule, causing it to supercoil. • Supercoiling is controled by topoisomerase enzymes. • Most cellular DNA is negetively supercoiled, which eases the seperation of nucleotide strands during replication and transcription and allow DNA to be packed into small spaces.
- 7. • Individual eukaryotic chromosome contain enormous amounts of DNA. • Chromosome are in an elongated relatively uncondensed state during interphase of the cell cycle. p q
- 8. • Walther Flemming first used the term Chromatin in 1882. At that time, Flemming assumed that within the nucleus there was some kind of a nuclear-scaffold. • Chromatin, which consists of DNA complexed to proteins, is the material that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes. • The most abundant of these proteins are the five types of positively charged histone proteins H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. • Variant histones may at times be incorporated into chromatin in place of the normal histones. • In non-dividing cells there are two types of chromatin: euchromatin and heterochromatin.
- 9. Electron micrographs of “chromatin” preparations • Two classes of chromatin proteins: a. Histones (core Histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4) b. Non- histone proteins
- 10. Types of Histone Amino acid composition M.W. No. of A.A. Variation H1 Lysine rich 21,130 223 Wide H2A Slightly lysine rich 13,960 129 Fairly conserved H2B Slightly lysine rich 13,774 125 Fairly conserved H3 Arginine rich 15,273 135 Highly conserved H4 Arginine rich 11,236 102 Highly conserved
- 11. • The histone octamer and associated DNA that form the nucleosome combine with histone H1 to form the chromatosome. • The addition of H1 to a nucleosome results in protection of an additional 20 to 22 bp of linker DNA adjacent to the nucleosome, and thus H1 is often referred to as the linker histone. • Only one H1 subunit is present per chromatosome, unlike the core histones, which are present in two copies each. • DNA binding in H1 is intrinsic to the central globular region, which contains two DNA-binding sites. • H1 binds only one of the linker DNA strands, and the second DNA site in histone H1 binds to the central region of the DNA supercoil in the nucleosome
- 12. • Histones are rich in the basic amino acids arginine and lysine, which together make up about 25% of the amino acid residues in any given histone protein. • Histone proteins are highly conserved among eukaryotic cells. • Histones H3 and H4 are nearly identical in all eukaryotes, suggesting strict conservation of their functions. • Histones H1, H2A, and H2B show less sequence similarity, but on the whole, they are more conserved than other types of proteins. • Salt bridges between positively charged histones and negatively charges DNA play a major role in stabilizing DNA-histone complex.
- 13. o H1, H2A & H2B, are rich in lysine whereas H3 & H4 are arginine rich H1 is highly unconserved and mutable H3 & H4 are highly conserved molecules. o According to molecular weight the relation is H1 > H3 >H2A >H2B >H4. o Histones proteins lack Tryptophan amino acid. o Histones octamer has a structural core of an H3.H4 tetramer associated with two H2A.H2B dimmers. o Each Histones is extensively interdigitated with its partner. o All core Histones have the structural motif of the Histones fold. o The Histones N-terminal tails extend out of the nucleosome.
- 15. • In chromatin, those protein which remain after the histone have been removed as classified as non histone protein . • Scaffold proteins, DNA polymerase, heterochromatin protein 1 and paycomb are common non histone . • Non-histone protein Higher molecular weight - Approximately 1.0 to 1.5 lakh dalton Acidic in nature Mostly act as enzyme Promotes gene action.
- 16. o DNA is roughly 3 meter long and it has to be packed in nucleus which is few micrometres in diameter, hence higher order of packaging is required. o There are various order of packaging a. First order of packaging – Nucleosome b. Second order of packaging – Solenoid fibre c. Scaffold loop Chromatids Chromosome are third order of packaging.
- 18. The nucleosome is basic repeating unit of chromatin. It provides the lowest level of compaction of double-strand DNA into the cell nucleus. It often associates with transcription. 1974: Roger Kornberg discovers nucleosome who won Nobel Prize in 2006.
- 19. • The nucleosome consists of a core particle of eight histone proteins and DNA that wraps around the core. • Chromatosome, which are nucleosomes bound to an H1 histone, are separated by linker DNA. • Nucleosmes fold to form a 30-nm chromatin fiber, which appears as a series of loops that pack to create a 250 nm wide fiber. • Helical coiling of the 250 nm fiber produces a chromatid.
- 20. • Solenoid is known as Second level of packaging . • Solenoid – Second level of packaging Proposed by Finch & Klug 6 nucleosome together forms Solenoid Diameter is 30 nm H1 histone stabilizes the Structure.
- 21. o Super Solenoid : Super Solenoid The final level of packaging is characterized by the 700 nm structure seen in the metaphase Chromosome known as super solenoid structure. o The condensed piece of chromatin has a characteristic scaffolding structure that can be detected in metaphase chromosomes. o This appears to be the result of extensive looping of the DNA in the chromosome.
- 23. Compaction level of interphase chromosomes is not uniform Euchromatin a. Less condensed regions of chromosomes b. Transcriptionally active c. Regions where 30 nm fiber forms radial loop domains Heterochromatin a. Tightly compacted regions of chromosomes b. Transcriptionally inactive (in general) c. Radial loop domains compacted even further
- 24. Structure of heterochromatin and Euchromatin