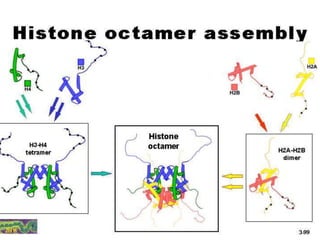
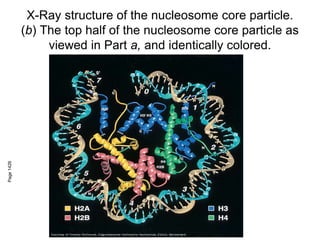
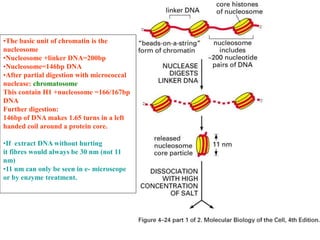
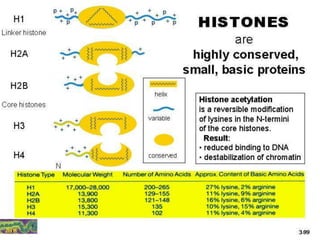
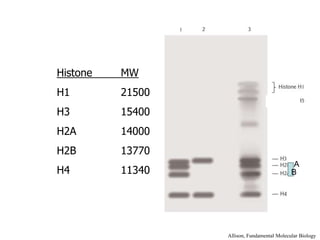
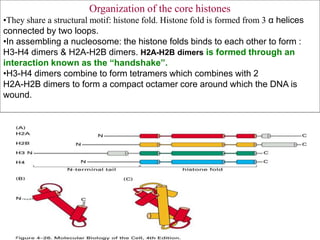
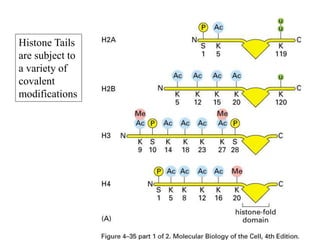
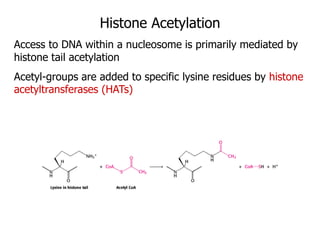
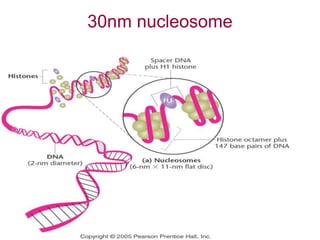
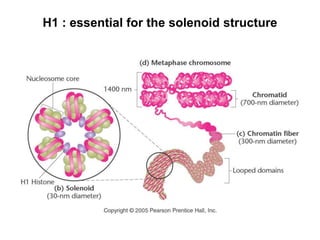
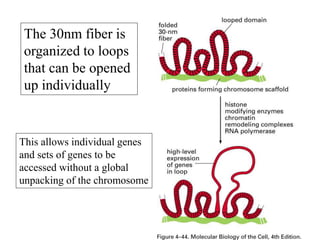
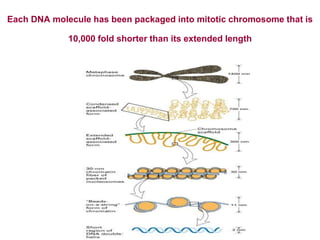
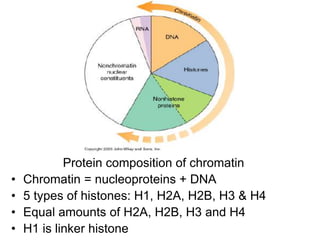
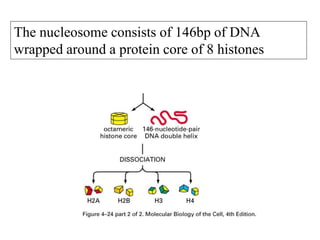
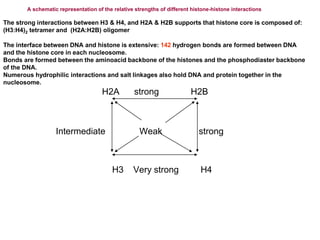
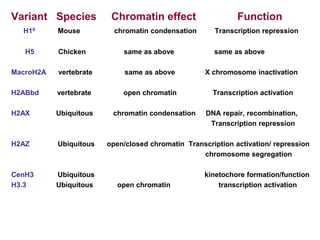
The document discusses chromatin structure and organization. It describes how DNA is packaged into nucleosomes, which consist of 146bp of DNA wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, H4). Nucleosomes interact with each other and linker histone H1 to form higher-order chromatin structures. Histone proteins play a key role in chromatin organization and undergo various post-translational modifications that influence chromatin structure and gene expression. The document also discusses histone variants and their different functions in chromatin.