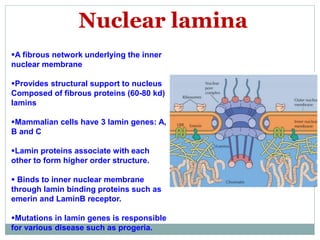
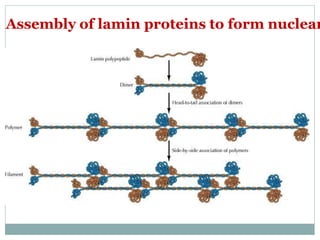
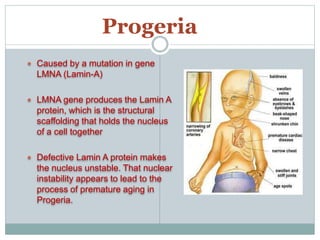
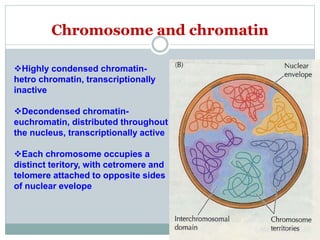
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that houses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. It was discovered in 1831 and named by Robert Brown. The nucleus stores DNA and RNA, enables protein synthesis, and houses the nucleolus where ribosomes are produced. It occupies about 10% of the cell volume and is surrounded by a double membrane with nuclear pores that regulate transport. The nuclear lamina provides structure and chromatin contains the genome. Within the nucleus, the nucleolus is the site of ribosome biogenesis through rRNA transcription and processing.