Embed presentation
Downloaded 84 times



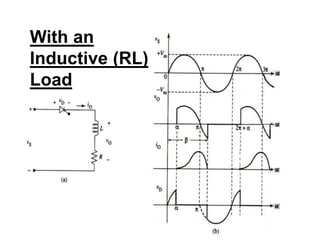
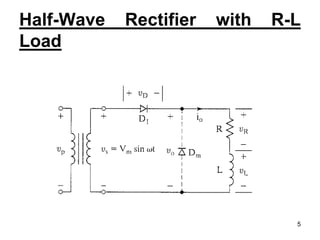
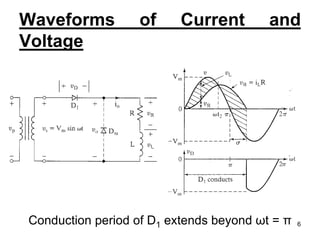
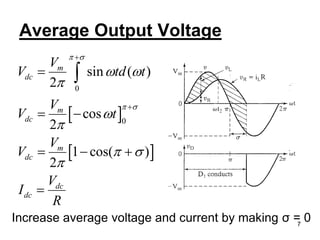
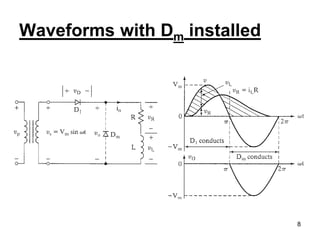
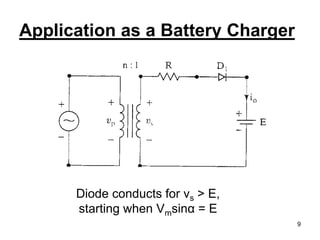
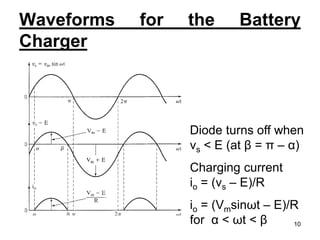

This document discusses half wave control rectifiers with RL loads, focusing on thyristor-based controlled rectifiers that allow for variable DC output through phase control. It highlights two types of controlled rectifiers: fully controlled, which can invert power flow, and half controlled, which delivers unidirectional output. The text also includes applications such as battery chargers, detailing the operational waveforms and formulas for current and voltage.










