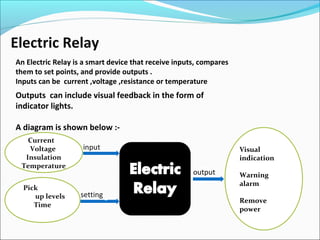
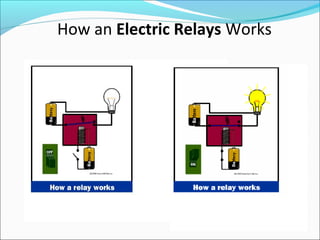
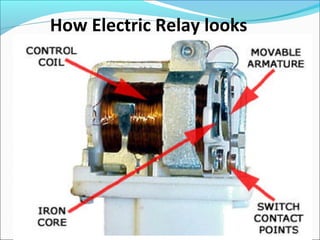
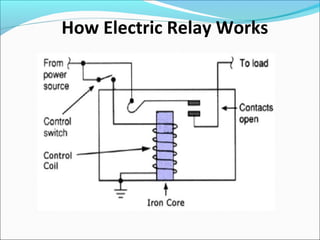
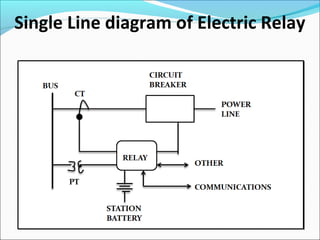
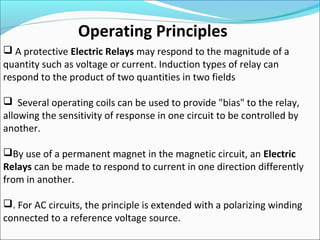
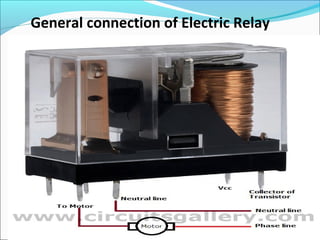
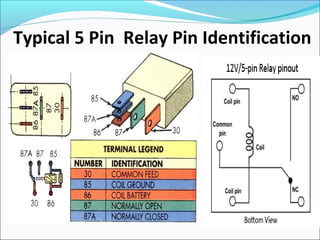
This document discusses electric relays. It begins by defining an electric relay as an automatic device that senses abnormal electric circuit conditions and closes its contacts. It then describes the basic components and operating principles of different types of relays, including electromagnetic, solid-state, and microprocessor-based relays. The document also covers relay applications, terminology, advantages, disadvantages, and concludes by emphasizing the importance of relays for safety and protection in electric systems.