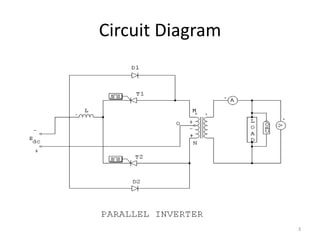
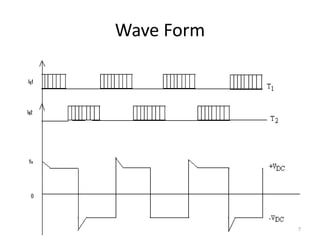
This document discusses a parallel inverter circuit. It contains two SCRs that act as the main load carrying components. Diodes allow reactive power from the load to be fed back to the DC supply. When SCR1 conducts, the load voltage is positive and equal to the input voltage. When SCR1 turns off, the energy stored in the capacitor is fed back to the load through the transformer. This reverses the load voltage polarity. The parallel inverter has advantages over series and bridge inverters in that the load voltage is not dependent on the load, only two SCRs are needed, and commutation components do not carry the full load current.