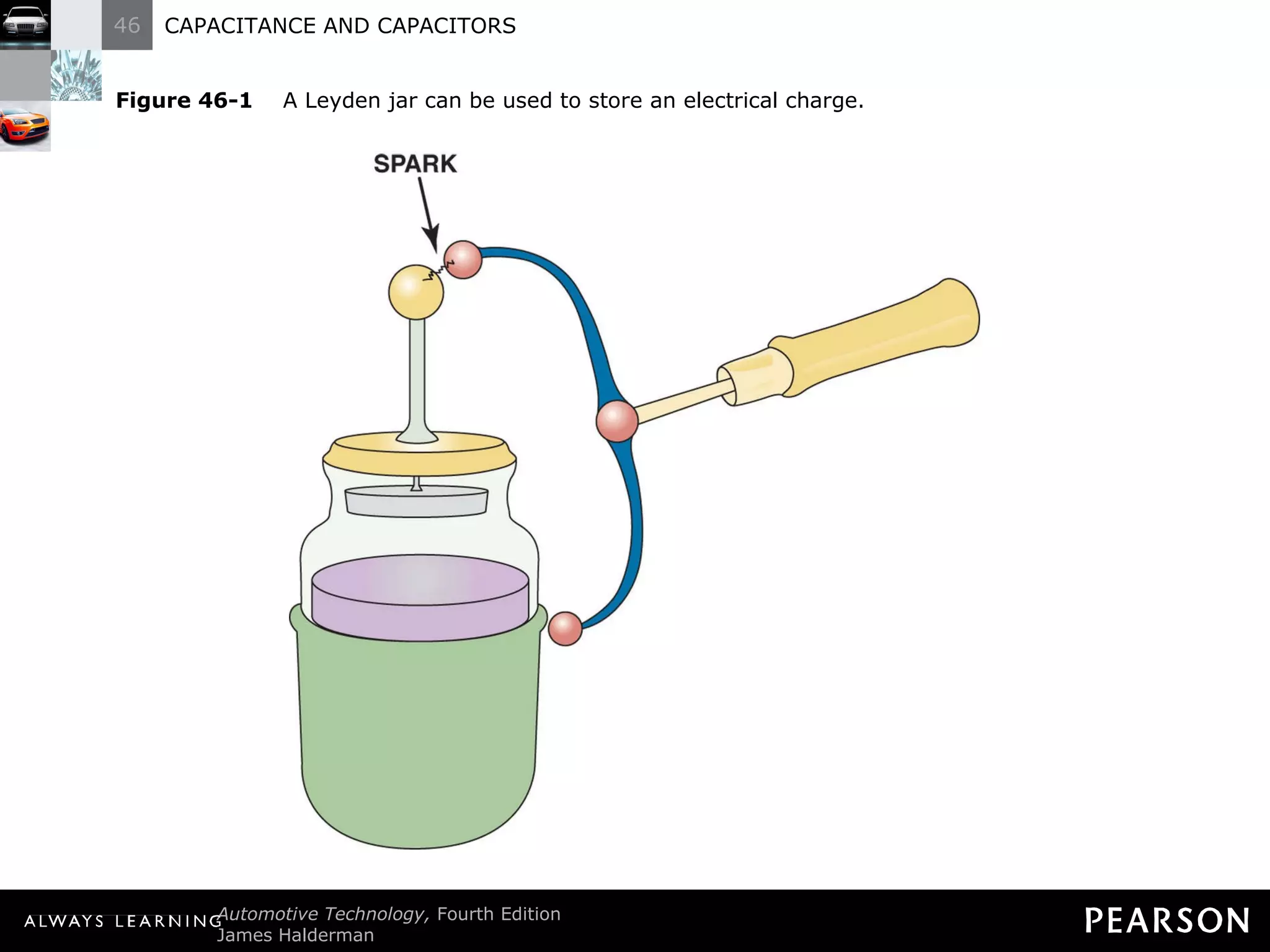
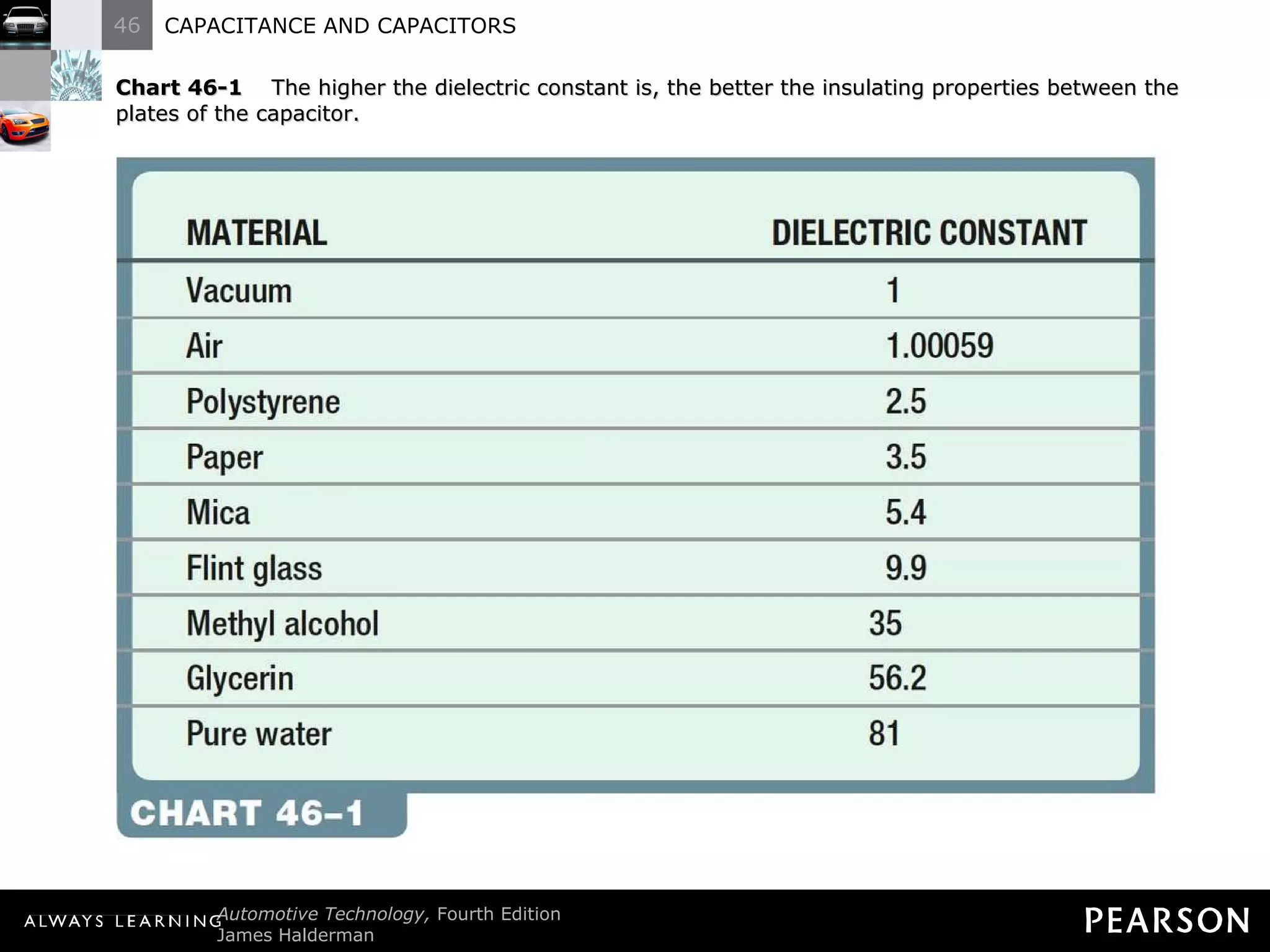
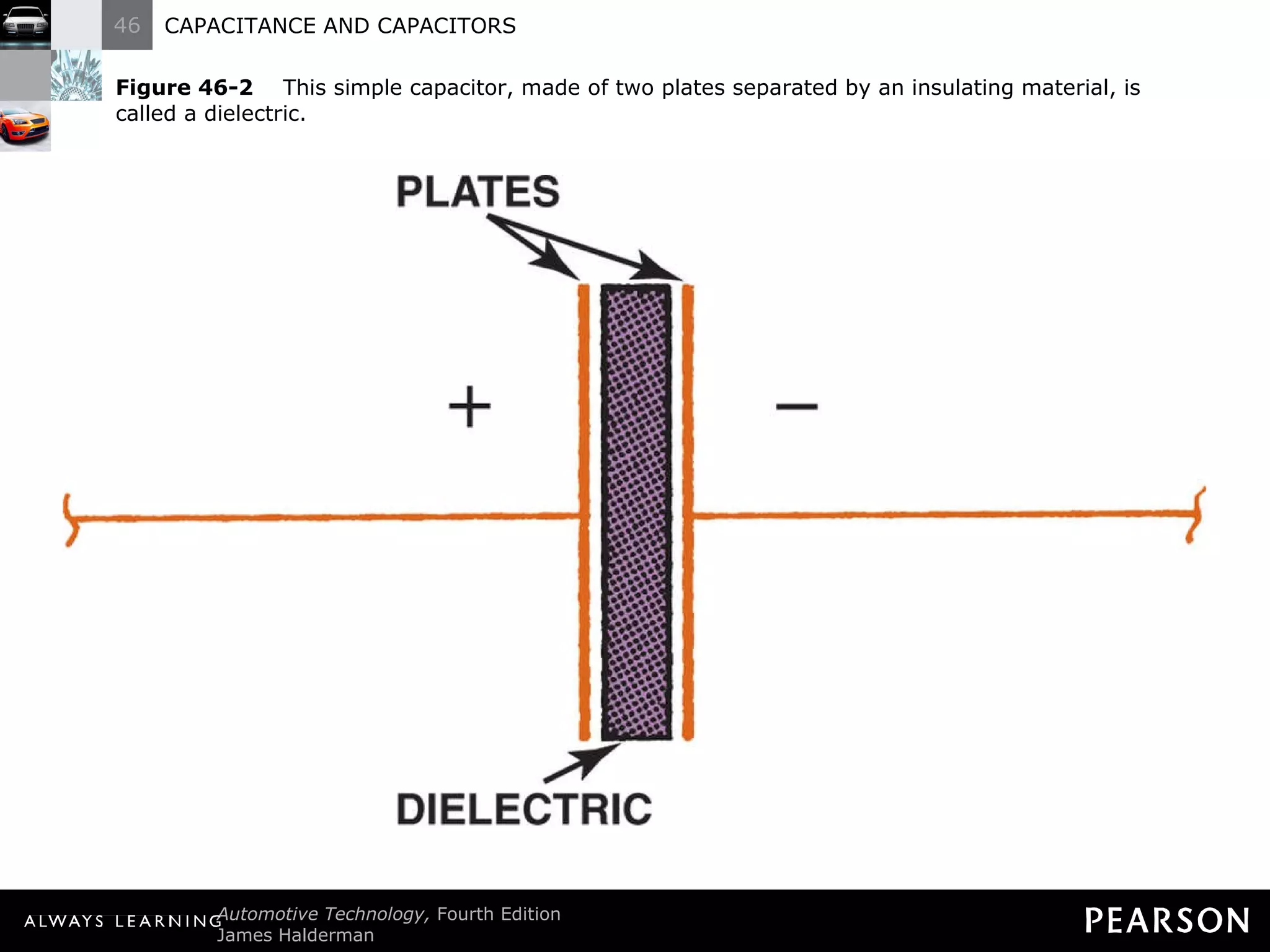
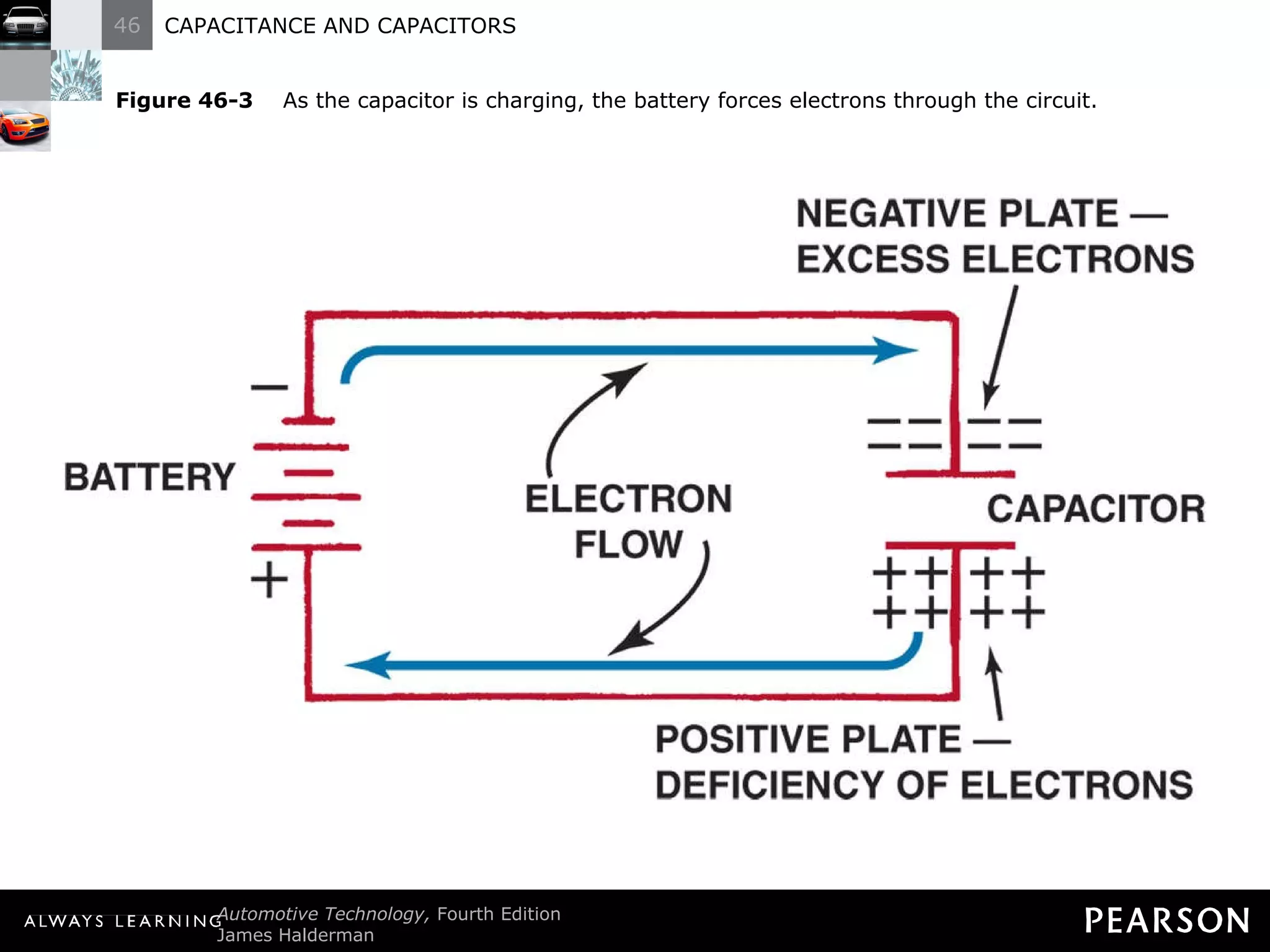
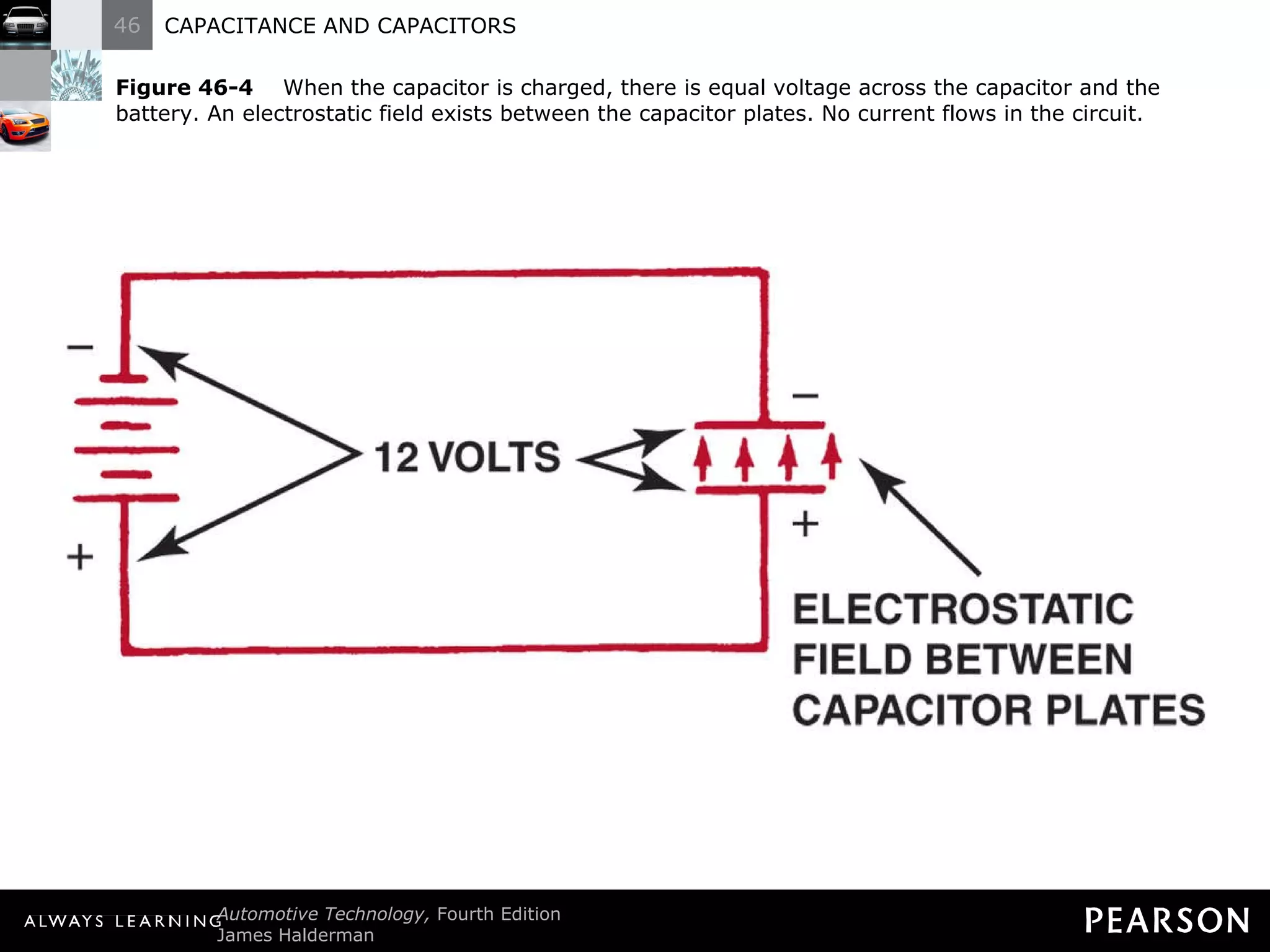
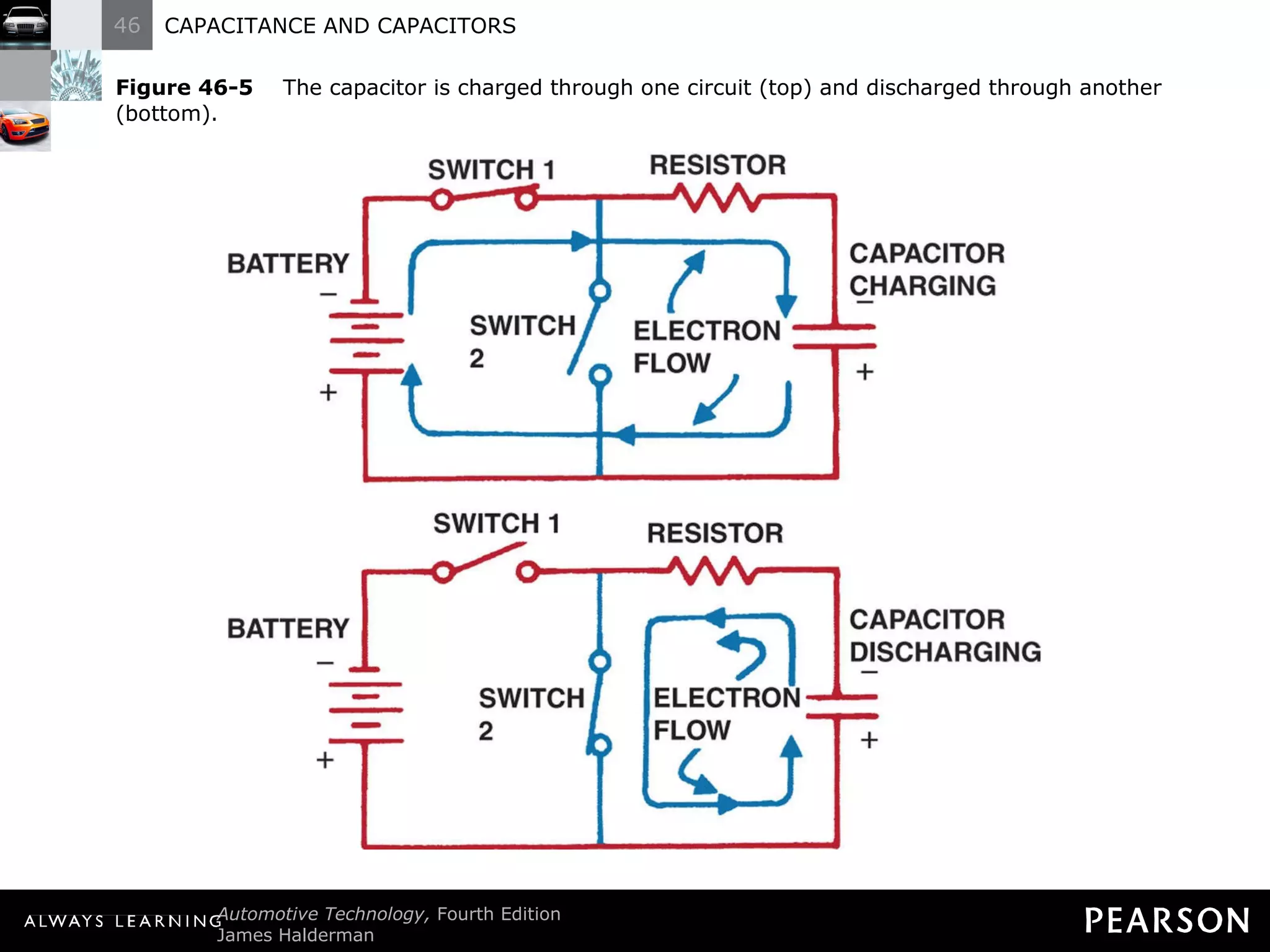
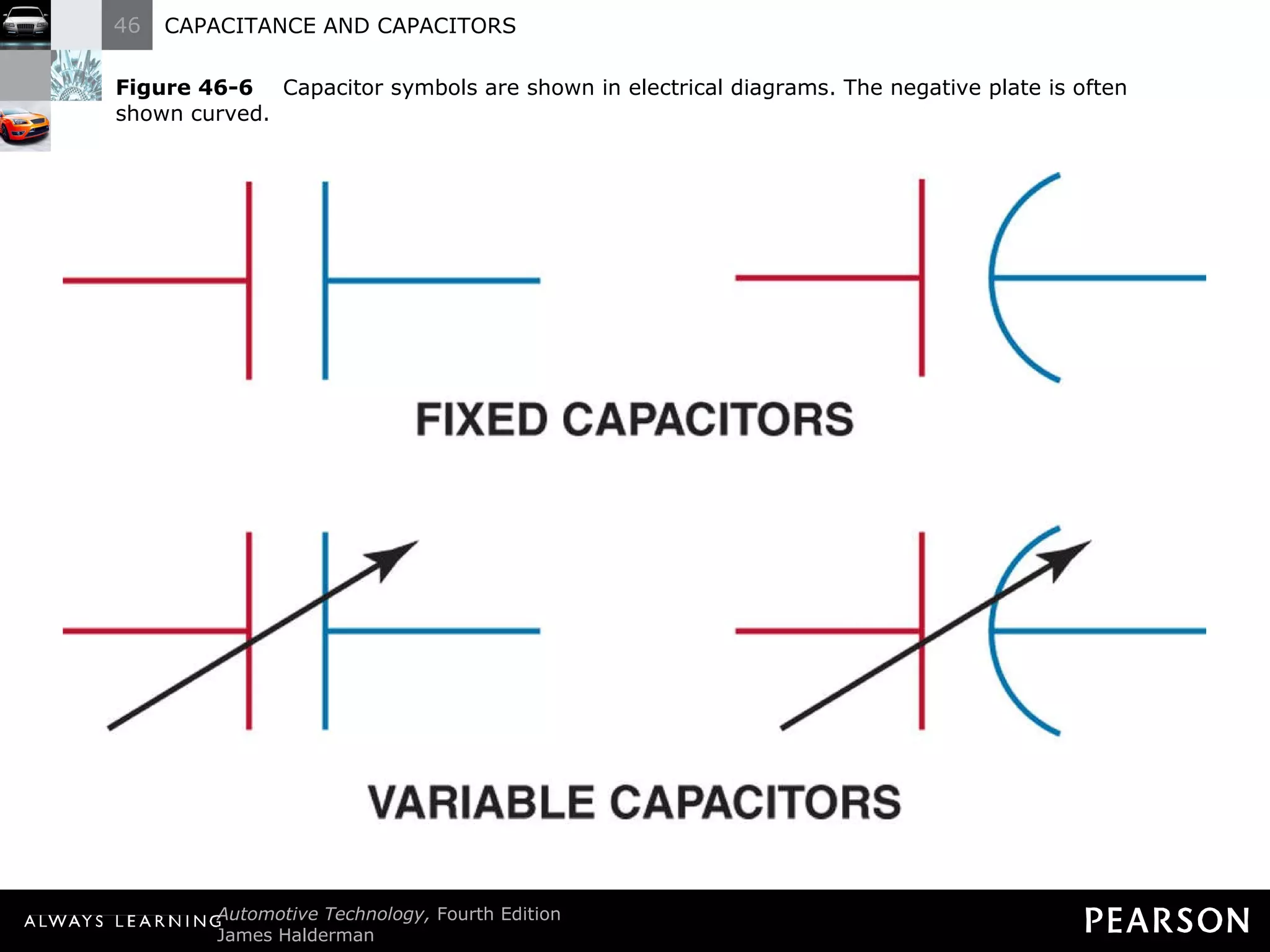
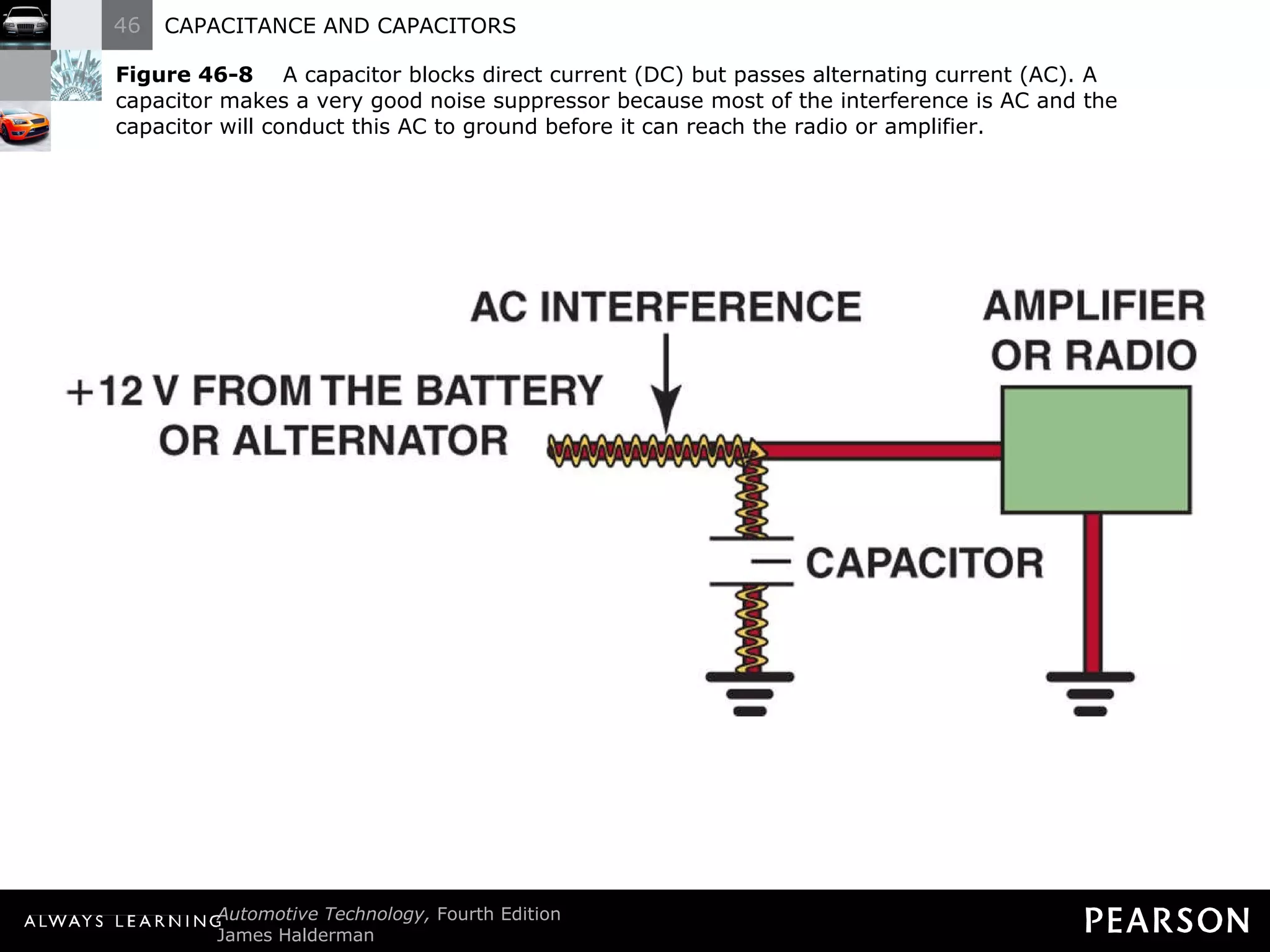
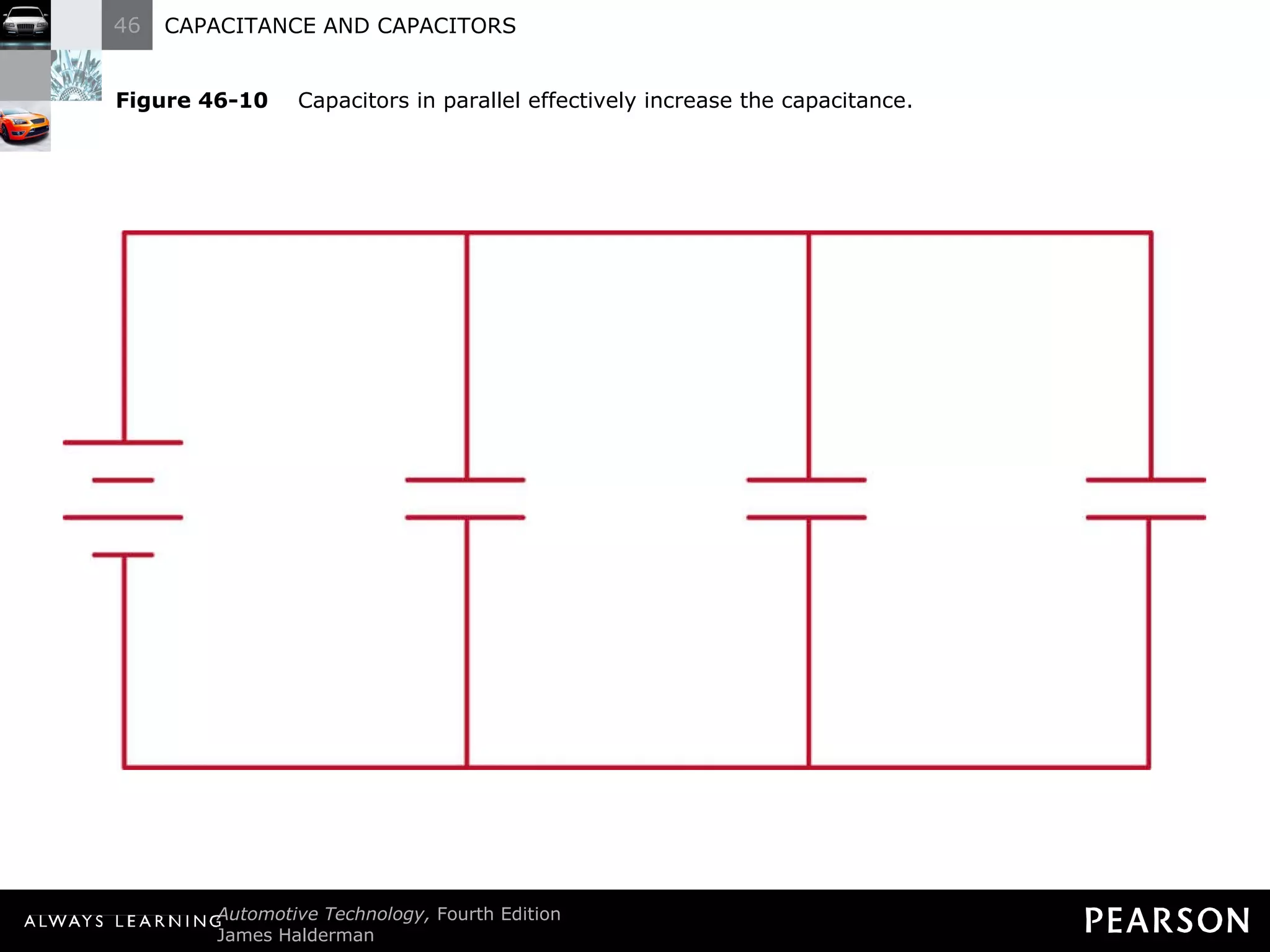
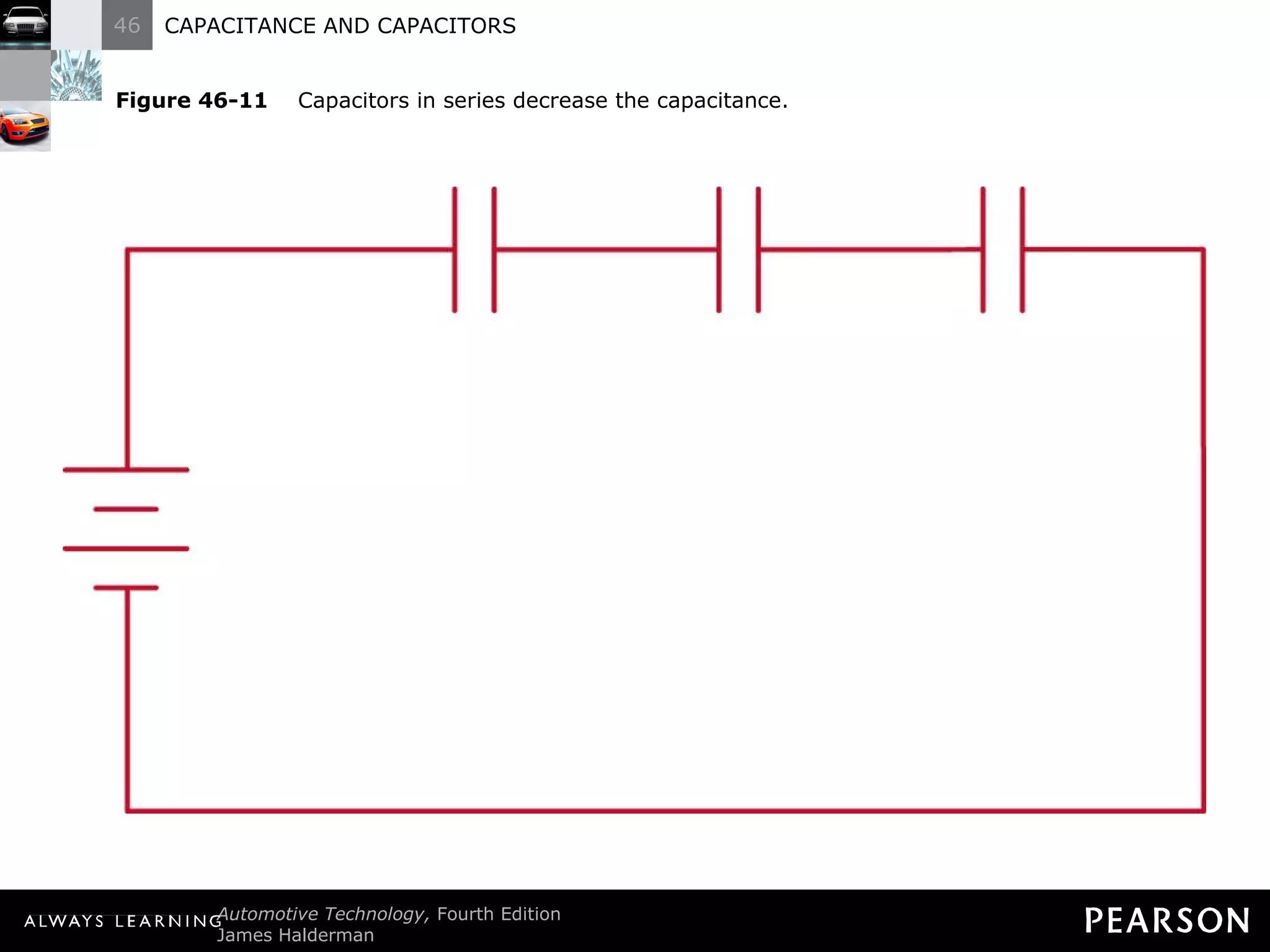
The document discusses capacitors and capacitance. It explains that a capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. A capacitor can store an electrical charge between its plates. Capacitance depends on the plate area, distance between plates, and insulating properties of the material between the plates. Capacitors have various uses including filtering electrical noise, storing temporary power, and functioning as timers in electronic circuits.