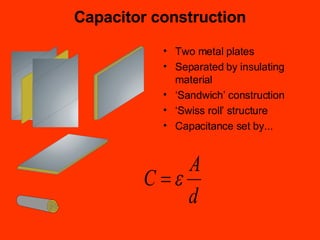
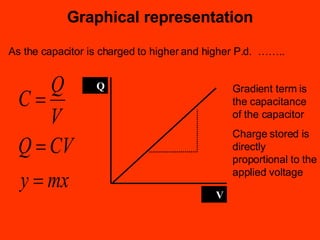
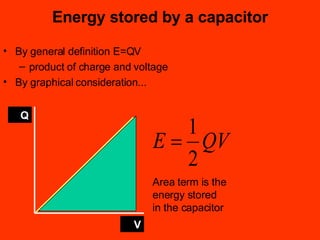
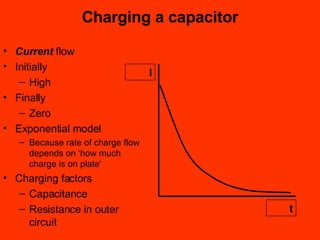
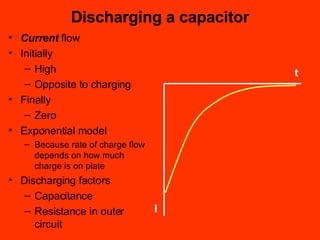
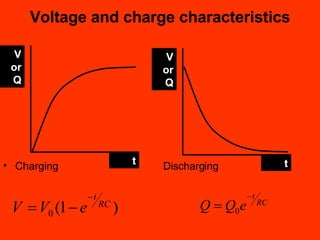
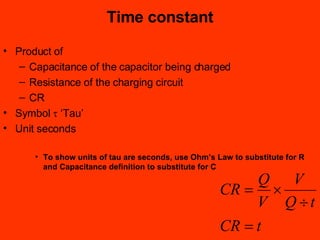
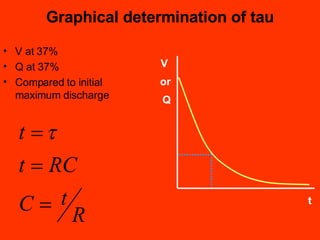
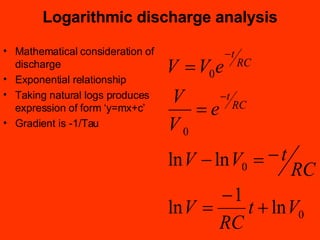
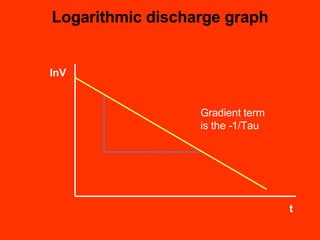
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores an electrical charge. It consists of two conducting surfaces separated by an insulating material. The amount of charge a capacitor can store is defined by its capacitance, which depends on the size and separation of the conducting plates and the material between them. When a voltage is applied across a capacitor's plates, electric current initially flows high as the capacitor charges, then tapers off to zero as it reaches full charge. This exponential charging and discharging process is characterized by the capacitor's time constant, the product of its capacitance and the resistance in the charging/discharging circuit.