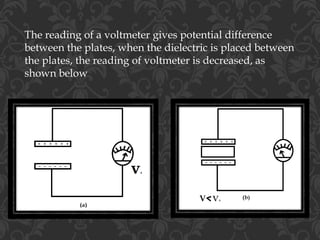
A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge. It consists of two parallel conductive plates separated by an insulator. When a voltage is applied, opposite charges accumulate on each plate. The amount of charge stored is directly proportional to the applied voltage. This proportionality is defined as capacitance, which depends on the geometry of the plates, the material between them, and their separation distance. When a dielectric material is placed between the plates, the electric field is reduced and capacitance increases due to polarization of the dielectric's molecules. The increase in capacitance is defined as the dielectric constant.