This document provides a table of contents and explanations of various Spanish grammar topics, including:
- The difference between "que" and "cual"
- How to use "ser" and "estar"
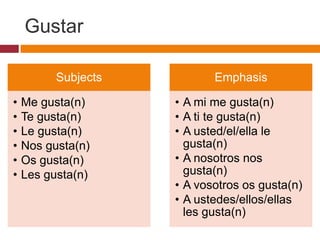
- The structure of sentences using verbs like "gustar"
- Common Spanish transition words
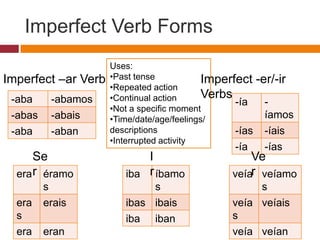
- Forms of imperfect verbs and how they are used
- Trigger words that indicate the imperfect tense
- The construction of "acabar de + infinitive"
- Formulas and expressions using "hacer"
- Characteristics of reflexive verbs and verbs like "gustar"
- Forming affirmative and negative tú commands
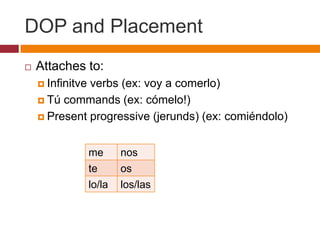
- Placement of the direct object pronoun and uses