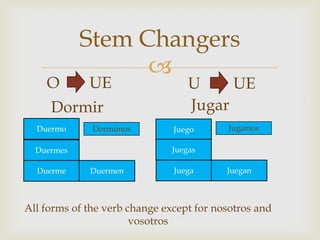
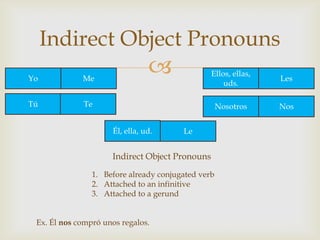
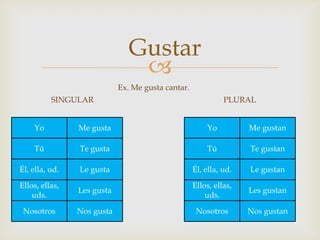
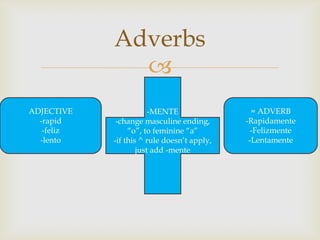
The document provides an overview of Spanish grammar topics including nationalities, stem changers, para, indirect object pronouns, pronoun placement, gustar verbs, affirmative and negative words, superlatives, reflexives, tu commands, preterite, trigger words, stem changing verbs ending in -car, -gar, -zar, deber + infinitive, modal verbs, present progressives, and adverbs. It includes definitions, examples, and rules for forming and using these various grammar structures in Spanish.