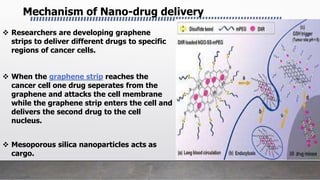
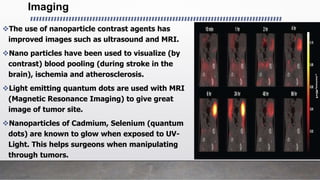
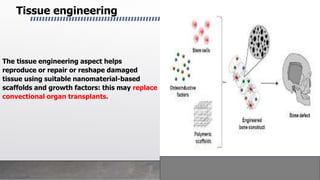
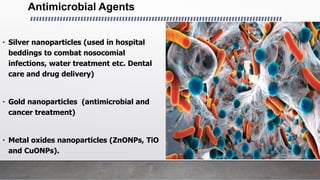
This document provides an overview of nanotechnology including definitions, materials, fabrication methods, applications, and toxicity concerns. Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the nanoscale (100nm or less). Nanoparticles can be organic, inorganic, or composites and are synthesized through various physical and biological methods. Applications include drug delivery, cancer treatment, imaging, and tissue engineering. However, toxicity depends on factors like size, shape, and chemistry, as smaller nanoparticles may more readily interact with and potentially damage biological systems. The future promises revolutionary advances through nanotechnology but continued research is still needed into its impacts.










![Nano drug delivery is known to:
[a] Improve the Pharmacokinetics of drugs
[b] Improve the bio distribution of drugs
[c] Ensure the passage of drugs through cell
membranes and cytoplasm (poorly water
soluble drugs).
[d] Triggered response (pH or Temperature) is
very beneficial in drug delivery.
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcpdpowerpointken1-190119201939/85/NANOTECHNOLOGY-17-320.jpg)
![Some of these nanotechnology-based drugs are
commercially available:
[a] Araxane: (FDA approved) for breast cancer,
this contain nanoparticle albumin bound
Paclitaxel.
[b] Doxil : (FDA approved) for HIV-related
Kaposi`s Sarcoma. (Encased in Liposomes)
[c] Onivyde, This is encapsulated Irinotecan
for metastatic cancer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcpdpowerpointken1-190119201939/85/NANOTECHNOLOGY-19-320.jpg)