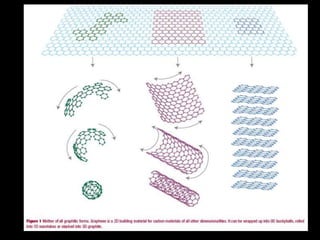
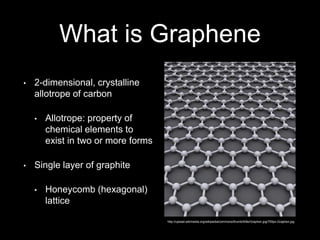
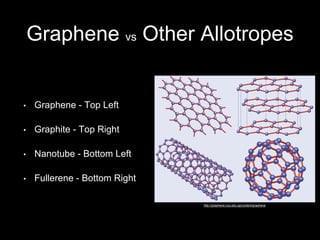
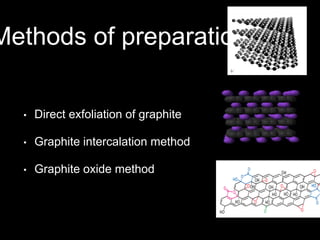
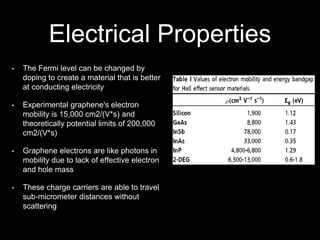
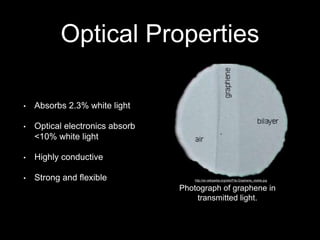
Graphene is a single-atom thick layer of carbon that was discovered in 2004. It has unique electrical, mechanical, and optical properties including high electron mobility, strength stronger than diamond but flexible like rubber, and ability to transmit light. These properties make it promising for applications in electronics, composites, energy storage, and more. Graphene is still in early stages of research and development.