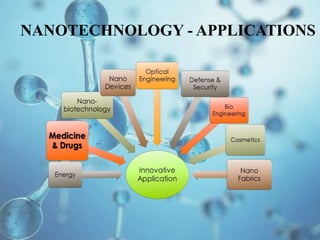
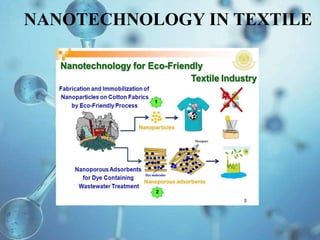
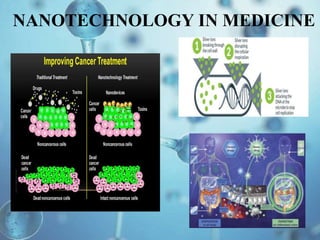
Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the nanoscale level between 1-100 nanometers to create structures with unique properties. One application is in water treatment where carbon nanotube membranes could reduce desalination costs and nanofilters may be used to clean contaminated ground and surface water. Nanotechnology also shows promise for air pollution control through nanofilters in vehicle exhausts and factory smokestacks. However, more research is still needed to fully understand potential health and environmental risks of nanoparticles.