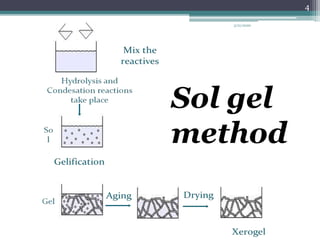
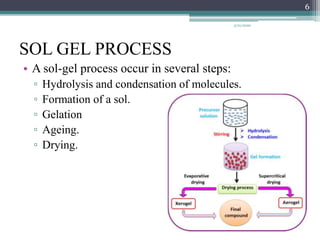
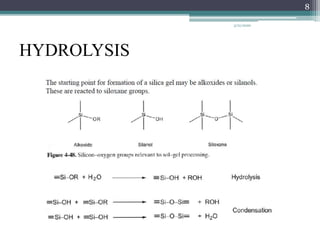
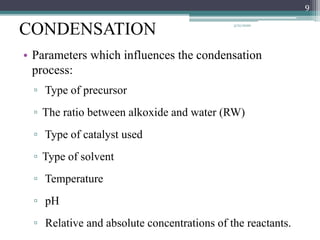
The sol gel method is a process for synthesizing nanoparticles that involves dissolving a compound in a liquid to bring it back as a solid in a controlled manner. It allows mixing at an atomic level and results in small, easily sinterable particles. The key steps are hydrolysis and condensation of precursor molecules to form a sol, which then undergoes gelation and aging before drying to form the final product. The method offers advantages like precise size control and doping but is also substrate dependent and time consuming.