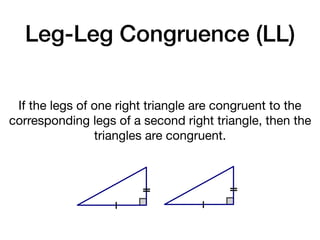
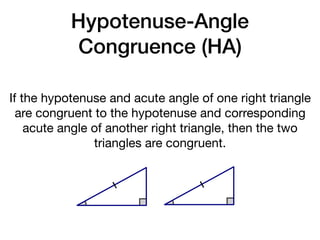
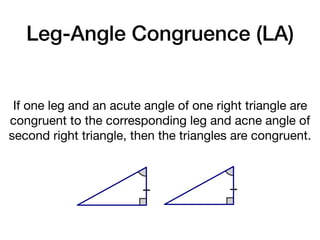
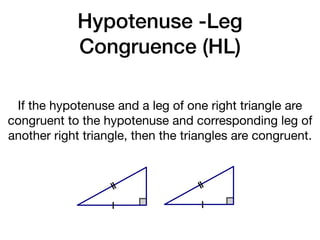
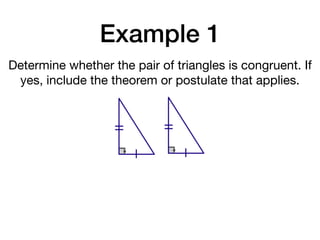
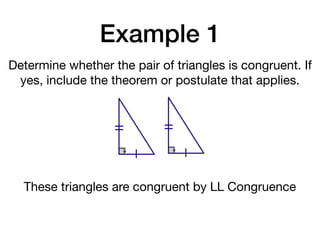
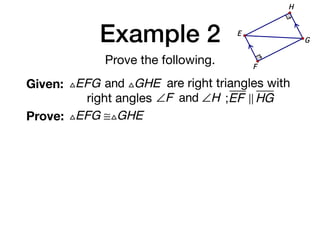
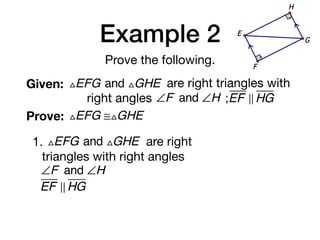
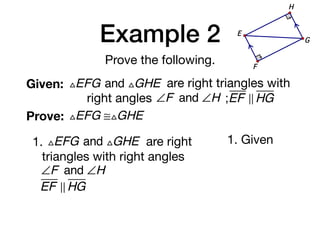
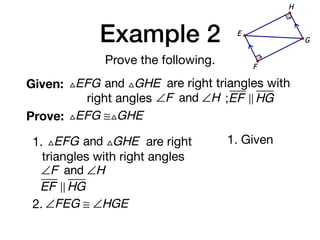
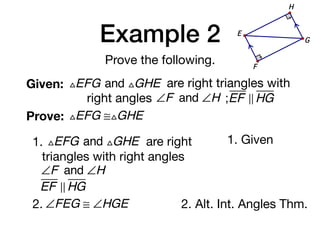
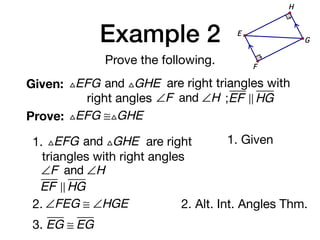
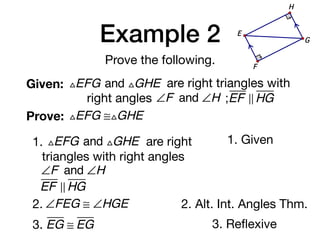
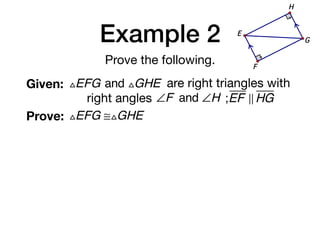
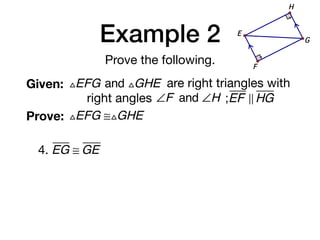
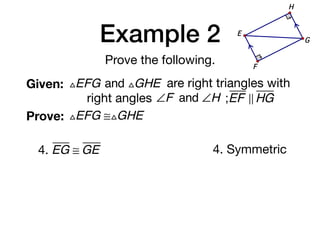
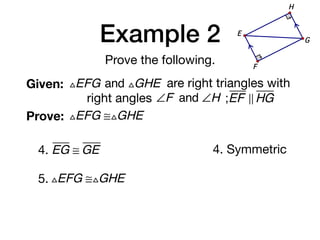
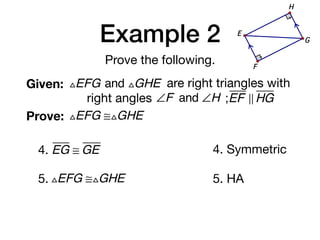
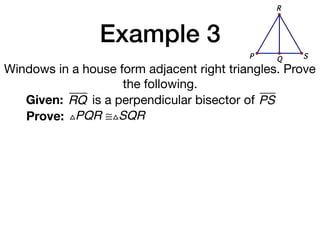
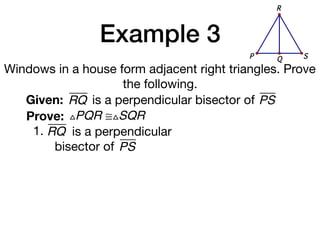
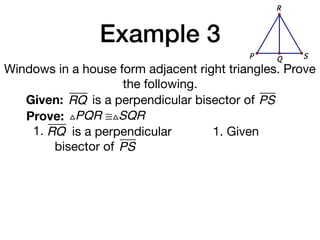
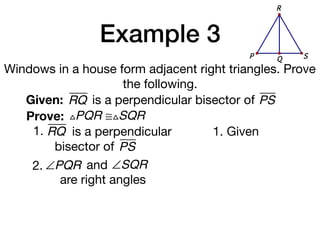
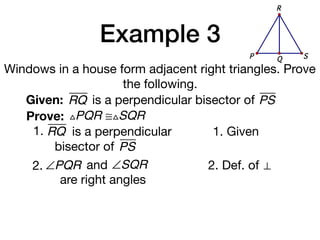
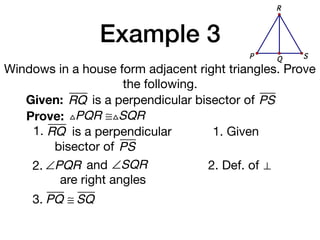
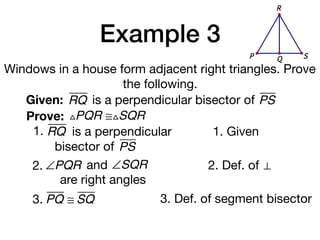
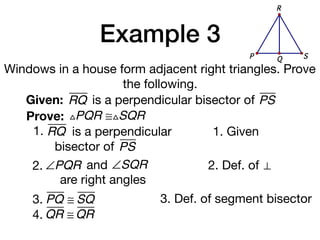
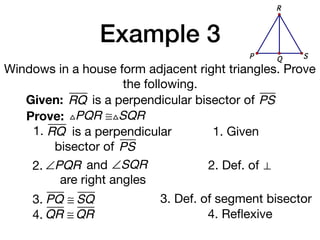
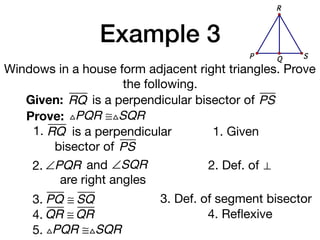
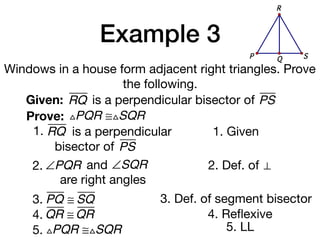
The document discusses four right triangle congruence theorems: leg-leg (LL), hypotenuse-angle (HA), leg-angle (LA), and hypotenuse-leg (HL). It then provides three examples of proving right triangles congruent using these theorems, showing the steps of the proofs.