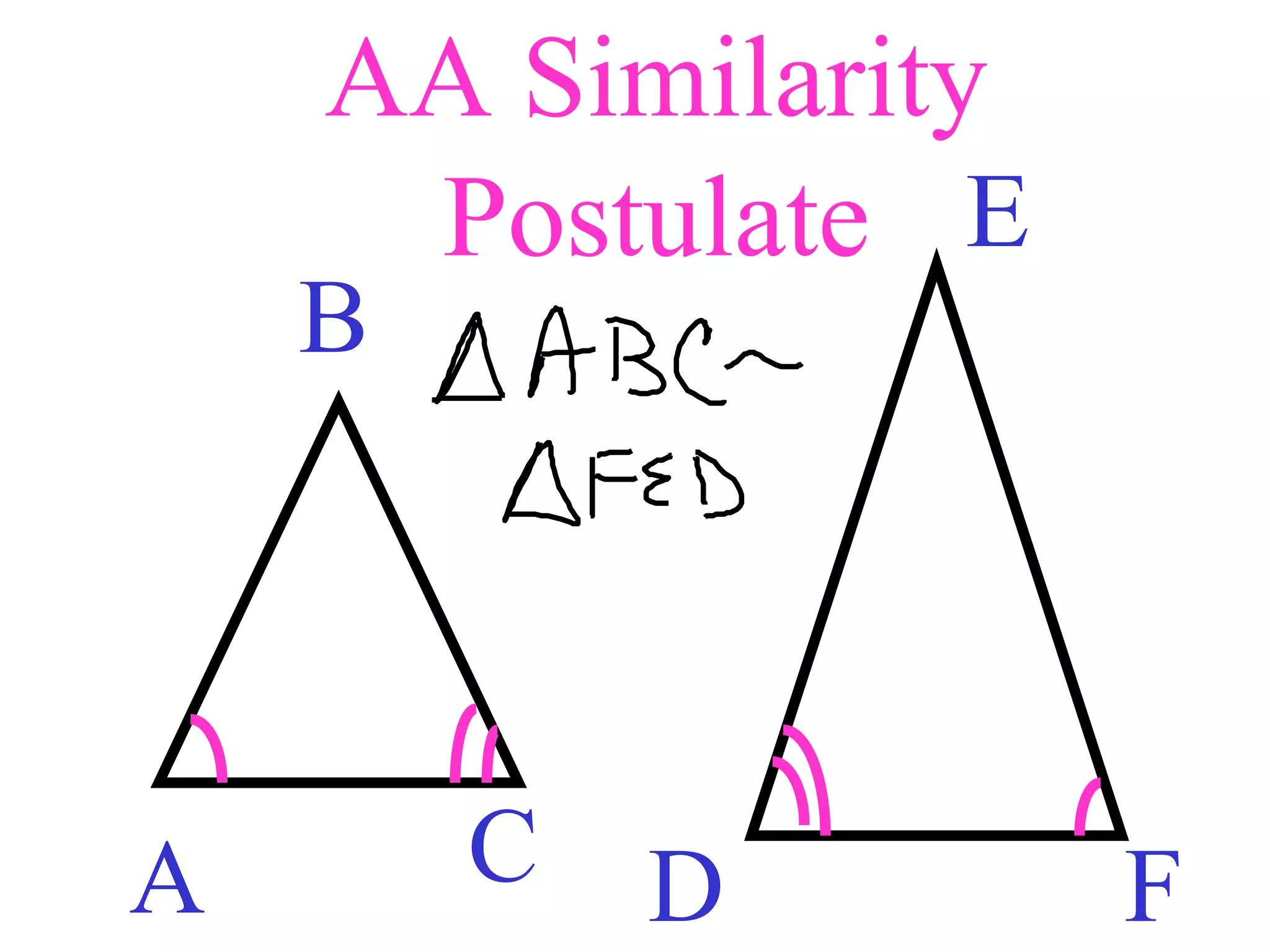
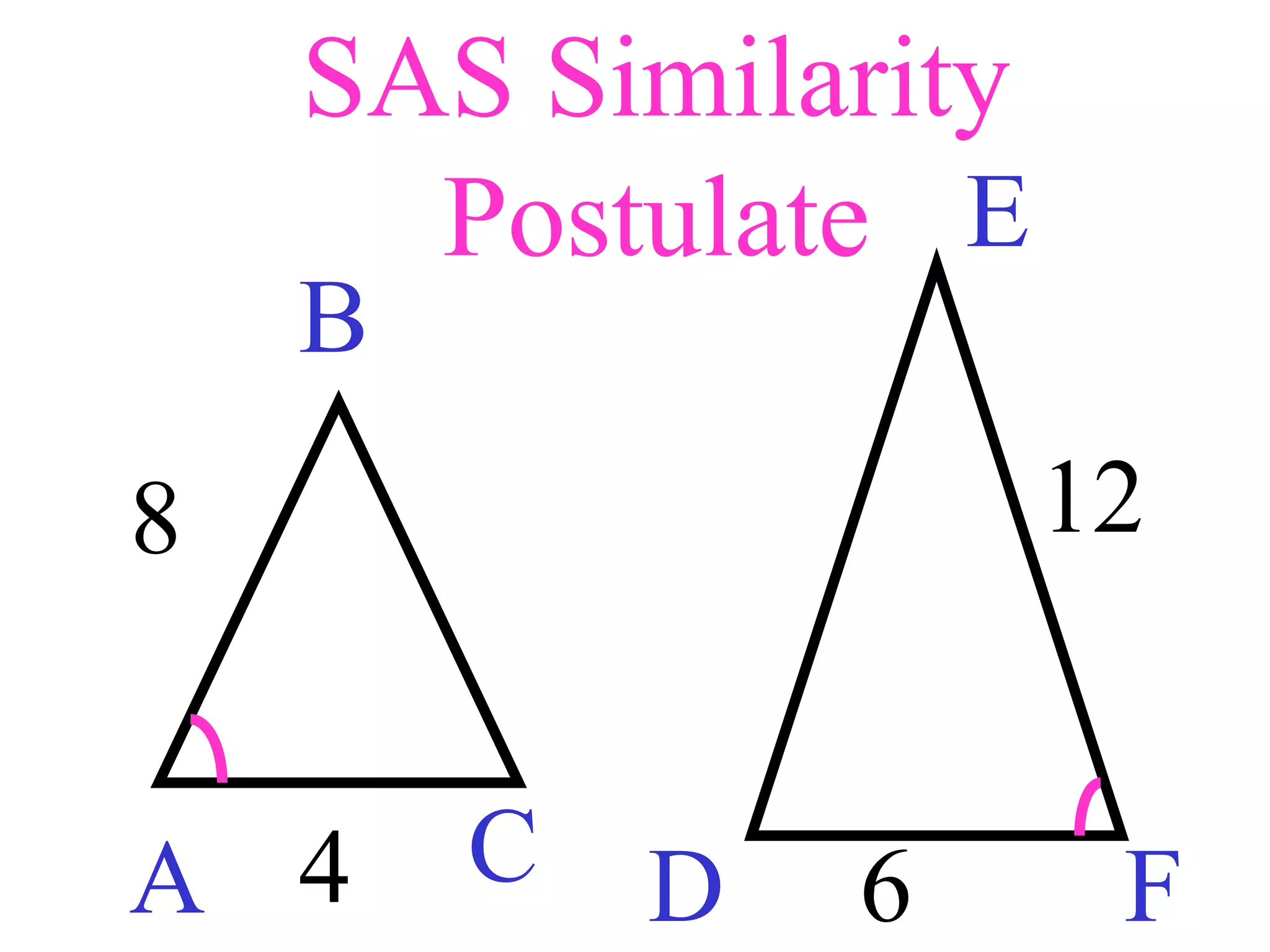
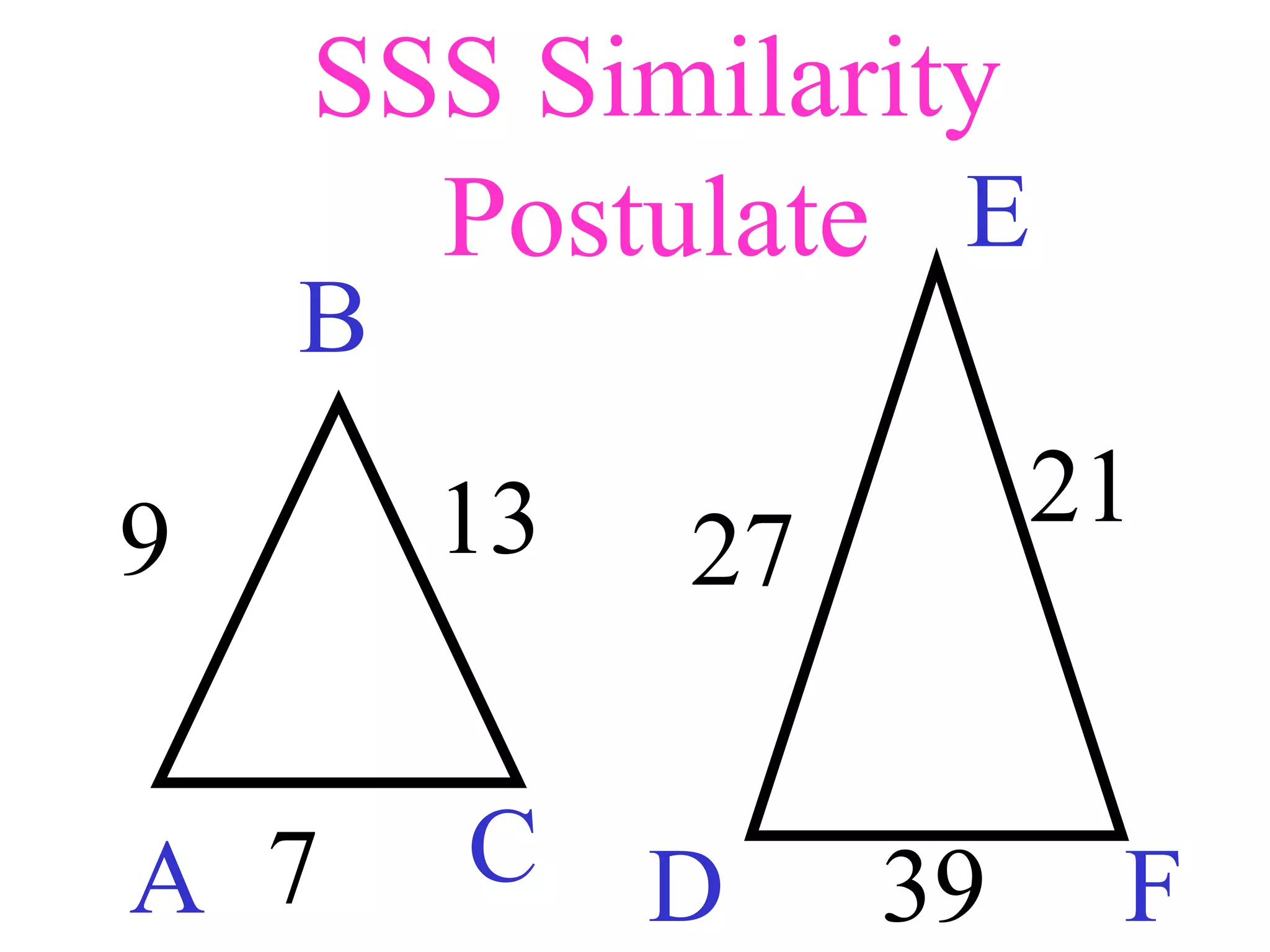
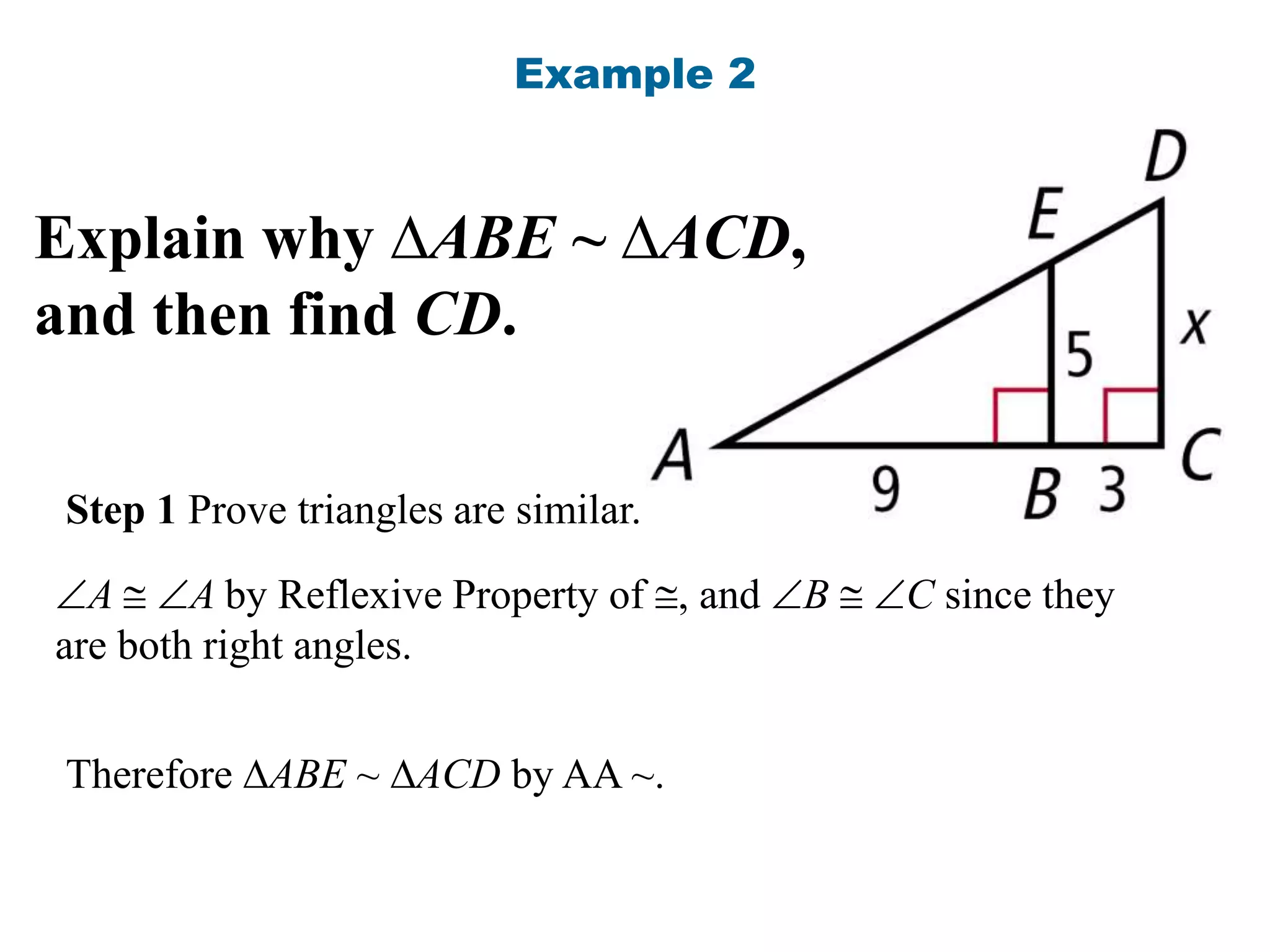
The document contains information about using similarity postulates to determine if triangles are similar and find unknown side lengths. It provides examples of using the AA, SAS, and SSS similarity postulates to show triangles are similar. It also shows using proportional sides to find missing lengths. The objective is for students to use similarity postulates to decide if triangles are similar and find unknowns.