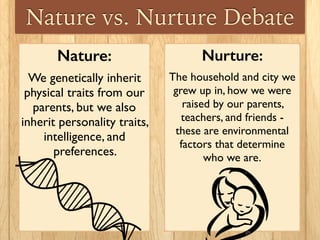
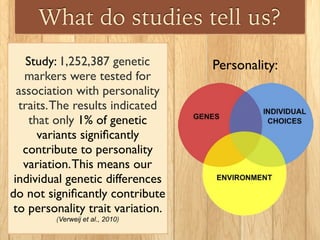
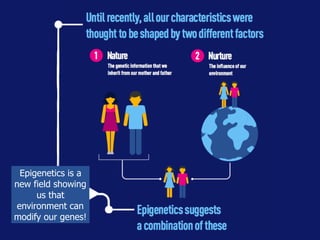
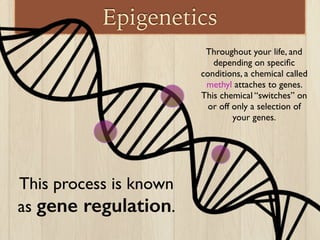
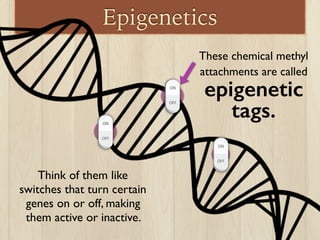
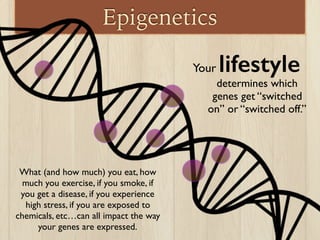
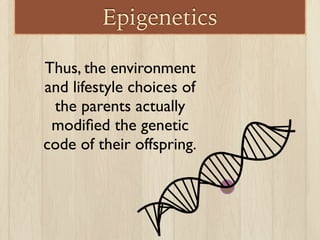
This document discusses the nature vs nurture debate around factors that influence human behavior. It explores how both genetics and environment play a role, using examples from twin studies and research on genes, test scores, success, and stress response. A key point is that a new field of epigenetics has shown that environment can modify genes through chemical tags, turning some on or off, meaning nature and nurture have a more complex interaction than previously understood. Overall, the document aims to show that both genetics and life experiences influence human behavior in complex ways.