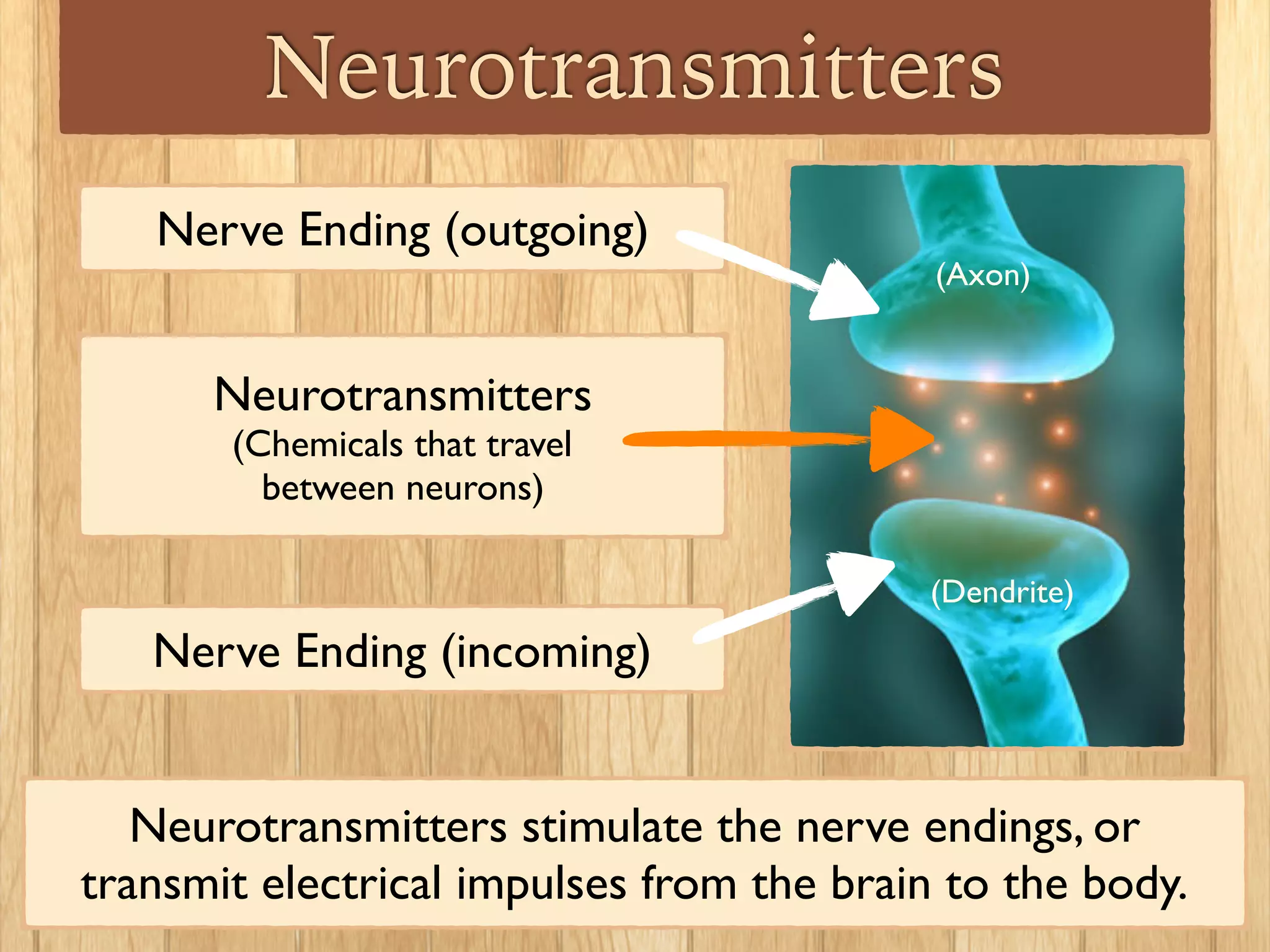
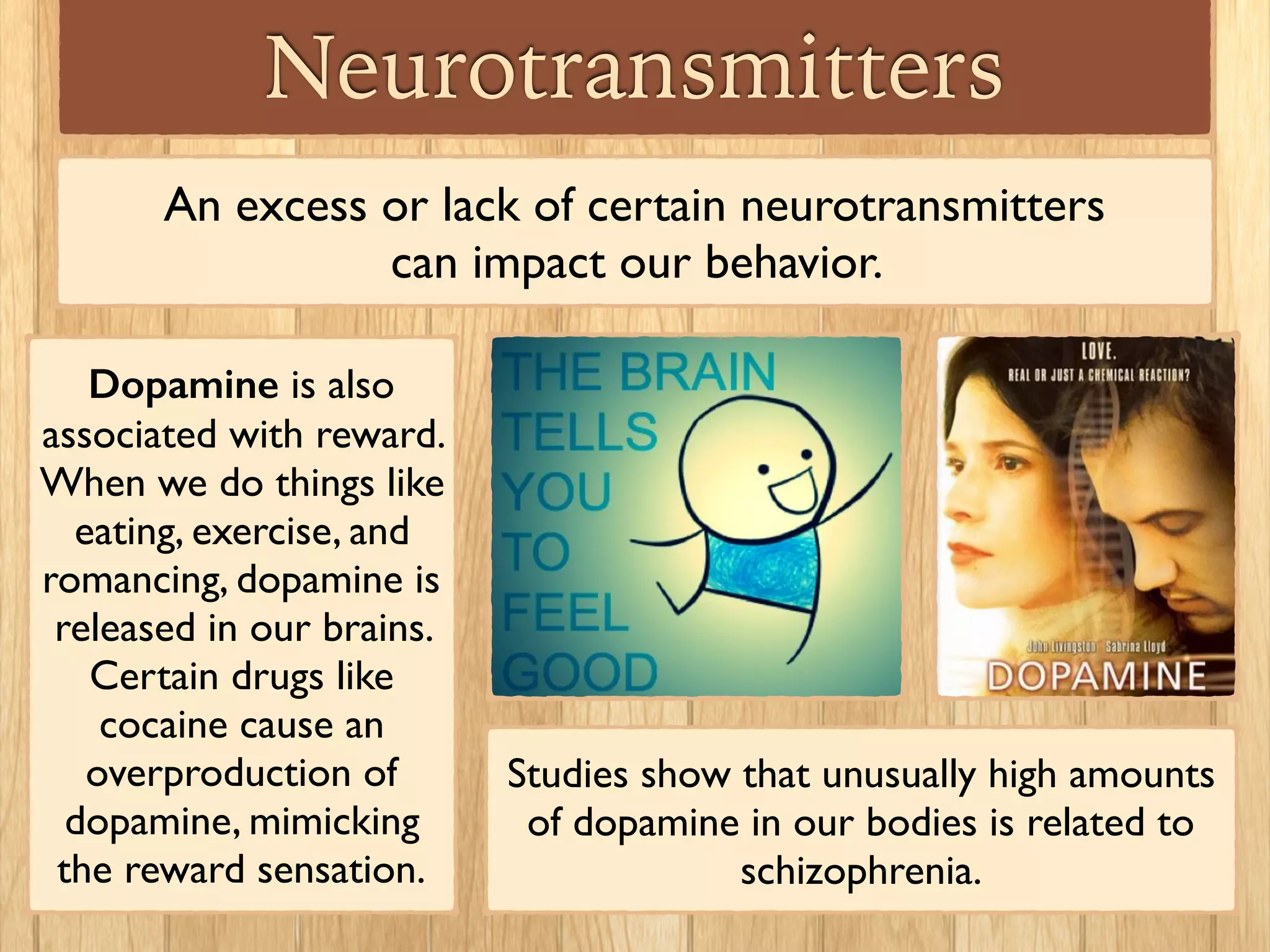
Psychologists study the brain and nervous system to understand how biological functions influence human behavior. Some psychologists called behavioral neuroscientists specialize in studying the effects of biological processes like neurotransmitters on behavior. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals between neurons in the brain and body. An imbalance of neurotransmitters can impact mood, movement, memory formation and other behaviors, and may be linked to conditions like depression, Parkinson's disease, and schizophrenia. Brain imaging techniques like PET and SPECT scans can detect abnormal levels of neurotransmitter activity and production in the brain.