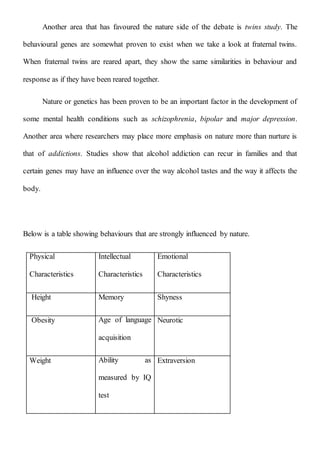
The document discusses the nature vs nurture debate in human development. It provides background on the long-standing controversy between the influence of innate qualities ("nature") versus personal experiences ("nurture"). While early theorists leaned towards one side, modern science recognizes an interaction between both. Nature includes genetic and hormonal influences, while nurture encompasses environmental and experiential factors. The document examines evidence for both positions and concludes that nurture has a stronger influence on behavior, since environmental inputs can affect gene expression, life experiences are strong predictors of mental illness, and behavior is not solely determined by genetics.