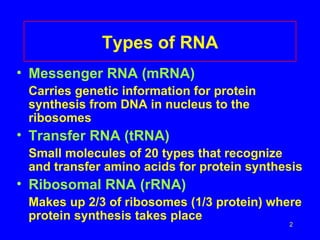
1) There are three main types of RNA - mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, tRNA transfers amino acids during protein synthesis, and rRNA makes up the ribosomes.
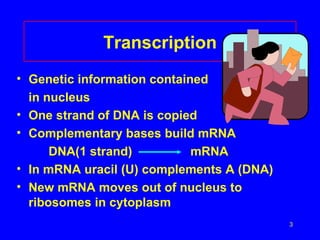
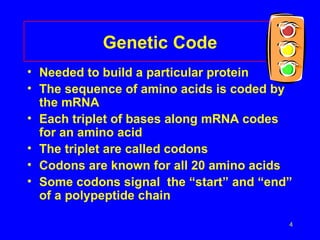
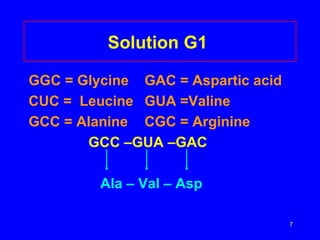
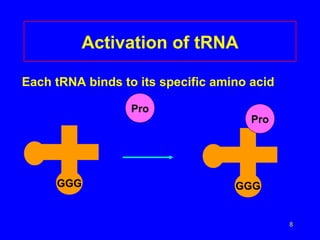
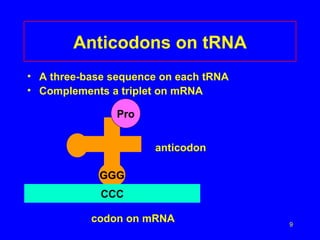
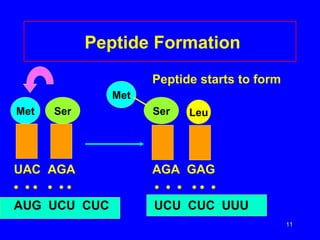
2) Transcription copies one DNA strand into mRNA which moves to ribosomes for translation. During translation, tRNAs match their anticodons to mRNA codons and add the corresponding amino acids.
3) Mutations in DNA can lead to production of defective proteins through altered mRNA and incorrect amino acid sequences, resulting in genetic diseases.