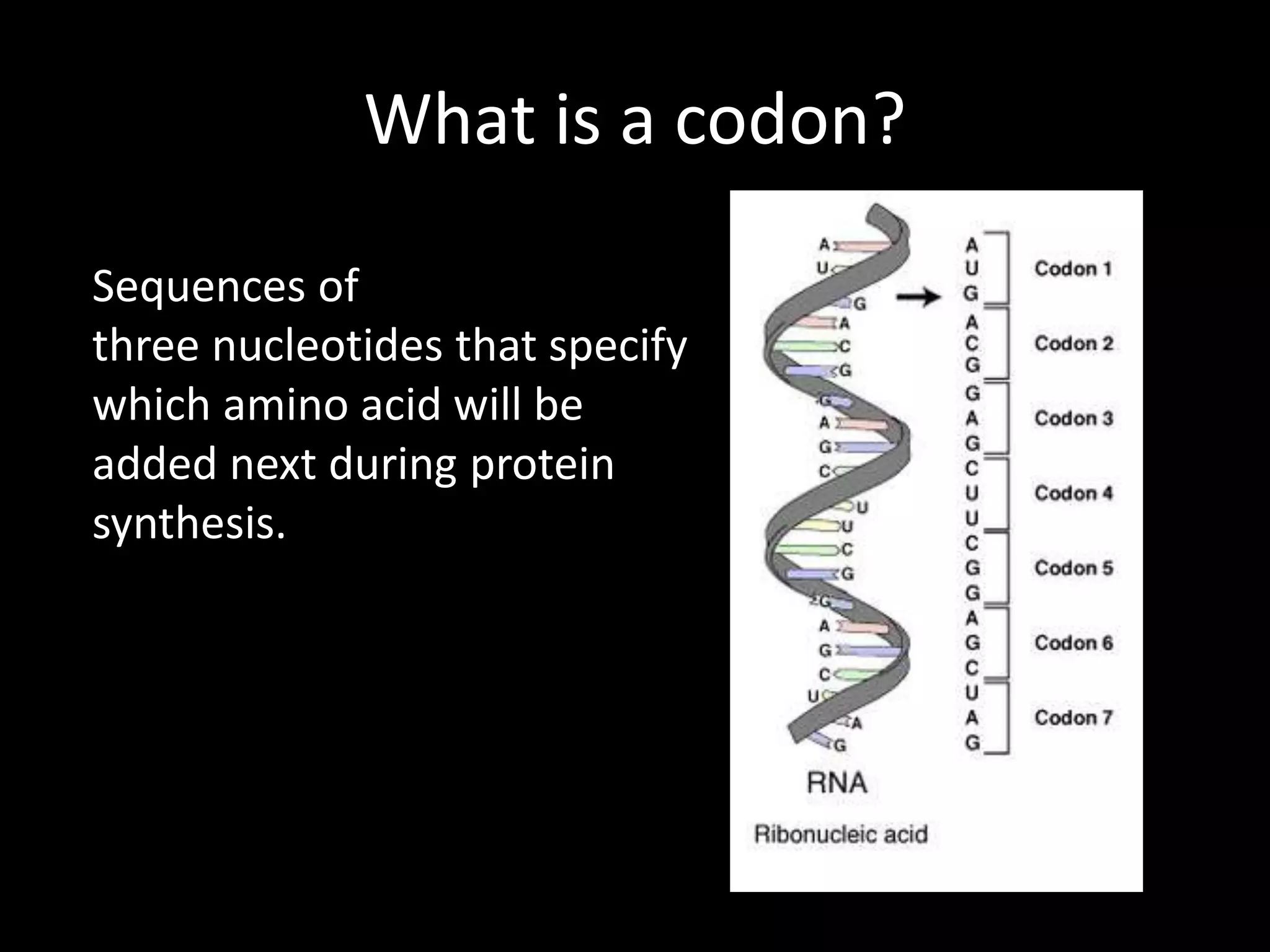
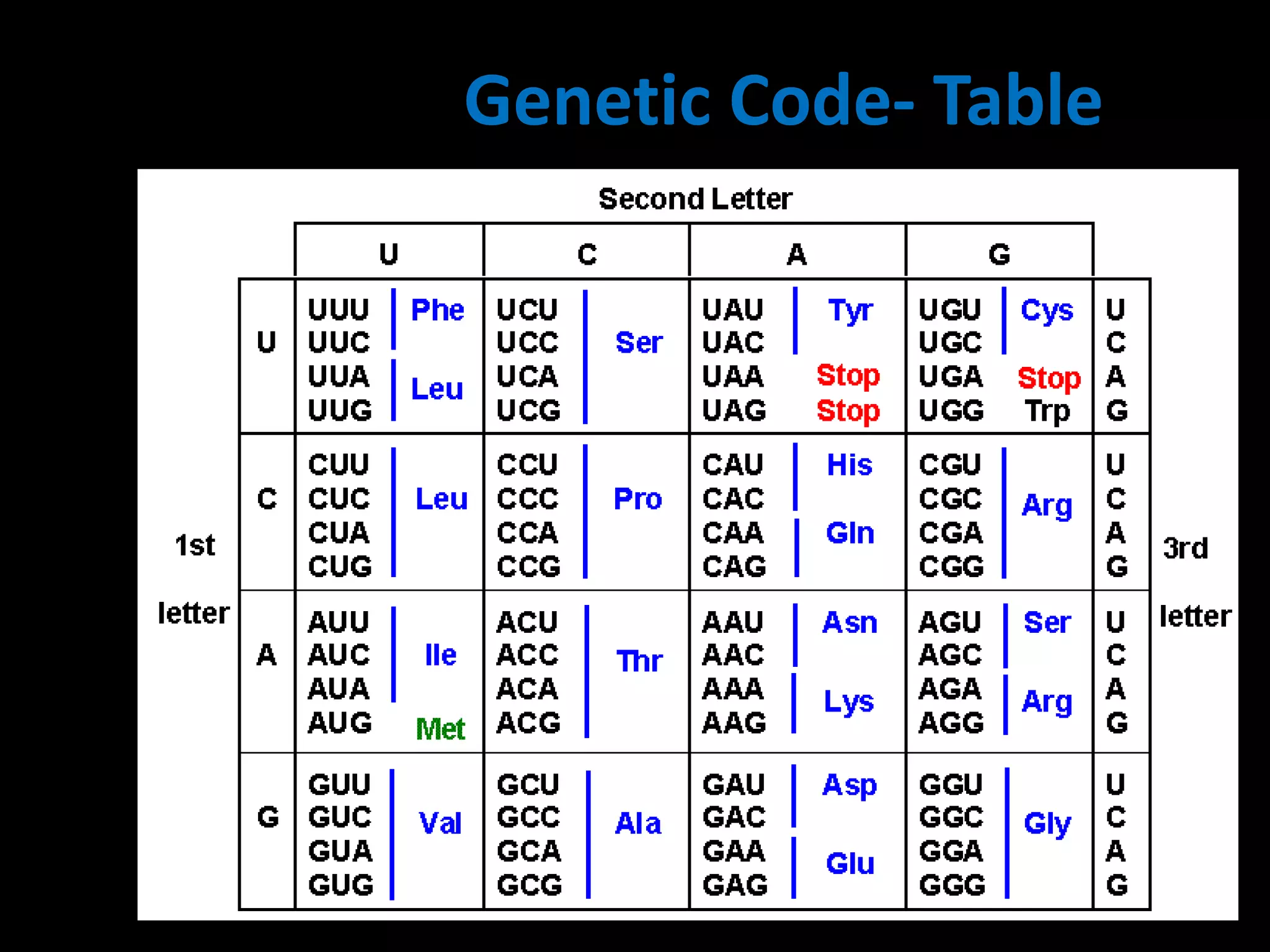
The document discusses the definition and characteristics of genetic codons, which are sequences of three nucleotides that determine amino acid addition during protein synthesis. Key features include specificity, universality, and redundancy of the genetic code, with exceptions noted for mitochondrial codons. It also identifies three nonsense or stop codons that do not encode for any amino acid.