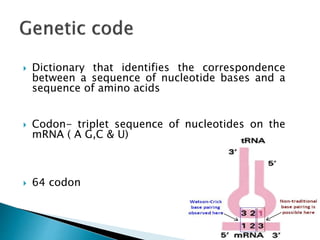
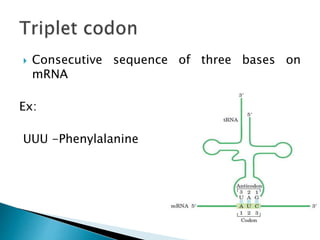
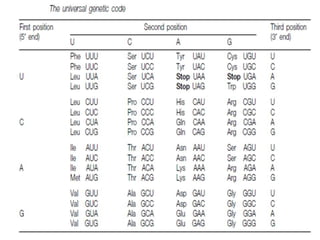
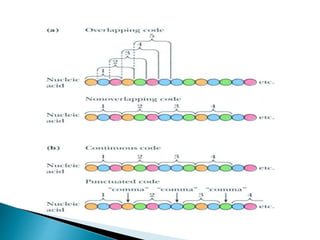
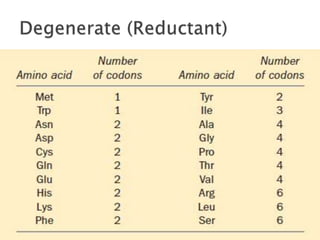
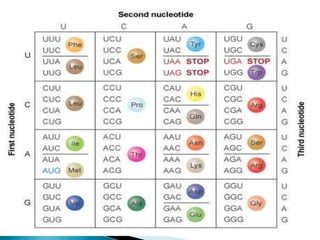
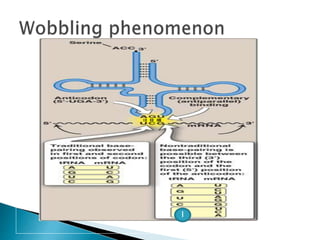
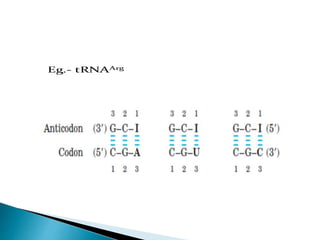
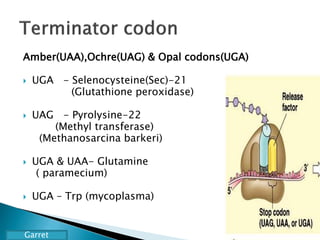
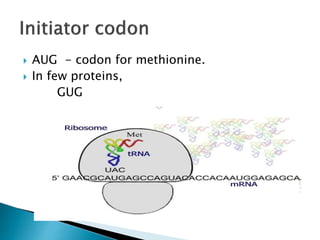
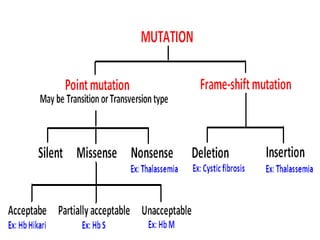
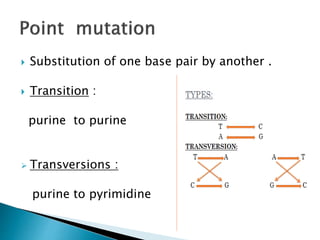
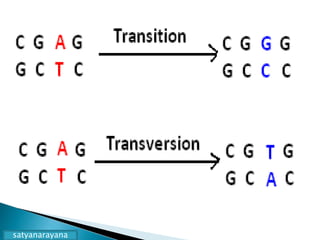
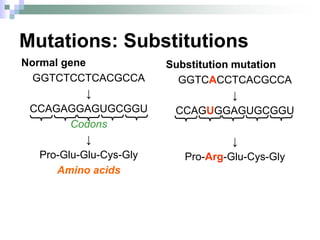
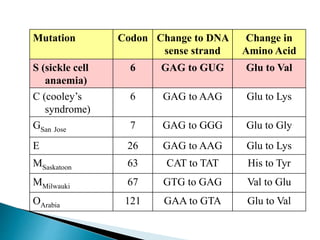
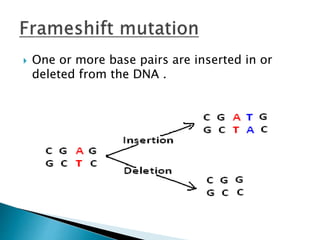
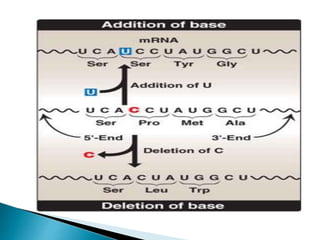
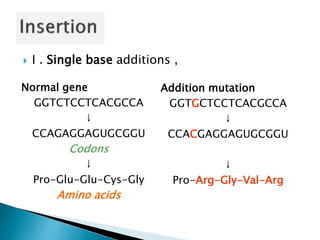
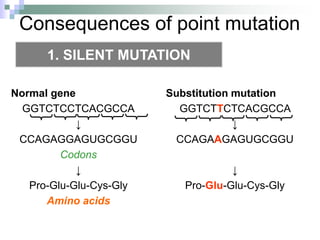
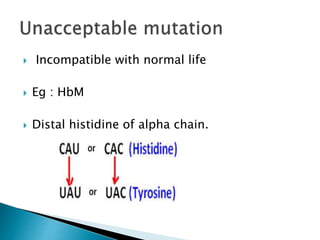
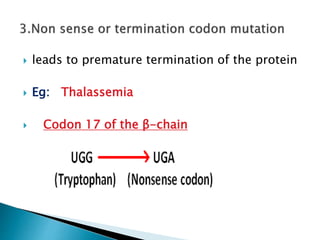
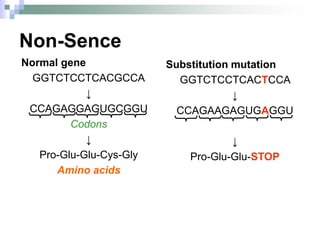
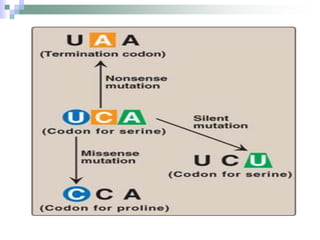
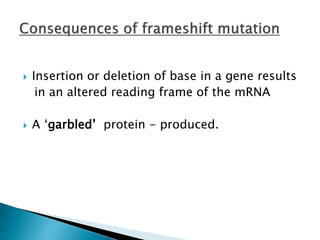
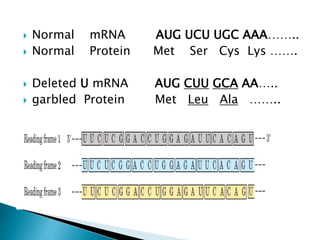
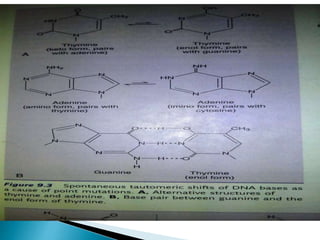
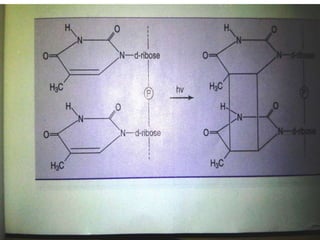
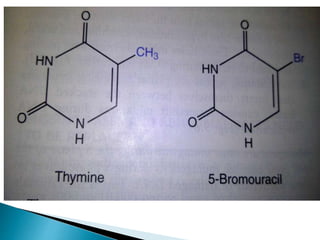
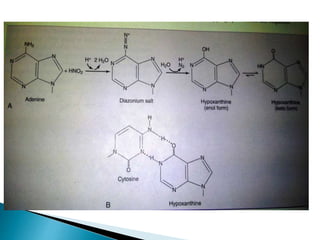
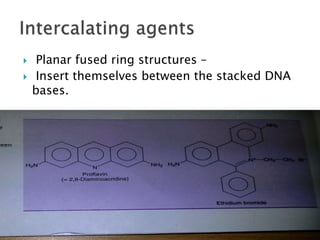
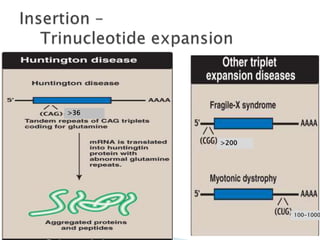
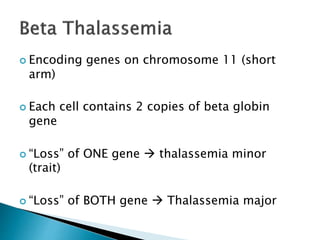
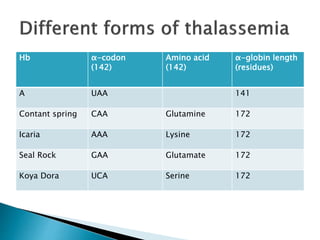
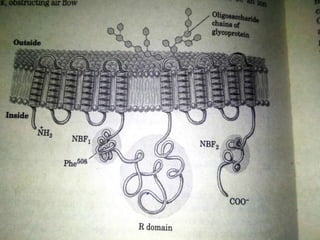
The document discusses the genetic code and mutations. It describes key discoveries such as the experiments demonstrating that codons consist of three DNA bases and the identification of the first genetic codes. It defines terms like codon, codon table, degenerate codons. It describes types of mutations like substitutions, insertions, deletions and their effects. It discusses mutagens like radiation, chemicals, and their mechanisms. It provides clinical examples of mutations causing conditions like sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis.