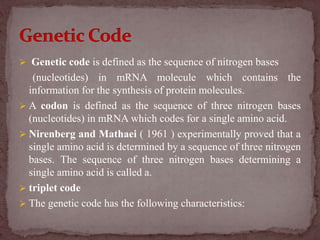
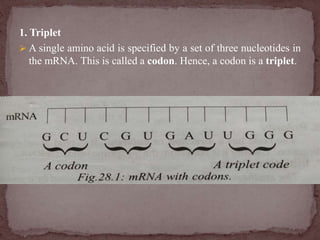
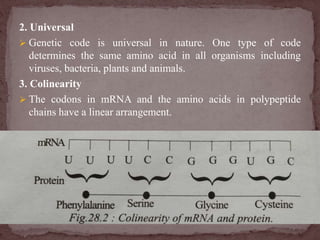
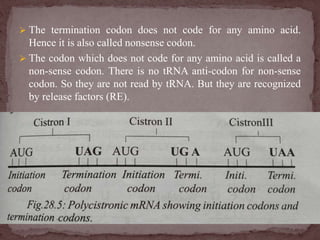
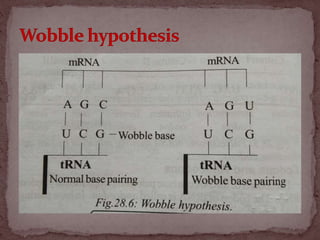
The genetic code is the sequence of nitrogen bases in mRNA that contains the information for protein synthesis. A codon is three nitrogen bases that code for a single amino acid. Nirenberg and Mathaei experimentally proved that codons determine amino acids. The genetic code is universal, uses non-overlapping triplets to specify amino acids in a linear, commaless fashion, and employs initiation and termination codons.