The document discusses the genetic code and how it is translated from DNA to protein. Some key points:
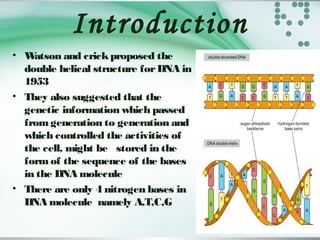
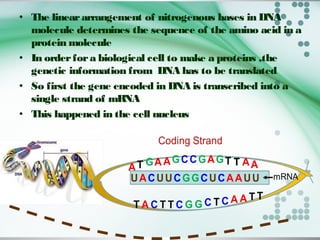
- The genetic code is stored in the sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA. DNA is transcribed into mRNA which moves to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
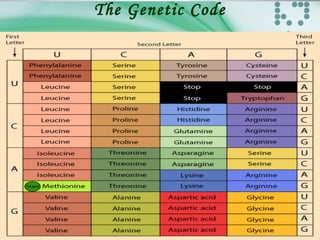
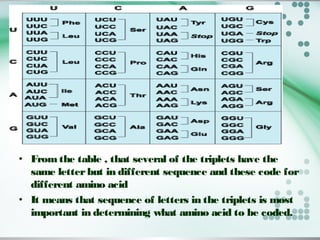
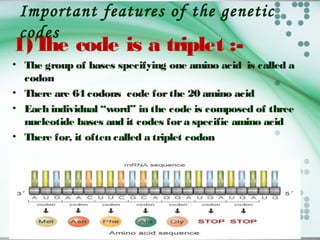
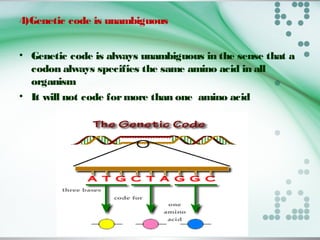
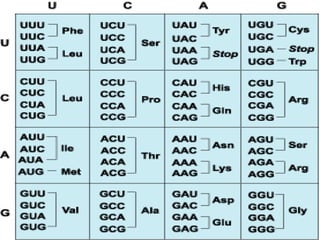
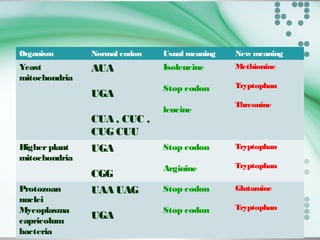
- There are 64 possible codon combinations of the 4 nitrogen bases, with 61 coding for 20 amino acids and 3 being stop codons. The sequence and order of the 3 bases in a codon determines which amino acid it codes for.
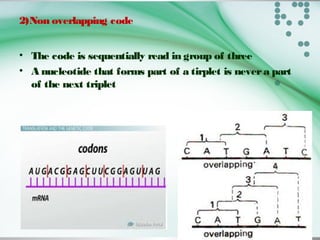
- Experiments by Crick and Brenner in 1961 proved the genetic code is read in triplets, with each codon made up of 3 nucleotides. Frameshift mutations that insert or delete a base pair change the reading frame